Malaria and Related Haemosporidian Parasites of Wildlife in Southeast Asia: A Risk for Global Health
Downloads
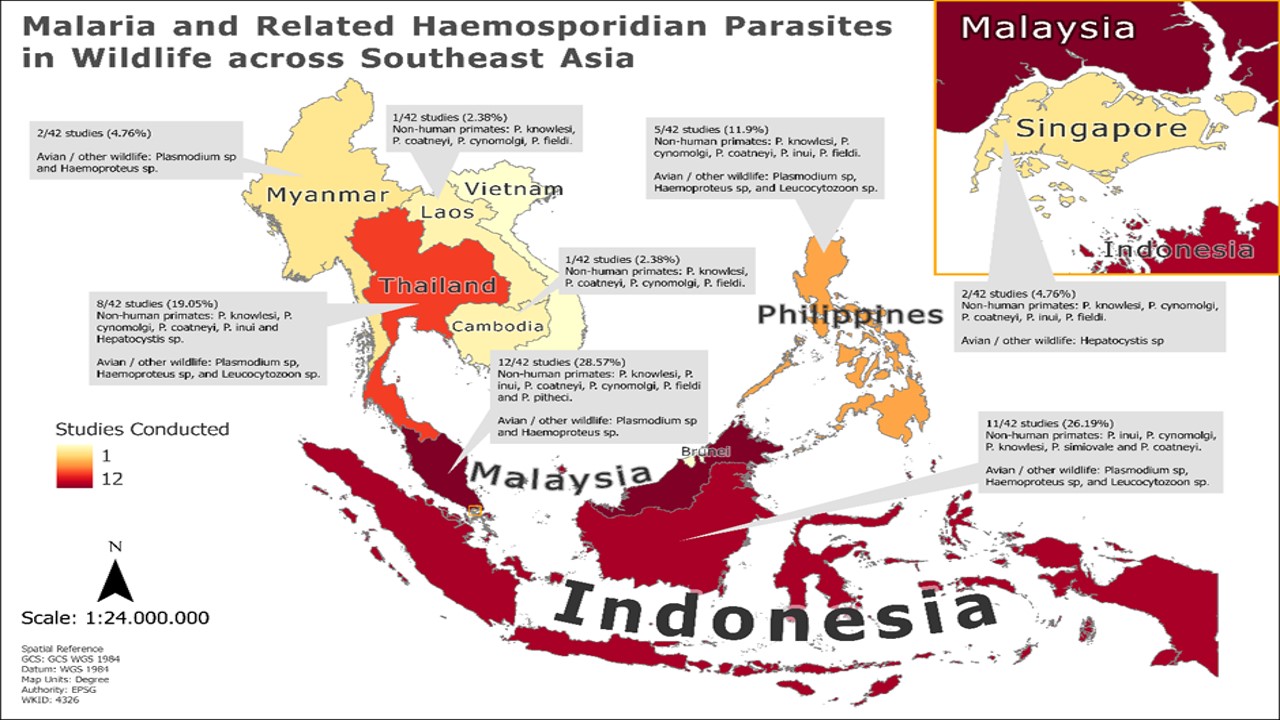
Malaria and related haemosporidian parasites are widespread diseases that can inflict severe harm on both humans and animals. These parasites are protozoans classified within the order Haemosporidia, which encompasses four families: Garniidae, Haemoproteidae, Leucocytozoidae, and Plasmodiidae. The majority of species belong to three primary genera—Haemoproteus, Leucocytozoon, and Plasmodium—which have the capacity to infect a diverse array of animal species, including birds, reptiles, snakes, and mammals. Diagnostic techniques, such as light microscopy and molecular methods like polymerase chain reaction (PCR), have been extensively developed to identify these infections. Despite these advancements, research on the prevalence of malaria in wildlife across Southeast Asia remains sparse. This review article examines the significance of malaria and related haemosporidian parasites in wildlife within Southeast Asia and their potential implications for global human health. A total of 285 articles were reviewed, with 42 qualitative studies being included in this analysis. The majority of these studies were conducted in Malaysia, Indonesia, Thailand, the Philippines, Singapore, Myanmar, Laos, and Cambodia. Among the reviewed studies, 27 out of 42 (64.28%) focused on non-human primates, while 15 out of 42 (35.71%) addressed other wildlife such as birds and bats. Macaca fascicularis (long-tailed macaque) was the primary subject in 18 studies (66.66%), followed by M. nemestrina, Pongo pygmaeus, and various other macaque species and gibbons. In contrast, studies involving other wildlife, including birds and bats, exhibited considerable variability in species and sample sizes, ranging from a minimum of 4 individuals to a maximum of 400 individuals. Molecular diagnostics are predominantly used for non-human primates and other wildlife, as opposed to conventional methods like blood smears. Zoonotic malaria has emerged as a significant concern due to factors such as deforestation, agricultural expansion, and forest fragmentation, which increase human-wildlife interactions and facilitate mosquito breeding, thereby heightening the risk of Plasmodium knowlesi malaria. In summary, malaria and related haemosporidian parasites represent a substantial public health threat in Southeast Asia.
