RECOMMENDATIONS TO IMPROVE EMPLOYEE PERSONAL ATTITUDE TOWARD REPORTING PATIENT SAFETY INCIDENTS
Background: Patient Safety Incidents (PSI) in hospitals are adverse events that need to be reported for effective identification and risk management, aiming to prevent reoccurrence of incidents. However, not all incidents are documented, as evidenced by the discrepancy in the number of phlebitis reported by employees as well as Infection IPCLN at three hospitals.
Aims: Provide recommendations to improve employee Personal Attitude towards reporting PSI at three hospitals owned by Company A.
Methods: The method adopted was a cross-sectional research design; data were collected from three hospitals owned by company A and tested using multiple logistic regression statistics tests. Data on Phlebitis reported from January to July 2018 at three hospitals owned by Company A was used. Furthermore,135 respondents were taken from the service installations of the three hospitals. The Lameshow formula and proportional random sampling are applied to determine the sample.
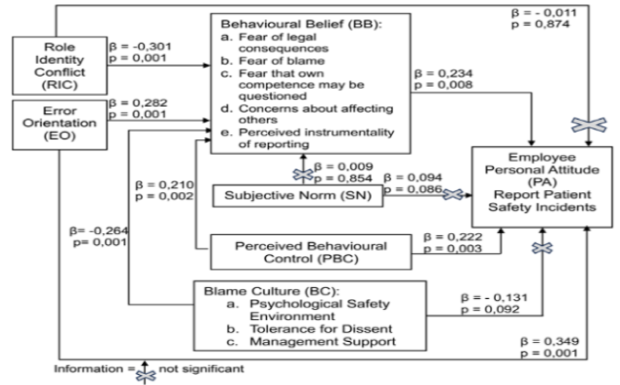
Results: The variables of error orientation (p = 0.001; β = 0.349), behavioral belief (p = 0.008; β = 0.234), and perceived behavioral control (p = 0.003; β = 0.222) had a positive and significant effect on the personal attitude of employees reporting PSI.
Conclusion: Two approaches were recommended to improve the personal attitude of employees in reporting PSI.
Keywords: Hospital, Patient safety incidents, Personal attitude, Underreporting
Abdelmaksoud, S., Salahudeen, M.S. and Curtain, C.M. (2024) ‘Medication Error Reporting Attitudes and Practices in a Regional Australian Hospital: A Qualitative Study’, Journal of Pharmacy Practice and Research, 54(1), pp. 41–47. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1002/jppr.1887.
Ajzen, I. (2005) Attitudes, Personality and Behaviour. 2nd edn. Berkshire, UK: Open University Press-McGraw Hill Education.
Barreto, R.S. et al. (2021) ‘Conceptions of Patient Safety Through the Prism of Social Representations of Intensive Care Nurses’, Investigación y Educación en Enfermería, 39(2). Available at: https://doi.org/10.17533/udea.iee.v39n2e06.
Benevento, M. et al. (2023) ‘Strengths and Weaknesses of the Incident Reporting System: An Italian Experience’, Journal of Patient Safety and Risk Management, 28(1), pp. 15–20. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1177/25160435221150568.
Borgia, M. et al. (2024) ‘The Relationship Between Respondents’ Characteristics and Their Perceptions of Enterprise Risk Management. Results of a Survey’, International Business Research, 17(3), pp. 1–1. Available at: https://doi.org/10.5539/ibr.v17n3p1.
Brabcová, I. et al. (2023) ‘Reasons for Medication Administration Errors, Barriers to Reporting Them and the Number of Reported Medication Administration Errors from the Perspective of Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Survey’, Nurse Education in Practice, 70, pp. 103642–103642. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2023.103642.
Dias, C.N. and Carreiro, M.D.A. (2020) ‘Perfil das notificações de incidentes em saúde em um hospital universitário’, Revista Enfermagem UERJ, 28, pp. e43213–e43213. Available at: https://doi.org/10.12957/reuerj.2020.43213.
Eldrwish, M.A. et al. (2022) ‘Attitude Towards Pharmaceutical Promotional Tools and Its Influence on Physicians’ Prescribing Behaviour in Sudan’, International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Marketing, 16(4), pp. 469–489. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPHM-03-2021-0036.
