Date Log
Copyright (c) 2025 Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. Copyright of the article is transferred to the journal, by the knowledge of the author, whilst the moral right of the publication belongs to the author.
2. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Atribusi-Non Commercial-Share alike (CC BY-NC-SA), (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/)
3. The articles published in the journal are open access and can be used for non-commercial purposes. Other than the aims mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation
The manuscript authentic and copyright statement submission can be downloaded ON THIS FORM.
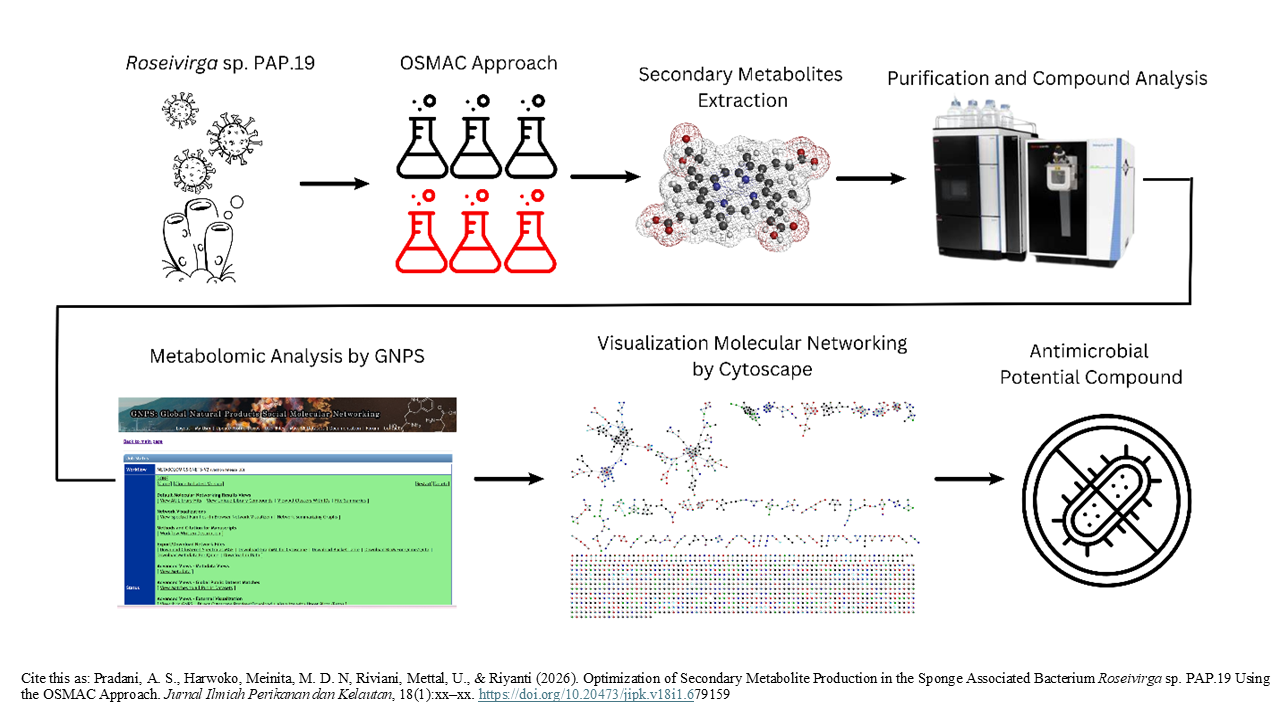
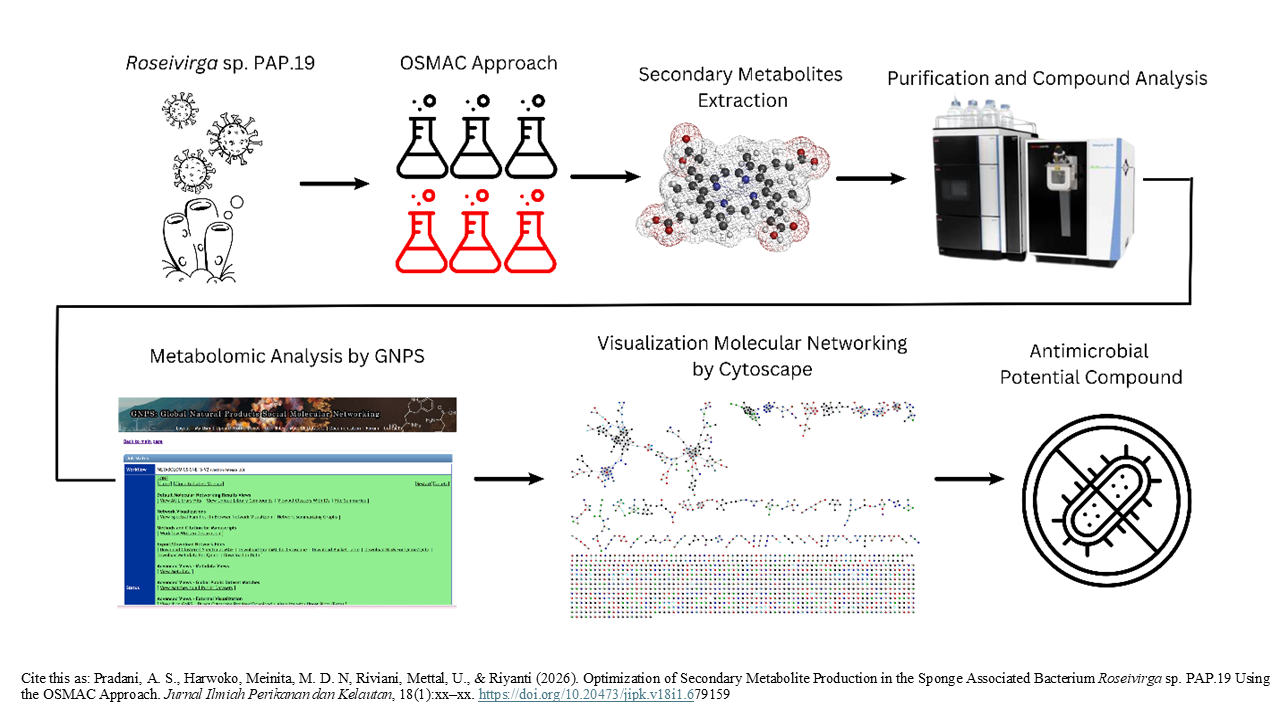
Optimization of Secondary Metabolite Production in the Sponge Associated Bacterium Roseivirga sp. PAP.19 Using the OSMAC Approach
Corresponding Author(s) : Riyanti
Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, 2025: IN PRESS ISSUE (JUST ACCEPTED MANUSCRIPT, 2025)
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Highlight Research
- Compounds produced by Roseivirga PAP.19 bacteria have potential as antimicrobials.
- The OSMAC approach was used successfully to activate BGCs of Roseivirga PAP.19.
- The use of medium in bacterial culture affects the secondary metabolites produced by Roseivirga PAP.19 bacteria. Bacteria cultured in A1Bfe+C medium produced more secondary metabolites compared to the other medium.
- The different incubation times during culture affect the amount of secondary metabolite compounds produced.