Akter, R., Vythilingam, I., Khaw, L. T., Qvist, R., Lim, Y. A. L., Sitam, F. T., Venugopalan, B., & Sekaran, S. D. (2015). Simian malaria in wild macaques: first report from Hulu Selangor district, Selangor, Malaysia. Malaria Journal, 14(1), 1–9.
Amir, A., Shahari, S., Liew, J. W. K., de Silva, J. R., Khan, M. B., Lai, M. Y., Snounou, G., Abdullah, M. L., Gani, M., Rovie-Ryan, J. J., & Lau, Y. L. (2020). Natural Plasmodium infection in wild macaques of three states in peninsular Malaysia. Acta Tropica, 211(April), 1–6.
Angelika, P., Kurniawan, F., & Santi, B. T. (2021). Malaria Knowlesi Pada Manusia. Damianus Journal of Medicine, 20(1), 72–88.
Aryaloka, S., Khairullah, A. R., Kusala, M. K. J., Fauziah, I., Hidayatik, N., Agil, M., Yuliani, M. G. A., Novianti, A. N., Moses, I. B., Purnama, M. T. E., Wibowo, S., Fauzia, K. A., Raissa, R., Furqoni, A. H., Awwanah, M., & Riwu, K. H. P. (2024). Navigating monkeypox: identifying risks and implementing solutions. Open Veterinary Journal, 14(12), 3144.
Asale, A., Duchateau, L., Devleesschauwer, B., Huisman, G., & Yewhalaw, D. (2017). Zooprophylaxis as a control strategy for malaria caused by the vector Anopheles arabiensis (Diptera: Culicidae): a systematic review. Infectious Diseases of Poverty, 6(1), 160.
Baird, J. K. (2009). Malaria zoonoses. Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease, 7(5), 269–277.
Bayu, D., Anggriawan, F., Yudhana, A., Edila, R., Aldila, A., Dosen, A., Veteriner, D. P., & Parasitologi, D. (2020). Laporan Pertama Kasus Infeksi Haemoproteus (Phylum: Apicomplexa, Famili: Haemoproteidae) pada Burung Kenari (Serinus canaria) di Kota Banyuwangi, Indonesia. 86–93.
Bordier, M., & Roger, F. (2013). Zoonoses in South-East Asia: a regional burden, a global threat. Animal Health Research Reviews / Conference of Research Workers in Animal Diseases, 14(1), 40–67.
Brown, R., Chua, T. H., Fornace, K., Drakeley, C., Vythilingam, I., & Ferguson, H. M. (2020). Human exposure to zoonotic malaria vectors in village, farm and forest habitats in Sabah, Malaysian Borneo. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 14(9), 1–18.
Chin, W., Contacos, P. G., Coatney, G. R., & Kimball, H. R. (1965). A Naturally Acquired Quotidian-Type Malaria in Man Transferable to Monkeys. Science, 149(3686), 865–865.
