Detection of Foot and Mouth Disease Virus in Salted Raw Cowhide from Malaysia in Tanjung Priok Port, Indonesia
Downloads
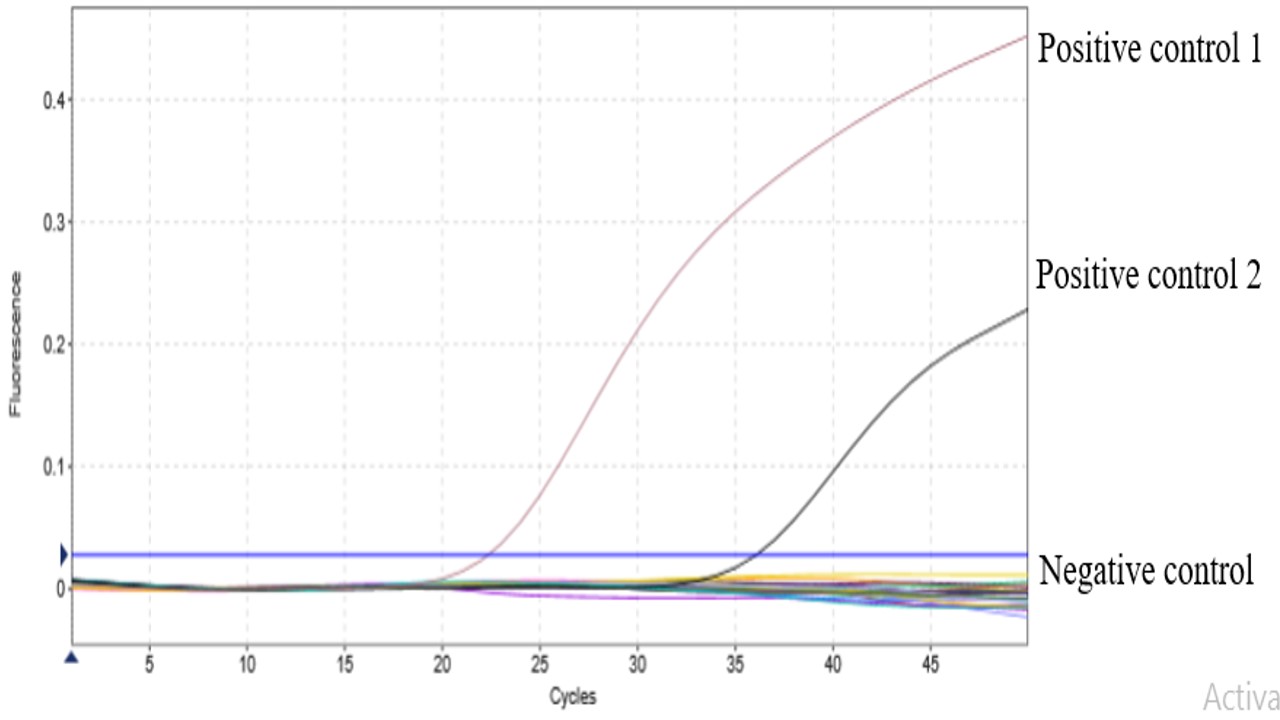
Animal products such as raw salted cowhide are thought to have the potential to transmit the foot and mouth disease (FMD) virus from the infected zone. Indonesia imports raw salted cowhide from Malaysia, so it has the potential to transmit FMD to Indonesia which enters through Tanjung Priok Port. This study aimed to investigate the presence of the FMD virus in raw salted cowhide from Malaysia. The number of samples was collected from each container of raw salted cowhide imported through Tanjung Priok Port during August–December 2022. A total of 21 samples were obtained from 21 bulk containers containing raw salted cowhide. Real time q Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR) was used to investigate foot and mouth disease virus in samples. The RT-qPCR screening test on 21 samples reported that salted raw cowhide was free from the FMD virus. Continuous monitoring and surveillance protocols for salted rawhide imported from non-free countries need to be carried out at other points of entry.
Badan Standardisasi Nasional (BSN). (1998). Petunjuk Pengambilan Contoh Padatan. Jakarta: Badan Standardisasi Nasional. pp: 3–7.
Blacksell, S. D., Siengsanan-Lamont, J., Kamolsiripichaiporn, S., Gleeson, L. J., & Windsor, P. A. (2019). A history of FMD research and control programmes in Southeast Asia: lessons from the past informing the future. Epidemiology Infectious, 147(e171), 1–13.
