ANALYSIS OF HOSPITAL INFORMATION MANAGEMENT SYSTEM USING HUMAN ORGANIZATION FIT MODEL
Downloads
Background: Hospital is a health care institution that provides public services for patients. It needs computerized information technology, for example, a hospital information management system.
Aims: This study was aimed at analyzing the implementation of hospital management information system using the human organization fit model at the Outpatient Department of Sabang General Hospital.
Methods: This study was conducted from March-June 2020 using a cross sectional design. The study's population was the hospital managers, administration staff and health workers at the hospital. The study's sample size was 106 respondents selected using a purposive sampling. This study used a quantitative design in which the data analysis was done using a spearman correlation test with P-value of =<0.05. The independent variables were the quality of system, quality of information, and quality of care. While the dependent variables included system user, user satisfaction and organization. The data were collected through questionnaire distributed to the respondents.
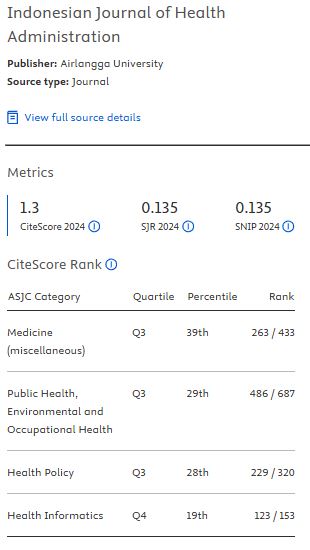
Results: The quality of system did not have a relationship with the system user (P=0.585), user satisfaction (P=0.541), and organization (P=0.256). The quality of information had a relationship with the system user(P=0.004) and user satisfaction (P=0.000), but it did not have a relationship with organization (P=0.132). The quality of care had a relationship with the system user(P=0.000), user satisfaction (P=0.000) and organization (P=0.000).
Conclusion: The Sabang General Hospital, Aceh, needs to improve the hospital management information system with the HOT-fit model, especially the quality of system. They can conduct training for users and provide applicable and attractive manuals.
Keywords: hospital, information management system, quality of care, quality of information, quality of system.
Agustina, R., & Susilani, A. T. (2018a). Evaluasi Sistem Informasi Manajemen Rumah Sakit ( SIMRS ) pada Bagian Pendaftaran Rawat Jalan dengan Metode HOT-FIT Evaluation Of Hospital Management Information System ( SIMRS ) On Registration Outpatient With Hot-Fit Keywords : Evaluation ., HOT-FIT .,. Prosiding Seminar Nasional Multimedia & Arttficial Intelligence, (84), 75–80.
Ayuardini, M., Ridwan, A., Sistem, J., Bisnis, I., & Rekayasa, D. (2019). Implementasi Metode Hot Fit pada Evaluasi Tingkat Kesuksesan Sistem Pengisian KRS Terkomputerisasi. Faktor Exacta, 12(2), 122–131. https://doi.org/10.30998/faktorexacta.v12i2.3639
DeLone, W. H., & McLean, E. R. (2003). The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: A ten-year update. Journal of Management Information Systems, 19(4), 9–30. https://doi.org/10.1080/07421222.2003.11045748
Diantono, P., & Winarno, W. W. (2018). Evaluasi Penerapan SIMRS Menggunakan Metode Hot-Fit Di RSUD Dr . Soedirman Kebumen. 2(1), 46–56.
Erimalata, S. (2016). Pendekatan Hot-Fit Framework dalam Generalized Structural Component Analysis pada Sistem Informasi Manajemen Barang Milik Daerah : Sebuah Pengujian Efek Resiprokal. 17(2), 141–157. https://doi.org/10.18196/jai.2016.0051.141-157
Erlirianto, L. M., Holil, A., Ali, N., & Herdiyanti, A. (2015). The Implementation of the Human , Organization , and Technology – Fit (HOT – Fit ) Framework to evaluate the Electronic Medical Record (EMR) System in a Hospital. Procedia - Procedia Computer Science, 72, 580–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.12.166
Farzandipou, Mehrdad. Meidani, Zahra. Gilasi, Hamidreza. Dehghan, R. (2017). Evaluation of Key Capabilities for Hospital Information System: A Milestone for Meaningfull Use of Information Technology. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Public Health, 10(6), 1579–1586.
Habiburrahman. (2016). Model-Model Evaluasi Dalam Sistem Informasi Perpustakaan. Ilmu Perpustakaan Dan Informasi. https://doi.org/http://dx.doi.org/10.30829/jipi.v1i1.111
Mudiono, D., & Hernawati, Sri. Bukhori, S. (2018). Dampak Kualitas Sistem, Pengguna Sistem dan Organisasi dalam Pemanfaatan Kinerja Sistem Informasi Manajemen Rumah Sakit di RSU Dr. H. Koesnadi. Journal Unej, 589(1), 25–29.