Chinsembu, K. C. (2015). Plants as antimalarial agents in Sub-Saharan Africa. Acta Tropica, 152, 32–48.
Chotivanich, K., Udomsangpetch, R., Simpson, J. A., Newton, P., Pukrittayakamee, S., Looareesuwan, S., & White, N. J. (2000). Parasite Multiplication Potential and the Severity of Falciparum Malaria. The Journal of Infectious Diseases, 181(3), 1206–1209.
Chua, A. C. Y., Ong, J. J. Y., Malleret, B., Suwanarusk, R., Kosaisavee, V., Zeeman, A. M., Cooper, C. A., Tan, K. S. W., Zhang, R., Tan, B. H., Abas, S. N., Yip, A., Elliot, A., Joyner, C. J., Cho, J. S., Breyer, K., Baran, S., Lange, A., Maher, S. P., Bifani, P. (2019). Robust continuous in vitro culture of the Plasmodium cynomolgi erythrocytic stages. Nature Communications, 10(1), 3635.
Collins, W. E., Contacos, P. G., Skinner, J. C., & Guinn, E. G. (1971). Studies on the Transmission of Simian Malaria. IV. Further Studies on the Transmission of Plasmodium knowlesi by Anopheles balabacensis balabacensis Mosquitoes. The Journal of Parasitology, 57(5), 961.
Collins, W. E., Sullivan, J. S., Galland, G. G., Nace, D., Williams, A., Williams, T., & Barnwell, J. W. (2007). Isolates Of Plasmodium inui Adapted To Macaca Mulatta Monkeys And Laboratory-Reared Anopheline Mosquitoes For Experimental Study. Journal of Parasitology, 93(5), 1061–1069.
Collins, W. E., Warren, M., Sullivan, J. S., & Barnwell, J. W. (2009). Plasmodium inui shortii: studies in old world and new world monkeys. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 80(1), 160–164.
Collins, W. E. (2012). Plasmodium knowlesi: a malaria parasite of monkeys and humans. Annu Rev Entomol, 57, 107–121.
Cox-Singh, J., Davis, T. M. E., Lee, K. S., Shamsul, S. S. G., Matusop, A., Ratnam, S., Rahman, H. A., Conway, D. J., & Singh, B. (2008). Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in humans is widely distributed and potentially life threatening. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 46(2), 165–171.
Desamero, M. J. M., & Eduardo, S. L. (2010). Some hemoprotozoa (Apicomplexa) of two Philippine owl species (Strigiformes) with description of a new species, haemoproteus topacioi Desamero & Eduardo (Haemoproteidae). Philippine Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 47(1), 34–40.
Dhamayanti, Y., Suryadiningrat, M., Mujiburrahman, A., Firdausy, L. W., Maslamama, S. T., & Purnama, M. T. E. (2025). The anatomy, histology, and oxidative stress level of the liver in fruit bat (Rousettus amplexicaudatus). Biodiversitas Journal of Biological Diversity, 26(1).
Dian, N. D., Rahim, M. A. F. A., Chan, S., & Idris, Z. M. (2022). Non-Human Primate Malaria Infections: A Review on the Epidemiology in Malaysia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(13).
Eudey, A. A. (2008). The Crab-Eating Macaque (Macaca fascicularis): Widespread and Rapidly Declining. Primate Conservation, 23(1), 129–132.
Eyles, D. E., Coatney, G. R., & Getz, M. E. (1960). Vivax -Type Malaria Parasite of Macaques Transmissible to Man. Science, 131(3416), 1812–1813.
Fikri, F., Hendrawan, D., Wicaksono, A. P., Purnomo, A., Khairani, S., Chhetri, S., Maslamama, S. T., & Purnama, M. T. E. (2023). Incidence, risk factors, and therapeutic management of equine colic in Lamongan, Indonesia. Veterinary World, 16(7), 1408.
Fikri, F., Hendrawan, D., Wicaksono, A. P., Purnomo, A., Khairani, S., Chhetri, S., Purnama, M. T. E., & Çalışkan, H. (2024). Colic incidence, risk factors, and therapeutic management in a working horse population in Tuban, Indonesia. Veterinary World, 17(5), 963.