Abstract
Marine sponge-associated bacteria are a rich source of bioactive metabolites. The biochemical interaction between bacteria and sponges enables symbiotic bacteria to produce metabolites similar to those of their host. Metabolite extracts from symbiotic bacteria contain bioactive compounds with cytotoxic, antiviral, and antimicrobial properties. There is an urgent need for new antimicrobial agents due to the increasing resistance to existing drugs. This study aims to optimize the medium and incubation time of secondary metabolites produced by the symbiotic bacteria of the sponge Roseivirga sp. PAP.19. To stimulate biosynthesis of silent gene clusters, the One Strain Many Compounds (OSMAC) approach was used. Bacteria were cultured in various media and at different incubation times. This has the potential to increase the production of secondary metabolites. Secondary metabolites were analyzed using LC-HRMS. The potential of these metabolites as antimicrobial agents was subsequently evaluated. Results showed six compounds with antimicrobial potential. Notably, the A1BFe+C medium produced more bioactive compounds than the other medium, and the highest compound production occurred on day 4. These findings suggest that optimizing culture conditions using the OSMAC approach can enhance the yield of potentially valuable antimicrobial secondary metabolites from symbiotic bacteria, which may contribute to the discovery of new antimicrobial agents.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- Alen, Y., Guslianti, E., & Suharti, N. (2018). Isolation and activity assay of secondary metabolites of Aspergillus niger in-habitating in the termite’s queen nest macrotermes gilvus hagen on enriched media. Indonesian Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology, 6(1):1-10.
- Ali, N., Pang, Z., Wang, F., Xu, B., & El-Seedi, H. R. (2022). Lipopeptide biosurfactants from Bacillus spp.: Types, production, biological activities, and applications in food. Journal of Food Quality, 2022(1):1-19.
- Aljeldah, M. M. (2022). Antimicrobial resistance and its spread is a global threat. Antibiotics, 11(8):1-14.
- Ambarwati, A., Wahyuono, S., Moeljopawiro, S., & Yuwono, T. (2020). Antimicrobial activity of ethyl acetate extracts of Streptomyces sp. CRB46 and the prediction of their bioactive compounds' chemical structure. Biodiversitas, 21(7):3380-3390.
- Anteneh, Y. S., Yang, Q., Brown, M. H., & Franco, C. M. M. (2021). Antimicrobial activities of marine sponge-associated bacteria. Microorganisms, 9(1):1-19.
- Ardiyanti, C. A. P. (2019). Production of yeast extract from spent brewer’s yeast. Jurnal Pendidikan Biologi, 12(1):52-60.
- Bibi, F., Yasir, M., Al-Sofyani, A., Naseer, M. I., & Azhar, E. I. (2020). Antimicrobial activity of bacteria from marine sponge Suberea mollis and bioactive metabolites of Vibrio sp. EA348. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 27(4):1139-1147.
- Brinkmann, C. M., Marker, A., & Kurtböke, D. I. (2017). An overview on marine sponge-symbiotic bacteria as unexhausted sources for natural product discovery. Diversity, 9(4):1-40.
- Desniar, Nurhayati, T., Suhartono, M. T., & Isa, E. M. (2006). Modification of marine broth media on protease inhibitors from Acinetobacter baumanni bacteria living in symbiosis with Sponge Plakortis nigra. Buletin Teknologi Hasil Perikanan, 9(1):72-81.
- Fouillaud, M. & Dufossé, L. (2022). Microbial secondary metabolism and biotechnology. Microorganisms, 10(1):1-9.
- Fukuda, T., Miller, E. D., Kauffman, C. A., Clark, B. R., Alnauman, A., Murphy, C. D., Jensen, P. R., & Fenical, W. (2011). Structures and biosynthesis of the pyridinopyrones, polyenepyrones from a marine-derived Streptomyces species. Journal of Natural Product, 74(8):1773-1778.
- Gray, V. L., Müller, C. T., Watkins, I. D., & Lloyd, D. (2008). Peptones from diverse sources: Pivotal determinants of bacterial growth dynamics. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 104(2):554-565.
- Hong, S. Y., Lee, D. H., Lee, J. H., Haque, M. A., & Cho, K. M. (2021). Five surfactin isomers produced during cheonggukjang fermentation by Bacillus pumilus HY1 and their properties. Molecules, 26(15):1-13.
- Hu, L., Chen, F., & Liang, Y. (2025). Polymerized ferric sulfate influences methane production from the anaerobic digestion of pig slurry: Performance and mechanism. Fuel, 389(15):1-10.
