Nephroprotective Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Papaya (Carica papaya) Seeds on Blood Urea Nitrogen and Creatinine Levels in Albino Rats Induced by Paracetamol
Downloads
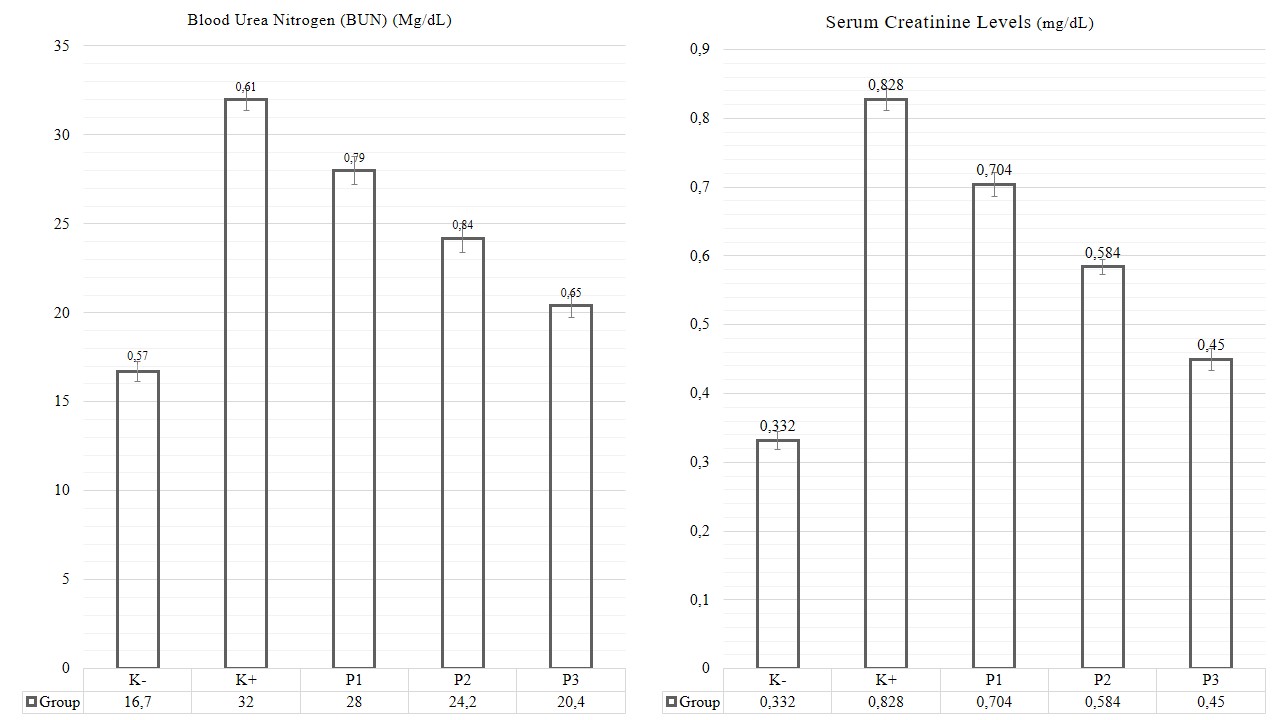
Kidney damage caused by high-dose paracetamol leads to elevated Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels as indicators of impaired renal function. This study aimed to evaluate the dose-dependent nephroprotective effects of ethanolic Carica papaya seed extract on BUN and creatinine levels in paracetamol-induced albino rats. A posttest-only control group design was applied using 25 male Wistar rats divided into five groups: negative control (1% CMC-Na), positive control (paracetamol 1000 mg/kgBW), and three treatment groups receiving Carica papaya seed extract at doses of 100, 200, and 400 mg/kgBW. The extract was administered orally for seven consecutive days before paracetamol induction on day 8 and continued until day 11. Blood samples were collected on day 11, and serum was stored at -20 °C before BUN and creatinine concentrations were analyzed spectrophotometrically. Data were statistically analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan’s Multiple Range Test (DMRT) at a significance level of p < 0.05. The results showed a significant and dose-dependent reduction in both parameters in all treated groups compared to the positive control, with the 400 mg/kgBW dose showing the strongest effect and restoring values close to physiological levels. The nephroprotective activity was associated with the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms of the bioactive compounds that counteract oxidative stress and preserve renal cellular integrity. In conclusion, the ethanolic extract of Carica papaya seeds demonstrates significant dose-dependent nephroprotection against paracetamol-induced kidney injury in rats.
