Thorax Space Fluid Aspiration During Pleural Effusion in A Cat
Downloads
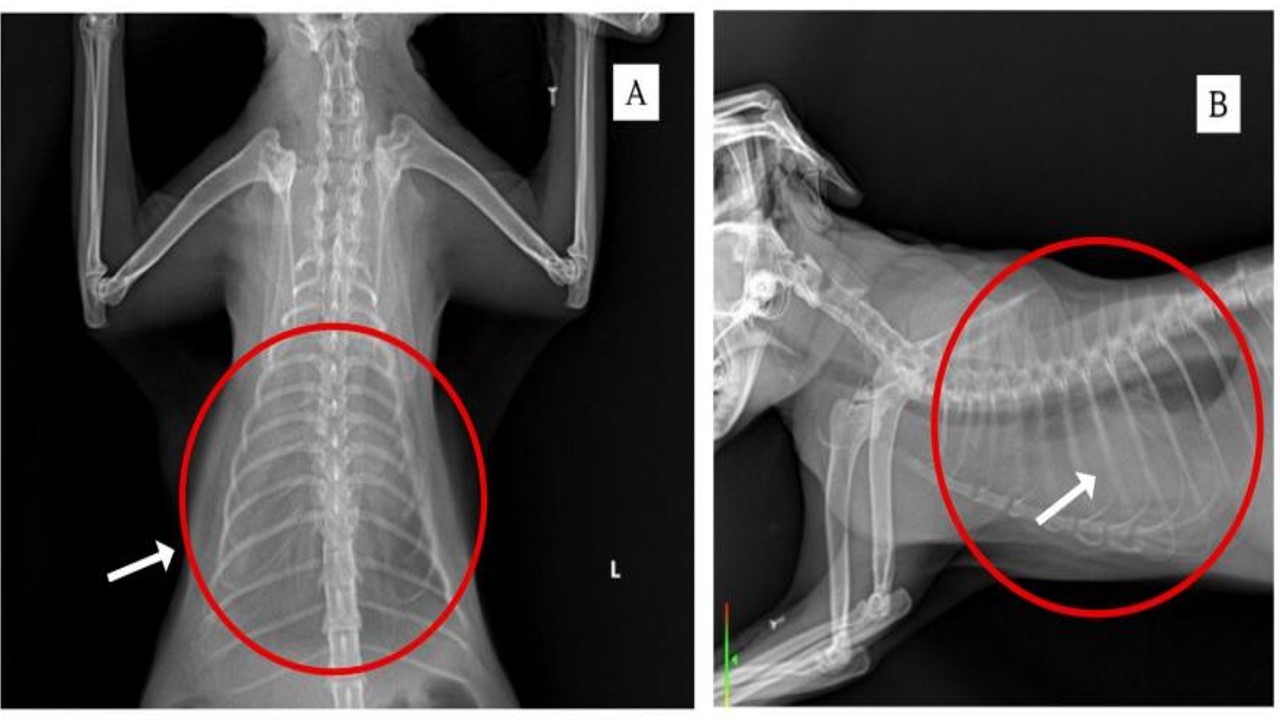
Pleural effusion is the abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity, which may result from infection, trauma, neoplasia or systemic disease. This condition often leads to acute respiratory distress in cats and requires immediate intervention. Thoracocentesis is the primary diagnostic and therapeutic method to evaluate the type of fluid and identify possible causative pathogens. This report to describe the management of pleural effusion in a four-year-old female Persian cat who presented with complaints of dyspnea, weakness, and decreased appetite. Physical examination and thoracic radiographs revealed fluid accumulation in the pleural cavity. Thoracocentesis was performed at the 7th or 8th intercostal space after the area was shaved and sterilized. The cat was placed in lateral recumbency and anesthetized before fluid aspiration with a syringe. Hematological examination revealed anemia, while radiographs showed radiopaque areas on the thorax. The aspirated fluid was clear pale yellow in color. Bacterial culture on NA medium revealed microbial growth, indicating infection as one of the causes of the effusion. In conclusion, thoracocentesis plays an important role in the diagnosis and therapy of pleural effusion, and helps speed up the patient's recovery. The cat recovered and was discharged after six days of intensive care.