Fooden, J. (1994). Malaria in macaques. International Journal of Primatology, 15(4), 573–596.
Fooden, J. (1995). Systematic review of Southeast Asian longtail macaques, Macaca fascicularis (Raffles, [1821]) / Jack Fooden. Field Museum of Natural History.
Fornace, K. M., Brock, P. M., Abidin, T. R., Grignard, L., Herman, L. S., Chua, T. H., Daim, S., William, T., Patterson, C. L. E. B., Hall, T., Grigg, M. J., Anstey, N. M., Tetteh, K. K. A., Cox, J., & Drakeley, C. J. (2019). Environmental risk factors and exposure to the zoonotic malaria parasite Plasmodium knowlesi across northern Sabah, Malaysia: a population-based cross-sectional survey. The Lancet Planetary Health, 3(4), e179–e186.
Fungfuang, W., Udom, C., Tongthainan, D., Kadir, K. A., & Singh, B. (2020). Malaria parasites in macaques in Thailand: Stump-tailed macaques (Macaca arctoides) are new natural hosts for Plasmodium knowlesi, Plasmodium inui, Plasmodium coatneyi and Plasmodium fieldi. Malaria Journal, 19(1), 1–7.
Gamalo, L. E., Dimalibot, J., Kadir, K. A., Singh, B., & Paller, V. G. (2019). Plasmodium knowlesi and other malaria parasites in long-tailed macaques from the Philippines. Malaria Journal, 18(1), 1–7.
Ishtiaq, F., Gering, E., Rappole, J. H., Rahmani, A. R., Jhala, Y. V., Dove, C. J., Milensky, C., Olson, S. L., Peirce, M. A., & Fleischer, R. C. (2007). Prevalence and diversity of avian hematozoan parasites in Asia: A regional survey. Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 43(3), 382–398.
Ivanova, K., Zehtindjiev, P., Mariaux, J., & Georgiev, B. B. (2015). Genetic diversity of avian haemosporidians in Malaysia: Cytochrome b lineages of the genera Plasmodium and Haemoproteus (Haemosporida) from Selangor. Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 31, 33–39.
Jeslyn, W. P. S., Huat, T. C., Vernon, L., Irene, L. M. Z., Sung, L. K., Jarrod, L. P., Singh, B., & Ching, N. L. (2011). Molecular epidemiological investigation of Plasmodium knowlesi in humans and macaques in Singapore. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases, 11(2), 131–135.
Jeyaprakasam, N. K., Liew, J. W. K., Low, V. L., Wan-Sulaiman, W. Y., & Vythilingam, I. (2020). Plasmodium knowlesi infecting humans in southeast asia: What’s next? PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 14(12), 1–16.
Jongwutiwes, S., Buppan, P., Kosuvin, R., Seethamchai, S., Pattanawong, U., Sirichaisinthop, J., & Putaporntip, C. (2011). Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in humans and macaques, Thailand. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 17(10), 1799–1806.
Kaewchot, S., Tangsudjai, S., Sariya, L., Mongkolphan, C., Saechin, A., Sariwongchan, R., Panpeth, N., Thongsahuan, S., & Suksai, P. (2022). Zoonotic pathogens survey in free-living long-tailed macaques in Thailand. International Journal of Veterinary Science and Medicine, 10(1), 11–18.
Kesumawati, U., Rosmanah, L., Soviana, S., Saepuloh, U., & Darusman, H. S. (2021). Morphological Features and Molecular of Plasmodium inui in Macaca fascicularis from Bogor, West Java. Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Veterinary, Animal, and Environmental Sciences (ICVAES 2020), 12(Icvaes 2020), 48–51.
Kilbourn, A. M., Karesh, W. B., Wolfe, N. D., Bosi, E. J., Cook, R. A., & Andau, M. (2003). Health evaluation of free-ranging and semi-captive orangutans (Pongo pygmaeus pygmaeus) in Sabah, Malaysia. Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 39(1), 73–83.
