Biofilm-Mediated Survival of Leptospira spp.: A Comprehensive Review on Molecular Basis and Control Strategies
Downloads
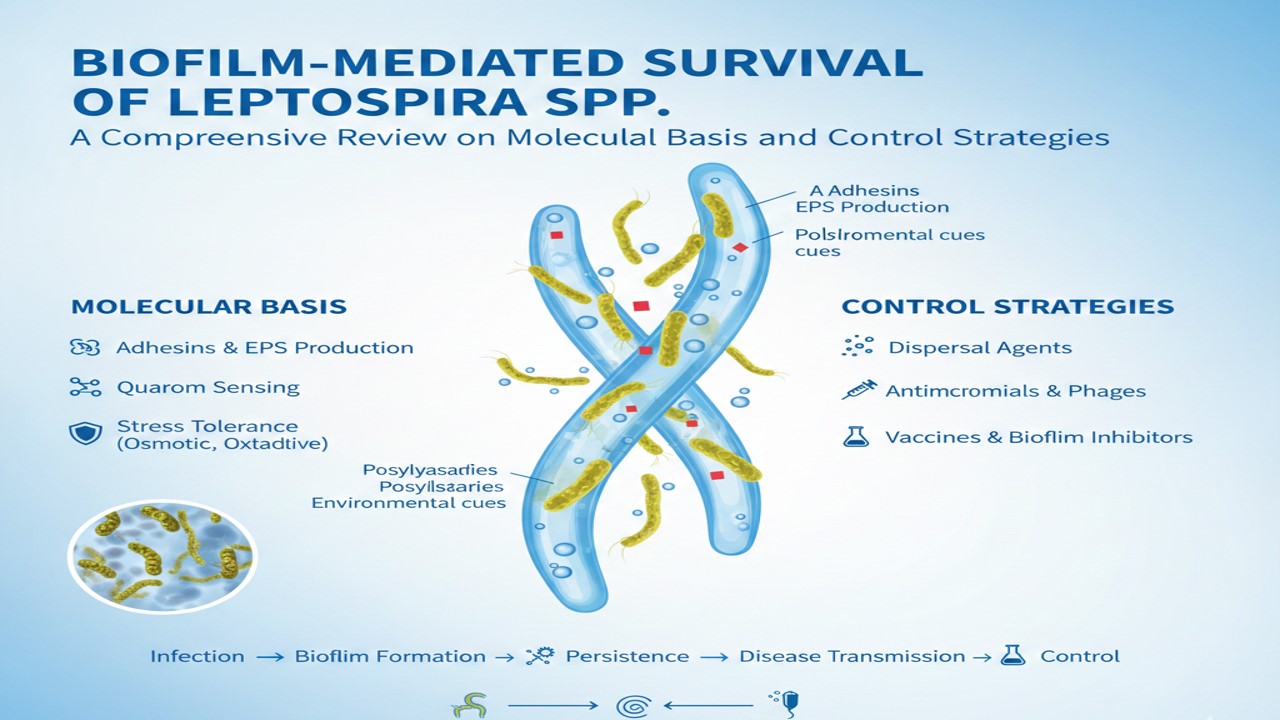
Leptospirosis is a significant tropical zoonosis, with a considerable burden on morbidity and mortality in humans as well as animals. One of the possible explanations is biofilm formation, which is the accumulation of EPS, eDNA, and c-di-GMP signals that respond to various environmental, antibiotic, or host-immune challenges. This review focuses on the molecular mechanisms underlying biofilm formation, ecological significance, connection to antimicrobial resistance, and the public health implications. Elucidation of the c-di-GMP regulatory networks, adhesin gene and protein expression, and other metabolic shifts account for the survival of Leptospira biofilms in autochthonous populations of aquatic habitats and kidney colonization of reservoir hosts. In addition, biofilms have been associated with long-term bacterial colonization, chronic urine stream associated with persistent bacterial shedding, and failed antibiotics. This scenario, from an epidemiological perspective, facilitates the emergence of anthropogenic infections, and perpetuates the endemic nature of the disease. From a disease-control perspective, biofilms increase the burden associated with persistent infections. This review emphasizes that, as a survival strategy, biofilms represent several potential avenues for the implementation of novel control strategies, including the use of antibiofilm agents, quorum-sensing inhibitors, and multi-epitope vaccines. The functional and integrated dissection of biofilms positioned Leptospira spp. to novel One Health-based control strategies for the disease.
Ackermann, K., Kenngott, R., Settles, M., Gerhards, H., Maierl, J., and Wollanke, B. 2021. In vivo biofilm formation of pathogenic Leptospira spp. in the vitreous humor of horses with recurrent uveitis. Microorganisms, 9(9), 1915.
Barazzone, G. C., Teixeira, A. F., Azevedo, B. O., Damiano, D. K., Oliveira, M. P., Nascimento, A. L., andamp; Lopes, A. P. 2022. Revisiting the development of vaccines against pathogenic Leptospira: innovative approaches, present challenges, and future perspectives. Frontiers in Immunology, 12, 760291.
Cilia, G., Bertelloni, F., and Fratini, F. 2020. Leptospira infections in Domestic and Wild Animals (p. 128). MDPI-Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute.
Costa, F., Hagan, J. E., Calcagno, J., Kane, M., Torgerson, P., Martinez-Silveira, M. S., and Ko, A. I. (2015). Global morbidity and mortality of leptospirosis: a systematic review. PLoS neglected tropical diseases, 9(9), e0003898.