- Joint, I., Mühling, M., & Querellou, J. (2010). Culturing marine bacteria - an essential prerequisite for biodiscovery. Microbial Biotechnology, 3(5):564-575.
- Jung, Y. T., Park, S., Lee, J. S., & Yoon, J. H. (2016). Roseivirga maritima sp. nov., isolated from seawater. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 66(7):2664-2670.
- Lappan, R., Shelley, G., Islam, Z. F., Leung, P. M., Lockwood, S., Nauer, P. A., Jirapanjawat, T., Ni, G., Chen, Y. J., Kessler, A. J., Williams, T. J., Cavicchioli, R., Baltar, F., Cook, P. L. M., Morales, S. E., & Greening C. (2023). Molecular hydrogen in seawater supports growth of diverse marine bacteria. Nature Microbiology, 8(4):581-595.
- Lewis, K., Epstein, S., D’Onofrio, A., & Ling, L. L. (2010). Uncultured microorganisms as a source of secondary metabolites. Journal of Antibiotics, 63(8):468-476.
- Lipphardt, A., Karmainski, T., Blank, L. M., Hayen, H., & Tiso, T. (2023). Identification and quantification of biosurfactants produced by the marine bacterium Alcanivorax borkumensis by hyphenated techniques. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 415(30):7067-7084.
- Liu, Z., Zhao, Y., Huang, C., & Luo, Y. (2021). Recent advances in silent gene cluster activation in Streptomyces. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 9(1):1-10.
- Llorens, J. M. N., Tormo, A., & Martínez-García, E. (2010). Stationary phase in gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 34(4):476-495.
- Mamangkey, J., Fadjri, C. L., Sunarto, Mustopa, A. Z., Suryanto, D., Hermana, N. S. P., Yanti, N. A., Kusmiati, K., Irawan, H., Hartanto, A., Rudia, L. O. A. P., Akmaliyah, R., Mendes, L. W., & Ferdin. (2025). In-vitro and bioinformatic studies of bioactive compounds from Oceanimonas sp. JM-AZM31 and Lysinibacillus fusiformis JM-AZM37 of sponge-associated marine bacteria from a mangrove habitat in Southeast Sulawesi. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, 23(3):1-15.
- Mangurana, W. O. I., Yusnaini, Y., & Sahidin, S. (2019). Analysis of LC-MS/MS (liquid crhomatogaph mass spectrometry) and secondary metabolites and antibacterial potential of N-Hexane spons extract of Callyspongia aerizusa taken under different coral reef cover conditions in the waters of Staring Bay. Jurnal Biologi Tropis, 19(2):131-141.
- Mardalena. (2019). Growth phase of lactic acid bacteria isolate Tempoyak from Jambi stored at room temperature. Jurnal Sain Peternakan Indonesia, 11(1):58-66.
- Martín, J. F., Sola-Landa, A., Santos-Beneit, F., Fernandez-Martinez, L. T., Prieto, C., & Rodríguez-García, A. (2011). Cross-talk of global nutritional regulators in the control of primary and secondary metabolism in Streptomyces. Microbial Biotechnology, 4(2):165-174.
- Marzuki, I., Noor, A., Nafie, N. L., & Djide M. N. (2014). Isolation and identifications bacterium symbionts of sponge as producer enzyme amylase from Melawai Beach of Balikpapan. Jurnal Ilmiah “dr. Aloei Saboe”, 1(2):1-8.
- Mehbub, M. F., Yang, Q., & Cheng, Y. (2024). Marine sponge-derived natural products : Trends and opportunities for the decade of 2011-2020. Frontiers in Marine Science. 11(1):1–20.
- Morrison, L. & Zembower, T. R. (2020). Antimicrobial resistance. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Clinics of North America, 30(4):619-635.