Faustino, T.N. et al. (2021) ‘National Patient Safety Program in Brazil: Incidents Reported Between 2014 and 2017’, Journal of Patient Safety, 17(8), pp. e1202–e1208. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1097/PTS.0000000000000496.
Fekonja, Z. et al. (2023) ‘Factors Contributing to Patient Safety During Triage Process in the Emergency Department: A Systematic Review’, Journal of Clinical Nursing, 32(17–18), pp. 5461–5477. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.16622.
Fernandez, R. et al. (2023) ‘Predicting Behavioural Intentions Towards Medication Safety Among Student and New Graduate Nurses Across Four Countries’, Journal of Clinical Nursing, 32(5–6), pp. 789–798. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.16330.
Härkänen, M. et al. (2021) ‘Factors Related to Medication Administration Incidents in England and Wales Between 2007 and 2016: A Retrospective Trend Analysis’, Journal of Patient Safety, 17(8), pp. e850–e857. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1097/PTS.0000000000000639.
Hidayat, A.A.A., Sukadiono and Wijayanti, E. (2020) ‘Predictor Factors of Phlebitis Incidence for Children in Hospital Private in Sidoarjo, Indonesia’, Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy, 11(06). Available at: https://doi.org/10.31838/srp.2020.6.39.
Koike, D. et al. (2022) ‘Change in the Number of Patient Safety Reports Through a 16-Year Patient Safety Initiative: A Retrospective Study Focusing on the Incident Severity and Type in a Japanese Hospital’, Risk Management and Healthcare Policy, Volume 15, pp. 2071–2081. Available at: https://doi.org/10.2147/RMHP.S385453.
Lemeshow, S. et al. (1990) Adequacy of sample size in health studies. 9th edn, p. 11.
Mahmoud, H.A. et al. (2023) ‘Barriers and Facilitators to Improving Patient Safety Learning Systems: A Systematic Review of Qualitative Studies and Meta-Synthesis’, BMJ Open Quality, 12(2), pp. e002134–e002134. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjoq-2022-002134.
van Marum, S., Verhoeven, D. and de Rooy, D. (2022) ‘The Barriers and Enhancers to Trust in a Just Culture in Hospital Settings: A Systematic Review’, Journal of Patient Safety, 18(7), pp. e1067–e1075. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1097/PTS.0000000000001012.
Mohan, M., Ghoshal, R. and Roy, N. (2022) ‘Maternal Referral Delays and a Culture of Downstream Blaming Among Healthcare Providers: Causes and Solutions’, Public Health Ethics, 15(3), pp. 268–276. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1093/phe/phac021.
Nurdin, D.A. and Wibowo, A. (2021) ‘Barriers to Reporting Patient Safety Incident in Healthcare Workers: Integrative Literature Review’, Jurnal Administrasi Kesehatan Indonesia, 9(2), pp. 210–210. Available at: https://doi.org/10.20473/jaki.v9i2.2021.210-217.
Oweidat, I. et al. (2023) ‘Awareness of Reporting Practices and Barriers to Incident Reporting Among Nurses’, BMC Nursing, 22, pp. 231–231. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-023-01376-9.
Pfeiffer, Y., Manser, T. and Wehner, T. (2010) ‘Conceptualising Barriers to Incident Reporting: A Psychological Framework’, BMJ Quality & Safety, 19(6), pp. e60–e60. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1136/qshc.2008.030445.
Rocco, C., Rodríguez, A.M. and Noya, B. (2022) ‘Elimination of Punitive Outcomes and Criminalization of Medical Errors’, Current Opinion in Anaesthesiology, 35(6), pp. 728–732. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1097/ACO.0000000000001197.
Rocha, R. et al. (2024) ‘Epidemiological and Clinical Trends of Visceral Leishmaniasis in Portugal: Retrospective Analysis of Cases Diagnosed in Public Hospitals Between 2010 and 2020’, Infectious Diseases of Poverty, 13(1), pp. 41–41. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40249-024-01204-5.
Schram, A. et al. (2021) ‘Patient Safety Culture Improves During an in Situ Simulation Intervention: A Repeated Cross-Sectional Intervention Study at Two Hospital Sites’, BMJ Open Quality, 10(1), pp. e001183–e001183. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjoq-2020-001183.
Scott, J. et al. (2021) ‘Content Analysis of Patient Safety Incident Reports for Older Adult Patient Transfers, Handovers, and Discharges: Do They Serve Organizations, Staff, or Patients?’, Journal of Patient Safety, 17(8), pp. e1744–e1758. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1097/PTS.0000000000000654.