Munzir, M., & Khaira, N. (2020). Evaluasi Keberhasilan Implementasi Sistem Informasi Manajemen Kuliah Kerja Nyata Menggunakan Metode Hot Fit. Ilmiah Rekayasa Dan Manajemen Sistem Informasi, 6(1), 100–108.
Nofikasari, I., & Sunyoto, A. (2017). Evaluasi Penerapan Sistem Informasi Akademik Dengan Pendekatan Model Delone & McLean, HOT FIT dan UTAUT (Studi Kasus: STMIK Duta Bangsa Surakarta) 1,2,3. 12(April), 81–90.
Nurlani, L., & Permana, B. (2017). Analisa Kesuksesan Sistem Informasi Akademik Menggunakan Model Terintegrasi. 2(2), 105–116.
Peraturan Menteri Kesehatan. (2013). Sistem Informasi Manajemen Rumah Sakit. Nomor 82.
Poluan, F., Lumenta, A., & Sinsuw, A. (2015). Evaluasi Implementasi Sistem E-Learning Menggunakan Model Evaluasi Hot Fit Studi Kasus Universitas Sam Ratulangi. Jurnal Teknik Informatika, 4(2), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.35793/jti.4.2.2014.6985
Rusdiana, H. A. (2014). Sistem Informasi Manajemen. Bandung: Cv. Pustaka Setia.
Saputra, A. B. (2016). Identifikas Faktor-Faktor Keberhasilan Implementasi Sistem Informasi Manajemen Rumah Sakit. Jurnal Penelitian Pers Dan Komunikasi Pembangunan, 19(3), 135–148.
Soraya, I., Adawiyah, W. R., & Sutrisna, E. (2019). Pengujian Model Hot Fit Pada Sistem Informasi Manajemen Obat di Instalasi Farmasi RSGMP Unsoed Purwokerto. Jurnal Ekonomi, Bisnis, Dan Akuntansi, 21(1), 1–16.
Soraya, I., Adawiyah, W., & Sutrisna, E. (2018). Pengujian Model HOT FIT Pada Sistem Informasi Manajemen Obat Di Instalasi Farmasi RSGMP Unsoed Purwokerto. Fakultas Ekonomi Dan Bisnis, Universitas Jenderal Sudirman, Indonesia, 1–16.
Sudiarti, T., Soepangat, S., & Wiyono, T. (2019). Analisis Implementasi Sistem Informasi Manajemen di Instalasi Rawat Jalan Klinik Paru Analysis of Implementation of Management Information System. 5(1), 57–67.
1. As an author you (or your employer or institution) may do the following:
- make copies (print or electronic) of the article for your own personal use, including for your own classroom teaching use;
- make copies and distribute such copies (including through e-mail) of the article to research colleagues, for the personal use by such colleagues (but not commercially or systematically, e.g. via an e-mail list or list server);
- present the article at a meeting or conference and to distribute copies of the article to the delegates attending such meeting;
- for your employer, if the article is a ‘work for hire', made within the scope of your employment, your employer may use all or part of the information in the article for other intra-company use (e.g. training);
- retain patent and trademark rights and rights to any process, procedure, or article of manufacture described in the article;
- include the article in full or in part in a thesis or dissertation (provided that this is not to be published commercially);
- use the article or any part thereof in a printed compilation of your works, such as collected writings or lecture notes (subsequent to publication of the article in the journal); and prepare other derivative works, to extend the article into book-length form, or to otherwise re-use portions or excerpts in other works, with full acknowledgement of its original publication in the journal;
- may reproduce or authorize others to reproduce the article, material extracted from the article, or derivative works for the author's personal use or for company use, provided that the source and the copyright notice are indicated.
All copies, print or electronic, or other use of the paper or article must include the appropriate bibliographic citation for the article's publication in the journal.
2. Requests from third parties
Although authors are permitted to re-use all or portions of the article in other works, this does not include granting third-party requests for reprinting, republishing, or other types of re-use.
3. Author Online Use
- Personal Servers. Authors and/or their employers shall have the right to post the accepted version of articles pre-print version of the article, or revised personal version of the final text of the article (to reflect changes made in the peer review and editing process) on their own personal servers or the servers of their institutions or employers without permission from JAKI;
- Classroom or Internal Training Use. An author is expressly permitted to post any portion of the accepted version of his/her own articles on the author's personal web site or the servers of the author's institution or company in connection with the author's teaching, training, or work responsibilities, provided that the appropriate copyright, credit, and reuse notices appear prominently with the posted material. Examples of permitted uses are lecture materials, course packs, e-reserves, conference presentations, or in-house training courses;