Abdullah, N. F., and N. Muda. 2022. An overview of homogeneity of variance tests on various conditions based on type 1 error rate and power of a test. J. of Quality Meas. and Analys. JQMA, 18(3):111-130.
Ahmad, S., S.A. Khan., M. Tayyab., A.Q. Arain., A. Ali., and H. Khalil. 2024. Effects Of Carica Papaya Seed Extract On Histopathological Changes In Aminoglycoside-Triggered Acute Nephrotoxicity In Experimental Rats. Pakistan J. Of Physiol. 20(3): 3-7.
Ahmed, S., M. Tahir., A. Munir., A. Hafeez., S.A. Khan., M. Tayyab., and T. Laique. 2021. Effect of Etanolic Extract of Carica papaya seeds in Drug-Induced Acute Nephrotoxicity. PJMHS, 15(11): 2951-2953.
Al-Arif, M. A. 2018. Buku Ajar Rancangan Percobaan. Surabaya: Mediatama dan Fakultas Kedokteran Hewan, Universitas Airlangga.
Arinze, K., O. Amole., A. Dada., A. Ojewale., E. Emiogun., and O. Yemitan. 2025. Antihepatotoxic Effects of Hydro ethanol Leaf and Aqueous Unripe Whole Fruit Extracts of Carica papaya on Paracetamol-induced Liver Injury in Rats. Iranian J. of Toxicol., 19(3): 146-152.
Bijanti, R., M. G. A. Yuliani., R. S. Wahjuni., dan R. B. Utomo. 2010. Buku Ajar Patologi Klinik Veteriner. Surabaya: Airlangga University Press.
Chandra, E., N. Lister., and E. Fachrial. 2022. Nephroprotective Effect of Ethanol Extract of Carica Papaya Seed on Rats Induced Rifampicin and Isoniazid. IOP Conf. Series: Earth and Environ. Sci. 1083: p012068
Chinnappan, S. M., A. George., P. Thaggikuppe., Y. Choudhary., V.K. Choudhary., Y. Ramani., and R. Dewangan. (2019). Nephroprotective effect of herbal extract Eurycoma longifolia on paracetamol‐induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Evidence‐Based Compl and Alt. Med. 2019(1): 4916519.
Dunaevich, A., H. Cheen., D. Musseri., S. Kuzi., M. Mazaki-Tovi., I. Aroch., and G. Segev. 2020. Acute on chronic kidney disease in dogs: Etiology, clinical and clinicopathologic findings, prognostic markers, and survival. J. J Vet. Intern. Med., 34(6): 2507-2515.
Gori, A., B. Boucherle., A. Rey., M. Rome., N. Fuzzati., and M. Peuchmaur. 2021. Development of an innovative maceration technique to optimize extraction and phase partition of natural products. J. Fitot., 148: 104798
Hidayatik, N., G.A. Yuliani., B. Agustono., L. Kristianingtyas., A.N. Novianti., E.P. Hestianah., and A.R. Khairullah. 2024. Effect of Garlic Extract (Allium sativum) on Hematological and Clinical Chemistry Parameters of Laying Quail. Asian J. Dairy Food Res. 43(4): 790-795.
Housseini, I., H. Dakdouk., and J. Borjac. 2025. Nephro-protective effect of Mucuna pruriens, Moringa oleifera, and Milk thistle extracts against APAP-induced Acute kidney injury in mice.. Kidney and blood press. res. 50(1): 1-24.
Jaeschke, H., and A. Ramachandran. 2020. Mechanisms and pathophysiological significance of sterile inflammation during acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. J. Food and Chem Toxic, 138: 111240
Jensen, M. S., I.B.B.A. de Araujo., H.A. Mutsaers., and R. Nørregaard. 2023. Transcutaneous measurement of renal function in two rodent models of obstructive nephropathy. BMC Res. NoteS, 16(1): 119.