- Novanti, R. & Zulaika, E. (2019). Growth patterns of ureolitic bacteria in medium calcium carbonate precipitation (CCP). Jurnal Sains dan Seni ITS, 7(2):34-35.
- Özkaya, F. C., Ebrahim, W., El-Neketi, M., Tanrıkul, T. T., Kalscheuer, R., Müller, W. E. G., Guo, Z., Zou, K., Liu, Z., & Proksch, P. (2018). Induction of new metabolites from sponge-associated fungus Aspergillus carneus by OSMAC approach. Fitoterapia, 131(8):9-14.
- Pinu, F. R., Boas, S. G. V., & Aggio, R. (2017). Analysis of intracellular metabolites from Microorganisms : Quenching and extraction protocols. Metabolites, 7(4):1-20.
- Risna, Fauziah, R., Subehan, & Djide, N. (2022). Isolation and characterization of bioactive compounds of antibacterial metabolites associated with sea sponges (Agelas Oroides). Majalah Farmasi dan Farmakologi, 26(3):96-100.
- Riyanti, Balansa, W., Liu, Y., Sharma, A., Mihajlovic, S., Hartwig, C., Leis, B., Rieuwpassa, J., Ijong, F. G., Wägele, H., König, G. M., & Schäberle, T. F. (2020). Selection of sponge-associated bacteria with high potential for the production of antibacterial compounds. Scientific Reports, 10(1):1-14.
- Rodrigues, M. S., Ferreira, L. S., Converti, A., Sato, S., & Carvalho, J. C. M. (2010). Fed-batch cultivation of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis: Potassium nitrate and ammonium chloride as simultaneous nitrogen sources. Bioresource Technology, 101(12):4491-4498.
- Romano, S., Jackson, S. A., Patry, S., & Dobson, A. D. W. (2018). Extending the “one strain many compounds” (OSMAC) principle to marine microorganisms. Marine Drugs, 16(7):1-29.
- Selvaratnam, C., Thevarajoo, S., Ee, R., Chan, K. G., Bennett, J. P., Goh, K. M., & Chong, C. S. (2016). Genome sequence of Roseivirga sp. strain D-25 and its potential applications from the genomic aspect. Marine Genomics, 28(4):29-31.
- Siahaan, S., Herman, M. J., & Fitri, N. (2022). Antimicrobial resistance situation in Indonesia: A challenge of multisector and global coordination. Journal of Tropical Medicine, 2022(1):1-10.
- Spyere, A., Rowley, D. C., Jensen, P. R., & Fenical, W. (2003). New neoverrucosane diterpenoids produced by the marine gliding bacterium Saprospira grandis. Journal of Natural Products, 66(6):818-822.
- Srinivasan, R., Kannappan, A., Shi, C., & Lin, X. (2021). Marine bacterial secondary metabolites: A treasure house for structurally unique and effective antimicrobial compounds. Marine Drugs, 19(10):1-36.
- Thawabteh, A. M., Swaileh, Z., Ammar, M., Jaghama, W., Yousef, M., Karaman, R., Bufo, S. A., & Scrano, L. (2023). Antifungal and antibacterial activities of isolated marine compounds. Toxins, 15(2):1-21.
- Varijakzhan, D., Loh, J. Y., Yap, W. S., Yusoff, K., Seboussi, R., Lim, S. H. E., Lai, K. S., & Chong, C. M. (2021). Bioactive compounds from marine sponges: Fundamentals and applications. Marine Drugs, 19(5):1-38.
- Vitale, G. A., Sciarretta, M., Cassiano, C., Buonocore, C., Festa, C., Mazzella, V., Pons, L. N., D’auria, V., & de Pascale, D. (2020). Molecular network and culture media variation reveal a complex metabolic profile in Pantoea cf. Eucrina D2 associated with an acidified marine sponge. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(17):1-18.
- Wahyuningsih, N. & Zulaika, E. (2018). Comparison of cellulolytic bacteria growth in nutrient broth and carboxy methyl cellulose media. Jurnal Sains dan Seni ITS, 7(2):36-38.