Aynalem IM, Adem N, Wendesson F, Misganaw B, Mintesnot, Nega Godo, Getawa IS, Adane T, Woldu B, Shiferaw E. 2022. Hematological abnormalities before and after initiation of cancer treatment among breast cancer patients attending at the University of Gondar comprehensive specialized hospital cancer treatment center. Journal Pone. 17(8): 1-10.
Baiti, N., Batan, I.W., dan Anthara, M.S. 2023. Laporan Kasus: Infeksi Saluran Pernapasan (ISP) pada Kucing Peliharaan. Indonesia Medicus Veterinus. 12(5): 734-744.
Beatty J, dan Barrs V. 2010. Pleural effusion in the cat: a practical approach to determining aetiology. J Feline Med Surg. 12(9):693-707.
Brockman, D.J., Holt, D.E., dan Haar, G.T. 2018. BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Head, Neck and Thoracic Surgery. BSAVA: UK.
Fossum, T.W. 2001. Chylothorax in cats: is there a role for surgery. Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery. 3(1): 73-79.
Gorris, F., Faut, S., Daminet, S., Rooster, H., Saunders, J.H., dan Paepe, D. 2017. Pyothorax in cats and dogs. Vlaams Diergeneeskundig Tijdschrift. 86(1): 183-197.
Hasanah, N., Mentari, U.D., Zaenab, S., dan Ichsanniyati, Z. 2022. Case Study: Pyothorax in Domestic Short Hair Cat. Vet Bio Clin J. 4(1): 1–9.
Hidayah, N., Atifah, Y., Ahda, Y., dan Cahyati, N. 2024. Analisis Kasus Anemia Pada Pasien Kucing Berdasarkan Indeks Eritrosit Melalui Pemeriksaan Hematologi Lengkap Di UPTD Rumah Sakit Hewan Sumatera Barat. Prosiding SEMNASBIO. 1(2): 258-265.
Hung, L., Hopper, B.J., dan Lenard, Z. 2022. Retrospective analysis of radiographic signs in feline pleural effusions to predict disease aetiology. BMC Veterinary Research. 18(118): 1-11.
König A, Hartmann K, Mueller RS, Wess G, Schulz BS. 2019. Retrospective analysis of pleural effusion in cats. J Feline Med Surg. 21(12):1102-1110.
Kurnianto, A., dan Millenia, M. 2023. Laporan Kasus: Feline Immunodeficiency Virus pada Kucing Moi di Surabaya. Jurnal Kajian Veteriner. 11(2): 103-113.
Mohanambal, K., Mohan, A., Rajyalakshmi, S., dan Vijayakumar, G. 2020. Pleural Effusion due to Meosthelioma in a Dog-A Case Report. Inter. J. Curr. Microbial. App.Sci. 9(6): 1512-1514.
Prudenta, O., Mardasella, A., Sahmiranda, D., Ardianto, Y., dan Aeka, A. 2021. Gagal ginjal kronis pada Kucing Domestik Rambut Pendek. Media Kedokteran Hewan. 32(1): 29-39.
Ruiz MD, Vessières F, Ragetly GR, Hernandez JL. 2018. Characterization of and factors associated with causes of pleural effusion in cats. J Am Vet Med. 253(2): 181-187.
Tilley, L.P., Smith, F.W.K., Sleeper, M.M., Brainard, B.M. 2021. Blackwell’s Five Minute Veterinary Consult Canine and Feline, Seventh Edition. Wiley Blackwell: USA.
Widagdo, H.S., Batan, I.W., dan Jayanti, P.D. 2024. Laporan Kasus: Pengobatan Herbal untuk Bronkopneumonia Kronis pada Kucing. Indonesia Medicus Veterinus. 13(4): 368-381.
Zoia, A., dan Drigo, M. 2016. Diagnostic value of Light’s criteria and albumin gradient in classifying the pathophysiology of pleural effusion formation in cats. Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery. 18(8): 666-672.
Copyright (c) 2025 Wudhia Windy Toliu, Muhammad Zulfadillah Sinusi, A. Rifqatul Ummah, Wa Ode Santa Monica

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Journal of Basic Medical Veterinary (JBMV) by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions.
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA).
4. The Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA) license allows re-distribution and re-use of a licensed work on the conditions that the creator is appropriately credited and that any derivative work is made available under "the same, similar or a compatible license”. Other than the conditions mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation.







 Perhimpunan Dokter Hewan Indonesia
Perhimpunan Dokter Hewan Indonesia