Klein, T. A., Harrison, B. A., Dixon, S. V, & Burge, J. R. (1991). Comparative susceptibility of Southeast Asian Anopheles mosquitoes to the simian malaria parasite Plasmodium cynomolgi. Journal of the American Mosquito Control Association, 7(3), 481–487.
Knowles, R., & Gupta, B. M. Das. (1932). A Study of Monkey-Malaria, and Its Experimental Transmission to Man. The Indian Medical Gazette, 67(6), 301–320.
Kosaisavee, V., Suwanarusk, R., Chua, A. C. Y., Kyle, D. E., Malleret, B., Zhang, R., Imwong, M., Imerbsin, R., Ubalee, R., Sámano-Sánchez, H., Yeung, B. K. S., Ong, J. J. Y., Lombardini, E., Nosten, F., Tan, K. S. W., Bifani, P., Snounou, G., Rénia, L., & Russell, B. (2017). Strict tropism for CD71+/CD234+ human reticulocytes limits the zoonotic potential of Plasmodium cynomolgi. Blood, 130(11), 1357–1363.
Latif, E. N. M., Shahari, S., Amir, A., Cheong, F. W., Lau, Y. L., Abdullah, M. L., & Fong, M. Y. (2022). Genetic diversity of Duffy binding protein 2 region II of Plasmodium cynomolgi from wild macaques in Peninsular Malaysia. Tropical Biomedicine, 39(1), 66–72.
Lee, K. S., Cox-Singh, J., & Singh, B. (2009). Morphological features and differential counts of Plasmodium knowlesi parasites in naturally acquired human infections. Malaria Journal, 8(1), 73.
Lee, K. S., Divis, P. C. S., Zakaria, S. K., Matusop, A., Julin, R. A., Conway, D. J., Cox-Singh, J., & Singh, B. (2011). Plasmodium knowlesi: Reservoir hosts and tracking the emergence in humans and macaques. PLoS Pathogens, 7(4).
Lempang, M. E. P., Permana, D. H., Asih, P. B. S., Wangsamuda, S., Dewayanti, F. K., Rozi, I. E., Setiadi, W., Syahrani, L., Malaka, R., Muslimin, L., & Syafruddin, D. (2023). Prevalence of Plasmodium sp. infection on endemic primates in the Buton Utara Wildlife Sanctuary, Southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia.
Lertwatcharasarakul, P., Salakij, C., Prasopsom, P., Kasorndorkbua, C., Jakthong, P., Santavakul, M., Suwanasaeng, P., & Ploypan, R. (2021). Molecular and Morphological Analyses of Leucocytozoon Parasites (Haemosporida: Leucocytozoidae) in Raptors From Thailand. Acta Parasitologica, 66(4), 1406–1416.
Li, M. I., Mailepessov, D., Vythilingam, I., Lee, V., Lam, P., Ng, L. C., & Tan, C. H. (2021). Prevalence of simian malaria parasites in macaques of Singapore. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 15(1), 1–12.
Liew, J. W. K., Bukhari, F. D. M., Jeyaprakasam, N. K., Phang, W. K., Vythilingam, I., & Lau, Y. L. (2021). Natural Plasmodium inui Infections in Humans and Anopheles cracens Mosquito, Malaysia. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 27(10), 2700–2703.
Low, D. H. W., Hitch, A. T., Skiles, M. M., Borthwick, S. A., Neves, E. S., Lim, Z. X., Lee, B. P. Y. H., Su, Y. C. F., Smith, G. J. D., & Mendenhall, I. H. (2021). Host specificity of Hepatocystis infection in short-nosed fruit bats (Cynopterus brachyotis) in Singapore. International Journal for Parasitology: Parasites and Wildlife, 15(January), 35–42.
Lubis, I. N. D., Wijaya, H., Lubis, M., Lubis, C. P., Divis, P. C. S., Beshir, K. B., & Sutherland, C. J. (2017). Contribution of Plasmodium knowlesi to multispecies human Malaria infections in North Sumatera, Indonesia. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 215(7), 1148–1155.