Kanadi, M.A, A.J. Alhassan., A.I. Yaradua., A. Nasir., and A. M. Wudil. 2021. Sub-fractions from Carica papaya Seed Extracts Can Prevent Potassium Bromate- induced Changes in Activities of Renal Brush Border Membrane Enzymes and Some Enzymes of Carbohydrate Metabolism in the Kidney of Rats. Asian J. Biochem. Genet. Mol., 8(4): 1-9.
Kurnijasanti, R., G. Wardani., M.R. Mustafa., and S.A. Sudjarwo. 2023. Protective mechanism of Swietenia macrophylla ethanol extract nanoparticle on streptozotocin-induced renal damage in rats. Open Vet. J., 13(12): 1623–1630
Liao, J., Q. Lu., Z. Li., J. Li., Q. Zhao., and J. Li. 2023. Acetaminophen-induced Liver Injury : Molecular Mechanism and Treatments from Natural Products. Front. in Pharm. 14: 1663-9812.
Moshaei-Nezhad, P., S.M. Hosseini., M. Yahyapour., M. Iman., and A. Khamesipour. 2019. Protective effect of ivy leaf extract on paracetamol-induced oxidative stress and nephrotoxicity in mice. J. of Herbmed Pharm. 8(1): 64-68.
Naggayi, M, N. Mukibii., and I. Ezekiel., 2015. The protective effects of aqueous extract of Carica papaya seeds in paracetamol induced nephrotoxicity in male wistar rats. African health sci J., 15(2): 598-605.
Nnaemeka, U., I.A. Ukamaka., U.S. God’swealth., and G.R. Resame 2023. Comparative study of aqueous, methanol and petroleum ether extracts of unripe Carica papaya seed on liver and kidney function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. GSC Biol Pharm Sci. 22: 038-047
Noel, D. D., K.G.A. Justin., A.K. Alphonse., L.H. Désiré., D. Dramane., D. Nafan., and G. Malerba. 2021. Normality assessment of several quantitative data transformation procedures. Biostat. and Biom Open Acc J., 10(3):51-65
Olagunju, J. A., A. Adeneye., B. S. Fagbohunka., A. Benebo., A. O. Ketiku., O. M. Olufowobi., A. G. Adeoye., M. A. Alimi., A. G. Adeleke. 2023. Nephroprotective activities of the aqueous seed extract of Carica papaya Linn. in carbon tetrachloride-induced renal injured Wistar rats: a dose-dependent study. Bio. Med., 16(4): 160-167.
Ottuh, P., and H. E. Kadiri., 2023. Evaluation of Protective Potential of Aqueous Seed extract of Ripe Fruits of Carica papaya on Cyanide Induced Kidney Damage in Male Wister Rats. J of App Sci Environ Manag. 27(1): 51-55
Parker, V. J. 2021. Nutritional Management for Dogs and Cats with Chronic Kidney Disease. Vet. Clinics: Small Anim. Pract. 51(3): 685-710.
Phang, H. C. 2016. Effect Of Solvent: Solid Ratio, Solvent, Temperature, Time And Method On Extraction On Total Phenolic Compound From Propolis (Trigona Thoracica) [Tesis]. Universiti Malaysia Pahang.
Pokhrel, S., and P. Karki., 2021. Phytochemical Screening, Antioxidant and Antidiabetic of Ectracts of Leaves and Seeds of Carica papaya. Nepal J. Scien. and Techn., 20(1): 126-135.
Rezanty, L. 2020. Efek Nefrotoksik dari Penggunaan Obat Paracetamol Dosis Tinggi. J. Farm. Klin. Indonesia, 9(2): 81-87.
Safdar, N., R. Roohullah., Z. Qureshi., and S. Khan. 2023. Toxicological Studies Of Paracetamol Positional Isomers. J of Xi’an Shiyou University, Nat Sci Edit, 19(3): 835-848.