- Zulaika, E. & Khofifah, S. S. R. (2021). Production of amylocellulolytic enzymes and their viability on carrier media by Bacillus sp. U4 and Pseudomonas sp. U3. Jurnal Ilmiah Biologi Eksperimen dan Keanekaragaman Hayati, 8(2):59-65.
References
Alen, Y., Guslianti, E., & Suharti, N. (2018). Isolation and activity assay of secondary metabolites of Aspergillus niger in-habitating in the termite’s queen nest macrotermes gilvus hagen on enriched media. Indonesian Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology, 6(1):1-10.
Ali, N., Pang, Z., Wang, F., Xu, B., & El-Seedi, H. R. (2022). Lipopeptide biosurfactants from Bacillus spp.: Types, production, biological activities, and applications in food. Journal of Food Quality, 2022(1):1-19.
Aljeldah, M. M. (2022). Antimicrobial resistance and its spread is a global threat. Antibiotics, 11(8):1-14.
Ambarwati, A., Wahyuono, S., Moeljopawiro, S., & Yuwono, T. (2020). Antimicrobial activity of ethyl acetate extracts of Streptomyces sp. CRB46 and the prediction of their bioactive compounds' chemical structure. Biodiversitas, 21(7):3380-3390.
Anteneh, Y. S., Yang, Q., Brown, M. H., & Franco, C. M. M. (2021). Antimicrobial activities of marine sponge-associated bacteria. Microorganisms, 9(1):1-19.
Ardiyanti, C. A. P. (2019). Production of yeast extract from spent brewer’s yeast. Jurnal Pendidikan Biologi, 12(1):52-60.
Bibi, F., Yasir, M., Al-Sofyani, A., Naseer, M. I., & Azhar, E. I. (2020). Antimicrobial activity of bacteria from marine sponge Suberea mollis and bioactive metabolites of Vibrio sp. EA348. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 27(4):1139-1147.
Brinkmann, C. M., Marker, A., & Kurtböke, D. I. (2017). An overview on marine sponge-symbiotic bacteria as unexhausted sources for natural product discovery. Diversity, 9(4):1-40.
Desniar, Nurhayati, T., Suhartono, M. T., & Isa, E. M. (2006). Modification of marine broth media on protease inhibitors from Acinetobacter baumanni bacteria living in symbiosis with Sponge Plakortis nigra. Buletin Teknologi Hasil Perikanan, 9(1):72-81.
Fouillaud, M. & Dufossé, L. (2022). Microbial secondary metabolism and biotechnology. Microorganisms, 10(1):1-9.
Fukuda, T., Miller, E. D., Kauffman, C. A., Clark, B. R., Alnauman, A., Murphy, C. D., Jensen, P. R., & Fenical, W. (2011). Structures and biosynthesis of the pyridinopyrones, polyenepyrones from a marine-derived Streptomyces species. Journal of Natural Product, 74(8):1773-1778.
Gray, V. L., Müller, C. T., Watkins, I. D., & Lloyd, D. (2008). Peptones from diverse sources: Pivotal determinants of bacterial growth dynamics. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 104(2):554-565.
Hong, S. Y., Lee, D. H., Lee, J. H., Haque, M. A., & Cho, K. M. (2021). Five surfactin isomers produced during cheonggukjang fermentation by Bacillus pumilus HY1 and their properties. Molecules, 26(15):1-13.
Hu, L., Chen, F., & Liang, Y. (2025). Polymerized ferric sulfate influences methane production from the anaerobic digestion of pig slurry: Performance and mechanism. Fuel, 389(15):1-10.
Joint, I., Mühling, M., & Querellou, J. (2010). Culturing marine bacteria - an essential prerequisite for biodiscovery. Microbial Biotechnology, 3(5):564-575.