Buetre B., Wicks S., Kruger H., Millist N., Yainshet A., Garner G., Duncan A., Abdalla A., Trestrail C., Hatt M., Thompson L.J., & Symes M. (2013). Potential socio-economic impacts of an outbreak of foot-andmouth disease in Australia (Research report). ABARES, 13, 2–53.
Chaters, G., Rushton, J., Dulu, T. D., & Lyons, N. A. (2018). Impact on foot and mouth disease on fertility performance in a large dairy herd in Kenya. Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 159(2018), 57–64.
Dinana, Z., Rantam, F. A., Mustofa, I., & Rahmahani, J. (2023). Detection of Foot and Mouth Disease Virus in Cattle in Lamongan and Surabaya, Indonesia Using RT-PCR Method. Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 6(2), 191–196.
Garcia, A. I. E., Lefebvre, D. J., Nyabongo, L., Haegeman, A., Nkundwanayo, C., Vleeschauwer, A., Ntakirutimana, D., Leeuw, I. D., Nsanganiyumwami, D., Niyokwizera, P., Berg, T., Niyokwishimira, A., & Clercq, K. (2022). Outbreaks of foot-and-mouth disease in Burundi, East Africa, in 2016, caused by different serotypes. Viruses, 14(5), 1077.
Gloster, J., & Burgin, L. (2007). UK outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease airborne transmission of virus. London (UK): Defra.
Gloster, J., Freshwater, A., Sellers, R. F., & Alexandersen, S. (2005). Re-assessing the likelihood of airborne spread of foot-and-mouth disease at the start of the 1967–1968 UK foot-and-mouth disease epidemic. Epidemiology Infectious, 133, 767–783.
Haskell, S. R. R. (2014). Blackwell' Five-Minute Veterinary Consult: Ruminant. West Sussex (UK): WilleyBlackwell, A Jhon Willey & Sons Ltd.
Hong, J. K., Lee, K. N., You, S. H., Kim, S. M., Tark, D., Lee, H. S., Ko, Y. J., Seo, M. G., Park, J. H., & Kim, B. (2015). Inactivation of foot and mouth disease virus by citric acid and sodium carbonate with deicers. Applied Environment Microbial, 81(21), 7610–7614.
Jones, T. K. (2014). The socio-economic impact of FMD. Global Foot-and-mouth Disease Research Alliance (GFRA) Newsletter. Fighting Foot-and-mouth Disease Together.
Juliyarsi, I., Melia, S., Novia, D., & Purwati, E. (2019). Kulit: ilmu, teknologi dan aplikasi. Padang: Unand. pp: 51–63.
Kementerian Pertanian (Kementan/ Ministry of Agriculture). (2022). Penetapan Daerah Wabah Penyakit Mulut dan Kuku (Foot and Mouth Disease). Jakarta: Kementerian Pertanian RI.
Kementerian Pertanian (Kementan/ Ministry of Agriculture). (2023). Penetapan Jenis Penyakit Hewan Menular Strategis. Jakarta: Kementerian Pertanian RI.
Khudori. (2022). Efek domino dari wabah penyakit Kaki dan Mulut. Jawa Pos, 9 Mei 2022. (Retrieved 10 Juni 2022). https://www.jawapos.com/opini/09/05/2022/efek-domino-wabah-penyakit-mulut-dan-kuku/.
Kristensen, T., Belsham, G.J., & Tjornehoj, K. (2021). Heat inactivation of foot-and-mouth disease virus, swine vesicular disease virus and classical swine fever virus when air-dried on plastic and glass surfaces. Biosafety Health, 3(4), 217–223.
MacLachlan, N. J., & Dubovi, E. J. (2017). Fenner's Veterinary Virology. 5th ed. Elsevier. Kidlington: Oxford Univ.
MacLachlan, N. J., & Dubovi, E. J. (2011). Fenner's Veterinary Virology. 4th edition. Oxford (UK): Elsevier. pp: 431–432.
Septiyani, Majid, R. A., Gradia, R., Setiawan, I., Yantini, P., & Novianti, A. N. (2023). Peripheral Blood Smear Analysis for Cattle with Foot and Mouth Diseases in Lembang, West Bandung. Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 6(3), 319–325.
Majid, R. A., Gradia, R., Rosdianto, A. M., & Hidayatik, N. (2023). Hematological Profile in Dairy Cattle with Foot and Mouth Diseases in Lembang, West Bandung. Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 6(3), 381–389.
Naipospos, T. S. P., & Suseno, P. P. (2017). Cost Benefit Analysis of Maintaining FMD Freedom Status in Indonesia. Paris: World Organisation of Animal Health. pp: 2.