Shanmuga Anandan, A. and Johnson, D. (2022) ‘Features of incident reports that prompt reviewer feedback and organisational change: A retrospective review’, Journal of Patient Safety and Risk Management, 27(5), pp. 209–217. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1177/25160435221124970.
Sherratt, F. et al. (2023) ‘The Unintended Consequences of No Blame Ideology for Incident Investigation in the Us Construction Industry’, Safety Science, 166, pp. 106247–106247. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2023.106247.
Suhardono et al. (2020) ‘The Effect of Aloe Vera Compress on the Injection Area of Infusion to Phlebitis Incidences in Local Government Hospital in Indonesia’, Journal of critical reviews, 7(04). Available at: https://doi.org/10.31838/jcr.07.04.105.
Tsai, A.Y.J. and Tan, A.Y.K. (2022) ‘Exploratory examination of environmental protection behaviors in a hospital setting using the theory of planned behavior and ethical leadership’, Environmental Research Communications, 4(7), pp. 75006–75006. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1088/2515-7620/ac7e31.
Villalba-Nicolau, M. et al. (2022) ‘Usefulness of Midline Catheters versus Peripheral Venous Catheters in an Inpatient Unit: A Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial’, Nursing Reports, 12(4), pp. 814–823. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep12040079.
Wachter, R.M. (2008) Understanding Patient Safety. USA. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Weprin, S.A. et al. (2021) ‘Incidence and or Team Awareness of “Near-Miss” and Retained Surgical Sharps: A National Survey on United States Operating Rooms’, Patient Safety in Surgery, 15(1), pp. 14–14. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13037-021-00287-5.
Zhang, Xue et al. (2021) ‘Composition and Risk Assessment of Perioperative Patient Safety Incidents Reported by Anesthesiologists from 2009 to 2019: A Single‐Center Retrospective Cohort Study’, BMC Anesthesiology, 21(1), pp. 8–8. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12871-020-01226-0.
Copyright (c) 2024 Purwo Andari, Candra Ferdian Handriyanto, Nyoman Anita Damayanti, Widodo Jatim Pudjirahardjo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. As an author you (or your employer or institution) may do the following:
- make copies (print or electronic) of the article for your own personal use, including for your own classroom teaching use;
- make copies and distribute such copies (including through e-mail) of the article to research colleagues, for the personal use by such colleagues (but not commercially or systematically, e.g. via an e-mail list or list server);
- present the article at a meeting or conference and to distribute copies of the article to the delegates attending such meeting;
- for your employer, if the article is a ‘work for hire', made within the scope of your employment, your employer may use all or part of the information in the article for other intra-company use (e.g. training);
- retain patent and trademark rights and rights to any process, procedure, or article of manufacture described in the article;
- include the article in full or in part in a thesis or dissertation (provided that this is not to be published commercially);
- use the article or any part thereof in a printed compilation of your works, such as collected writings or lecture notes (subsequent to publication of the article in the journal); and prepare other derivative works, to extend the article into book-length form, or to otherwise re-use portions or excerpts in other works, with full acknowledgement of its original publication in the journal;
- may reproduce or authorize others to reproduce the article, material extracted from the article, or derivative works for the author's personal use or for company use, provided that the source and the copyright notice are indicated.
All copies, print or electronic, or other use of the paper or article must include the appropriate bibliographic citation for the article's publication in the journal.
2. Requests from third parties
Although authors are permitted to re-use all or portions of the article in other works, this does not include granting third-party requests for reprinting, republishing, or other types of re-use.
3. Author Online Use
- Personal Servers. Authors and/or their employers shall have the right to post the accepted version of articles pre-print version of the article, or revised personal version of the final text of the article (to reflect changes made in the peer review and editing process) on their own personal servers or the servers of their institutions or employers without permission from JAKI;
- Classroom or Internal Training Use. An author is expressly permitted to post any portion of the accepted version of his/her own articles on the author's personal web site or the servers of the author's institution or company in connection with the author's teaching, training, or work responsibilities, provided that the appropriate copyright, credit, and reuse notices appear prominently with the posted material. Examples of permitted uses are lecture materials, course packs, e-reserves, conference presentations, or in-house training courses;