Sami, H., I. Tarique., S. Arain., R. Mughal., I. Majeed., R. Saba., J. Rajput., M. Altaf., L. Bux. 2023. Comparative assessment of urea, creatinine, and blood urea nitrogen in male and female patients with different age groups of chronic kidney disease in Shaheed Benazir Abad, Sindh. W J Bio and Biotech. 8(2): 39-42
Sevastre-Berghian, A. C., C. Casandra., D. Gheban., D. Olteanu., M.C. Olanescu Vaida Voevod., L. Rogojan., and I. Bâldea. 2022. Neurotoxicity of bisphenol A and the impact of melatonin administration on oxidative stress, ERK/NF-kB signaling pathway, and behavior in rats. Neurotoxicity Research, 40(6): 1882-1894.
Shaban, N. Z., S. M. El-Kot., O. M. Awad., A. M. Hafez., G. M. Fouad. 2021. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Carica papaya Linn. seeds extract on CCl4-induced liver injury in male rats. BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies, 21(1): 2-15.
Shafei, M., S. Shabab., N. Heravi., and R. Mohebbati. 2024. Ribes khorasanicum: A Potent Antioxidant Against Organ Toxicity by Effect on the NF‐κB Pathway. Food Sci and Nutr. 12(12): 10412 - 10423.
Singh, P. G., S.B. Madhu., G.T.S. Shailasreesekhar., K.M. Basalingappa., and B.V. Sushma. 2020. In vitro antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial activity of Carica papaya seeds. Global Journal of Medical Research, 20(2), 19-37.
Sulthana, M. S., R. R. Saha., S. N. Islam., T. Afrin., R. Afroz., M. J. Lotus. 2023. Nephroprotective Activity of Aqueous Extract of Carica papaya Seeds in Carbon Tetrachloride Induced Nephrotoxic Rats. Ibrahim Card Med J, 12(1): 9-17
Tripathi, S., D. Parmar., S. Raval., D.P. Singh., R. Palkhade., R. Mishra., and G. Singh. 2025. Natural compounds attenuate combined chromium and arsenic-induced oxidative stress and nephritic apoptosis by activating the Nrf2/Keap1 signaling and associated xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes. Scientific Reports, 15(1): 31716.
Ugo, C. H., E.K. Ngwu., P.N. Eze., G.O. Iheme., H.A. Obajaja., and A.E. Oemili. 2024. Nutrient and Hypoglycemic Effect of Carica papaya Seed Flour on Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Adult Male Wistar Rat. Cur Develop in Nutrit. 8(2): 283-284.
Wadekar, A. B., M. G., Nimbalwar., W. A. Panchale., B. R., Gudalwar., J.V., Manwar., and R. L. Bakal. 2021. Morphology, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Aspects Of Carica papaya, an review. GSC Biol and Pharmaceutic Sci, 14(03): 234-248.
Wahyuningsih, S.P.A., B.N.D. Atika., E.S. Sajidah. and D. Winarni. 2020. Nephroprotective activity of okra pods extract (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) in sodium nitrite-induced mice. Res. J. of Pharm. and Techn., 13(8): 3648-3652.
Wijayanti, H. N., Y. N.Fadhilah.,W.M. Yuniarti., B.S. Lukiswanto., A. Arimbi., E. Suprihati, ., and R. Kurnijasanti. 2023. Protective effect of Moringa oleifera leaves extract against gentamicin induced hepatic and nephrotoxicity in rats. Iraqi J Vet Sci, 37(1), 129-135.
Zain, D. N., A. Pebiansyah, dan A. Y. Aprilia. 2021. Aktivitas Nefroprotektif Ekstrak Etanol Bunga Telang (Clitoria ternatea L.) terhadap Tikus yang Diinduksi Parasetamol. Pharmacoscript, 4(2): 173-180.
Copyright (c) 2025 Muhammad Syahrul Mubarok, Gandul Atik Yuliani, Agus Sunarso, Nanik Hidayatik, Rochmah Kurnijasanti, Mirza Atikah Madarina Hisyam

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Journal of Basic Medical Veterinary (JBMV) by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions.
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA).
4. The Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA) license allows re-distribution and re-use of a licensed work on the conditions that the creator is appropriately credited and that any derivative work is made available under "the same, similar or a compatible license”. Other than the conditions mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation.







 Perhimpunan Dokter Hewan Indonesia
Perhimpunan Dokter Hewan Indonesia