Davignon, G., Cagliero, J., Guentas, L., Bierque, E., Genthon, P., Gunkel-Grillon, P., and Goarant, C. (2023). Leptospirosis: toward a better understanding of the environmental lifestyle of Leptospira. Frontiers in Water, 5, 1195094.
Davignon, G., Pietrosemoli, N., Benaroudj, N., Soupé-Gilbert, M. E., Cagliero, J., Turc, É., ... and Thibeaux, R. 2024. Leptospira interrogans biofilm transcriptome highlights adaptation to starvation and general stress while maintaining virulence. npj Biofilms and Microbiomes, 10(1), 95.
de Carvalho, R. R. M., Dias, C. S., Paz, L. N., de Lima Fires, T. M., Figueira, C. P., Damasceno, K. A., and Pinna, M. H. 2023. Biofilm formation in vitro by Leptospira interrogans strains isolated from naturally infected dogs and their role in antimicrobial resistance. Heliyon, 9(3).
Dias, C. S., and Pinna, M. H. 2025. Leptospira biofilms: implications for survival, transmission, and disease management. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 91(2), e01914-24.
Iraola, G., Spangenberg, L., Lopes Bastos, B., Graña, M., Vasconcelos, L., Almeida, Á.,and Naya, H. 2016. Transcriptome sequencing reveals wide expression reprogramming of basal and unknown genes in Leptospira biflexa biofilms. Msphere, 1(2), 10-1128.
Karpagam, K. B., and Ganesh, B. 2020. Leptospirosis: a neglected tropical zoonotic infection of public health importance—an updated review. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 39(5), 835–846.
Kumar, K. V., Lall, C., Raj, R. V., Vedhagiri, K., and Vijayachari, P. 2015. Coexistence and survival of pathogenic leptospires by formation of biofilm with Azospirillum. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 91(6), fiv051.
Kumar, K. V., Lall, C., Raj, R. V., Vedhagiri, K., Kartick, C., Surya, P., and Vijayachari, P. 2017. Overexpression of heat shock GroEL stress protein in Leptospira biofilm. Microbial Pathogenesis, 102, 8-11.
Kumar, K. V., Lall, C., Raj, R. V., Vedhagiri, K., Sunish, I. P., and Vijayachari, P. 2016. In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of pathogenic Leptospira biofilm. Microbial Drug Resistance, 22(7), 511–514.
Meganathan, Y., Vishwakarma, A., and Ramya, M. 2022. Biofilm formation and social interaction of Leptospira in natural and artificial environments. Research in Microbiology, 173(8), 103981.
Monahan, A. M., Callanan, J. J., and Nally, J. E. 2009. Host-Pathogen Interactions in the Kidney during Chronic Leptospirosis. Veterinary pathology, 46(5), 792-799.
Muhammad, M. H., Idris, A. L., Fan, X., Guo, Y., Yu, Y., Jin, X., and Huang, T. 2020. Beyond risk: bacterial biofilms and their regulating approaches. Frontiers in microbiology, 11, 928.
Phoka, T., Fule, L., Da Fonseca, J. P., Cokelaer, T., Picardeau, M., and Patarakul, K. 2021. Investigating the role of the carbon storage regulator A (CsrA) in Leptospira spp. Plos one, 16(12), e0260981.
Ratet, G., Veyrier, F. J., Fanton d'Andon, M., Kammerscheit, X., Nicola, M. A., Picardeau, M., and Werts, C. (2014). Live imaging of bioluminescent Leptospira interrogans in mice reveals renal colonization as a stealth escape from the blood defenses and antibiotics: PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 8(12), e3359.
Santos, A. A. N., Ribeiro, P. D. S., da França, G. V., Souza, F. N., Ramos, E. A. G., Figueira, C. P., and Ristow, P. 2021. Leptospira interrogans biofilm formation in Rattus norvegicus (Norway rats) natural reservoirs. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 15(9), e0009736.
Thibeaux, R., Soupé-Gilbert, M. E., Kainiu, M., Girault, D., Bierque, E., Fernandes, J., and Goarant, C. 2020. The zoonotic pathogen Leptospira interrogans mitigates environmental stress through cyclic-di-GMP-controlled biofilm production. npj Biofilms and Microbiomes, 6(1), 24.
Vasconcelos, L., Aburjaile, F., Andrade, L., Cancio, A. F., Seyffert, N., Aguiar, E. R., and Ristow, P. 2023. Genomic insights into the c-di-GMP signaling and biofilm development in the saprophytic spirochete Leptospira biflexa. Archives of Microbiology, 205(5), 180.
Yamaguchi, T., Higa, N., Okura, N., Matsumoto, A., Hermawan, I., Yamashiro, T., and Toma, C. 2018. Characterizing interactions of Leptospira interrogans with proximal renal tubule epithelial cells. BMC microbiology, 18(1), 64.
Yin, W., Wang, Y., Liu, L., and He, J. 2019. Biofilms: the microbial “protective clothing” in extreme environments. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(14), 3423.
Copyright (c) 2025 Robby Wijayanto, Chalida Nahendra Zilfiarani, Moch. Ilham Riza Fahlefi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Journal of Basic Medical Veterinary (JBMV) by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions.
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA).
4. The Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA) license allows re-distribution and re-use of a licensed work on the conditions that the creator is appropriately credited and that any derivative work is made available under "the same, similar or a compatible license”. Other than the conditions mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation.







 Perhimpunan Dokter Hewan Indonesia
Perhimpunan Dokter Hewan Indonesia