Nason, J. (2022). Foot and mouth disease reported in Indonesia. Beef Central, Senin, 11 Juli 2022. Nascon Media Pty Ltd. (Retrieved 11 Agustus 2022). https://www.beefcentral.com/news/foot-and-mouth-disease-outbreak-reported-in-indonesia/.
Oktanella, Y., Cahyani, A. A., Hendrawan, V. F., Nugroho, W., & Agustina, G. C. (2023). Foot and Mouth Disease Impact on Milk Productivity and Quality in KUD Kertajaya, Kediri, Indonesia. Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 6(2), 244–249.
Prihatin, K. W., Amaliya, A., Musaffak, T. R., & Rosyada, Z. N. A. (2023). Effect of Foot and Mouth Diseases Vaccination on Basic Semen Quality Parameter in Bali Cattle. Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 6(3), 348–352.
Purnama, M. T. E., Dewi, W. K., Prayoga, S. F., Triana, N. M., Aji, B. S. P., Fikri, F., & Hamid, I. S. (2019). Preslaughter stress in Banyuwangi cattle during transport. Indian Veterinary Journal, 96(12), 50–52.
Ramanoon, S. Z., Robertson, I. D., Edwards,J., Hassan,L., & Isa, K. M. (2013). Outbreaks of foot-and-mouth disease in Peninsular Malaysia from 2001 to 2007. Tropical Animal Health Production, 45(2), 373–377.
Rohma, R. M., Zamzami, A., Utami, H. P., Karsyam, H. A., & Widianingrum, D. C. (2022). Kasus penyakit mulut dan kuku di Indonesia: epidemiologi, diagnosis penyakit, angka kejadian, dampak penyakit dan pengendalian. Di dalam: Prayitno, A. H., Waskithorini, G. Z. E., editor. Tantangan Industri Peternakan melalui Penerapan Green Economy untuk Mewujudkan Kedaulatan Pangan Berkelanjutan di Era Society 5.0. The 3rd National Conference of Applied Animal Science; 2022 Agu 27–28; Jember, Indonesia. Jember: Jurusan Peternakan Politeknik Negeri Jember. pp: 15–22.
Rushton, J., & Knight-Jones, T. (2015). The impact of foot and mouth disease. In: FAO and OIE. Proceedings of the FAO/OIE Global Conference on Foot and Mouth Disease Control 2012; 2012 June 27–29; Bangkok, Thailand. Bangkok. pp. 205–220.
Sarker, M., Long, W., & Liu, C. (2018). Preservation of bovine hide using less salt with low concentration of antiseptic, part I: effectiveness of developed formulations. Journal American Leather Chemical Association, 113(2018), 335–342.
Silitonga, R. (2016). Analisis risiko kualitatif pemasukan virus penyakit mulut dan kuku melalui daging ilegal di perbatasan darat Indonesia-Malaysia [disertasi]. Fakultas Kedokteran Hewan. Institut Pertanian Bogor. pp: 1–3.
United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS), Veterinary Service. (2020). Foot and Mouth Disease Standard Operating Procedures: 1. Overview of Etiology and Ecology. Retrieved from [https://www.aphis.usda.gov/animal_health/emergency_management/downloads/sop/sop_fmd_e-e.pdf].
Valeika, V., Beleska, K., Mikulyte, S., & Valeikiene, V. (2017). Short-term preservation of hide or skin as an approach to greener process. Proceedings of the International Conference on Indonesian Science Education Research 2017. 2017 September 3–4, Buenos Aires, Argentina.
World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH). (2021). Foot and mouth disease. https://www.woah.org/app/uploads/2021/09/foot-and-mouth-disease-1.pdf (Retrieved 20 Juli 2023).
World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH). (2023). Infection with foot and mouth disease virus chapter 8.8. https://www.woah.org/en/what-we-do/standards/codes-and-manuals/terrestrial-code-online-access/?id=169&L=1&htmfile=chapitre_fmd (Retrieved 18 Juli 2023).
Wu, J., Zhao, L., Liu, X., Chen, W., & Gu, H. (2017). Recent progress in cleaner preservation of hides and skins. Journal Clean Production, 148(2017), 158–173.
Copyright (c) 2024 Disty Ayu Sekarsana, Chaerul Basri, Denny Widaya Lukman

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions;
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions;
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-SA).






11.jpg)




