Jung, Y. T., Park, S., Lee, J. S., & Yoon, J. H. (2016). Roseivirga maritima sp. nov., isolated from seawater. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 66(7):2664-2670.
Lappan, R., Shelley, G., Islam, Z. F., Leung, P. M., Lockwood, S., Nauer, P. A., Jirapanjawat, T., Ni, G., Chen, Y. J., Kessler, A. J., Williams, T. J., Cavicchioli, R., Baltar, F., Cook, P. L. M., Morales, S. E., & Greening C. (2023). Molecular hydrogen in seawater supports growth of diverse marine bacteria. Nature Microbiology, 8(4):581-595.
Lewis, K., Epstein, S., D’Onofrio, A., & Ling, L. L. (2010). Uncultured microorganisms as a source of secondary metabolites. Journal of Antibiotics, 63(8):468-476.
Lipphardt, A., Karmainski, T., Blank, L. M., Hayen, H., & Tiso, T. (2023). Identification and quantification of biosurfactants produced by the marine bacterium Alcanivorax borkumensis by hyphenated techniques. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 415(30):7067-7084.
Liu, Z., Zhao, Y., Huang, C., & Luo, Y. (2021). Recent advances in silent gene cluster activation in Streptomyces. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 9(1):1-10.
Llorens, J. M. N., Tormo, A., & Martínez-García, E. (2010). Stationary phase in gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 34(4):476-495.
Mamangkey, J., Fadjri, C. L., Sunarto, Mustopa, A. Z., Suryanto, D., Hermana, N. S. P., Yanti, N. A., Kusmiati, K., Irawan, H., Hartanto, A., Rudia, L. O. A. P., Akmaliyah, R., Mendes, L. W., & Ferdin. (2025). In-vitro and bioinformatic studies of bioactive compounds from Oceanimonas sp. JM-AZM31 and Lysinibacillus fusiformis JM-AZM37 of sponge-associated marine bacteria from a mangrove habitat in Southeast Sulawesi. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, 23(3):1-15.
Mangurana, W. O. I., Yusnaini, Y., & Sahidin, S. (2019). Analysis of LC-MS/MS (liquid crhomatogaph mass spectrometry) and secondary metabolites and antibacterial potential of N-Hexane spons extract of Callyspongia aerizusa taken under different coral reef cover conditions in the waters of Staring Bay. Jurnal Biologi Tropis, 19(2):131-141.
Mardalena. (2019). Growth phase of lactic acid bacteria isolate Tempoyak from Jambi stored at room temperature. Jurnal Sain Peternakan Indonesia, 11(1):58-66.
Martín, J. F., Sola-Landa, A., Santos-Beneit, F., Fernandez-Martinez, L. T., Prieto, C., & Rodríguez-García, A. (2011). Cross-talk of global nutritional regulators in the control of primary and secondary metabolism in Streptomyces. Microbial Biotechnology, 4(2):165-174.
Marzuki, I., Noor, A., Nafie, N. L., & Djide M. N. (2014). Isolation and identifications bacterium symbionts of sponge as producer enzyme amylase from Melawai Beach of Balikpapan. Jurnal Ilmiah “dr. Aloei Saboe”, 1(2):1-8.
Mehbub, M. F., Yang, Q., & Cheng, Y. (2024). Marine sponge-derived natural products : Trends and opportunities for the decade of 2011-2020. Frontiers in Marine Science. 11(1):1–20.
Morrison, L. & Zembower, T. R. (2020). Antimicrobial resistance. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Clinics of North America, 30(4):619-635.
Novanti, R. & Zulaika, E. (2019). Growth patterns of ureolitic bacteria in medium calcium carbonate precipitation (CCP). Jurnal Sains dan Seni ITS, 7(2):34-35.
Özkaya, F. C., Ebrahim, W., El-Neketi, M., Tanrıkul, T. T., Kalscheuer, R., Müller, W. E. G., Guo, Z., Zou, K., Liu, Z., & Proksch, P. (2018). Induction of new metabolites from sponge-associated fungus Aspergillus carneus by OSMAC approach. Fitoterapia, 131(8):9-14.
Pinu, F. R., Boas, S. G. V., & Aggio, R. (2017). Analysis of intracellular metabolites from Microorganisms : Quenching and extraction protocols. Metabolites, 7(4):1-20.
Risna, Fauziah, R., Subehan, & Djide, N. (2022). Isolation and characterization of bioactive compounds of antibacterial metabolites associated with sea sponges (Agelas Oroides). Majalah Farmasi dan Farmakologi, 26(3):96-100.
Riyanti, Balansa, W., Liu, Y., Sharma, A., Mihajlovic, S., Hartwig, C., Leis, B., Rieuwpassa, J., Ijong, F. G., Wägele, H., König, G. M., & Schäberle, T. F. (2020). Selection of sponge-associated bacteria with high potential for the production of antibacterial compounds. Scientific Reports, 10(1):1-14.
Rodrigues, M. S., Ferreira, L. S., Converti, A., Sato, S., & Carvalho, J. C. M. (2010). Fed-batch cultivation of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis: Potassium nitrate and ammonium chloride as simultaneous nitrogen sources. Bioresource Technology, 101(12):4491-4498.
Romano, S., Jackson, S. A., Patry, S., & Dobson, A. D. W. (2018). Extending the “one strain many compounds” (OSMAC) principle to marine microorganisms. Marine Drugs, 16(7):1-29.
Selvaratnam, C., Thevarajoo, S., Ee, R., Chan, K. G., Bennett, J. P., Goh, K. M., & Chong, C. S. (2016). Genome sequence of Roseivirga sp. strain D-25 and its potential applications from the genomic aspect. Marine Genomics, 28(4):29-31.
Siahaan, S., Herman, M. J., & Fitri, N. (2022). Antimicrobial resistance situation in Indonesia: A challenge of multisector and global coordination. Journal of Tropical Medicine, 2022(1):1-10.
Spyere, A., Rowley, D. C., Jensen, P. R., & Fenical, W. (2003). New neoverrucosane diterpenoids produced by the marine gliding bacterium Saprospira grandis. Journal of Natural Products, 66(6):818-822.
Srinivasan, R., Kannappan, A., Shi, C., & Lin, X. (2021). Marine bacterial secondary metabolites: A treasure house for structurally unique and effective antimicrobial compounds. Marine Drugs, 19(10):1-36.
Thawabteh, A. M., Swaileh, Z., Ammar, M., Jaghama, W., Yousef, M., Karaman, R., Bufo, S. A., & Scrano, L. (2023). Antifungal and antibacterial activities of isolated marine compounds. Toxins, 15(2):1-21.
Varijakzhan, D., Loh, J. Y., Yap, W. S., Yusoff, K., Seboussi, R., Lim, S. H. E., Lai, K. S., & Chong, C. M. (2021). Bioactive compounds from marine sponges: Fundamentals and applications. Marine Drugs, 19(5):1-38.
Vitale, G. A., Sciarretta, M., Cassiano, C., Buonocore, C., Festa, C., Mazzella, V., Pons, L. N., D’auria, V., & de Pascale, D. (2020). Molecular network and culture media variation reveal a complex metabolic profile in Pantoea cf. Eucrina D2 associated with an acidified marine sponge. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(17):1-18.
Wahyuningsih, N. & Zulaika, E. (2018). Comparison of cellulolytic bacteria growth in nutrient broth and carboxy methyl cellulose media. Jurnal Sains dan Seni ITS, 7(2):36-38.
Zulaika, E. & Khofifah, S. S. R. (2021). Production of amylocellulolytic enzymes and their viability on carrier media by Bacillus sp. U4 and Pseudomonas sp. U3. Jurnal Ilmiah Biologi Eksperimen dan Keanekaragaman Hayati, 8(2):59-65.