Maeno, Y., Quang, N. T., Culleton, R., Kawai, S., Masuda, G., Nakazawa, S., & Marchand, R. P. (2015). Humans frequently exposed to a range of non-human primate malaria parasite species through the bites of Anopheles dirus mosquitoes in South-central Vietnam. Parasites & Vectors, 8(1), 376.
Marchand, R. (2011). Co-infections of Plasmodium knowlesi, P. falciparum, and P. vivax among Humans and Anopheles dirus Mosquitoes, Southern Vietnam. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 17(7), 1232–1239.
Mawson, A. R. (2013). The pathogenesis of malaria: A new perspective. Pathogens and Global Health, 107(3), 122–129.
Mewara, A., Sreenivasan, P., & Khurana, S. (2023). Primate malaria of human importance. Tropical Parasitology, 13(2), 73–83.
Ihsan, A. Z. M. A., Mohd Rohaizat, H., & Rozita, H. (2020). Distribution and Prevalence of Plasmodium Knowlesi Among Macaques In Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia. 1–16.
Muehlenbein, M. P., Pacheco, M. A., Taylor, J. E., Prall, S. P., Ambu, L., Nathan, S., Alsisto, S., Ramirez, D., & Escalante, A. A. (2015). Accelerated diversification of nonhuman primate malarias in Southeast Asia: Adaptive radiation or geographic speciation? Molecular Biology and Evolution, 32(2), 422–439.
Muhammad, A., Azman, E., Eddie, N., Azmi, N., Yee, V. T., & Idris, Z. (2022). The rise of Plasmodium knowlesi cases: Implication to Malaysia’s malaria-free status. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine, 15(8), 337.
Muriel, J., Marzal, A., Magallanes, S., García-Longoria, L., Suarez-Rubio, M., Bates, P. J. J., Lin, H. H., Soe, A. N., Oo, K. S., Aye, A. A., Wilbur, N. D., Win, N. N., Soe, Y. T., Linn, K. K., & Renner, S. C. (2021). Prevalence and diversity of avian haemosporidians may vary with anthropogenic disturbance in tropical habitats in myanmar. Diversity, 13(3), 1–19.
Nada-Raja, T., Kadir, K. A., Divis, P. C. S., Mohamad, D. S. A., Matusop, A., & Singh, B. (2022). Macaca fascicularis and Macaca nemestrina infected with zoonotic malaria parasites are widely distributed in Sarawak, Malaysian Borneo. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 1–6.
Ong, B. K. C., Paller, V. G. V, Guia, A. P. O. De, Balatibat, J. B., & Gonzalez, C. T. (2015). Prevalence of avian haemosporidians among understorey birds of Mt. Conservation Biology, 63(June), 279–286.
Pacheco, M. A., Reid, M. J. C., Schillaci, M. A., Lowenberger, C. A., Galdikas, B. M. F., Jones-Engel, L., & Escalante, A. A. (2012). The origin of malarial parasites in orangutans. PLoS ONE, 7(4).
Pasvol, G., Weatherall, D. J., & Wilson, R. J. M. (1980). The Increased Susceptibility of Young Red Cells to Invasion by the Malarial Parasite Plasmodium falciparum. British Journal of Haematology, 45(2), 285–295.
Permana, D. H., Hasmiwati, Suryandari, D. A., Rozi, I. E., Syahrani, L., Setiadi, W., Irawati, N., Rizaldi, Wangsamuda, S., Yusuf, Y., Irdayanti, Aswad, H., Asih, P. B. S., & Syafruddin, D. (2023). The potential for zoonotic malaria transmission in five areas of Indonesia inhabited by non-human primates. Parasites & Vectors, 16(1), 267.
Pornpanom, P., Fernandes Chagas, C. R., Lertwatcharasarakul, P., Kasorndorkbua, C., Valkiūnas, G., & Salakij, C. (2019). Molecular prevalence and phylogenetic relationship of Haemoproteus and Plasmodium parasites of owls in Thailand: Data from a rehabilitation centre. International Journal for Parasitology: Parasites and Wildlife, 9(June), 248–257.
Pornpanom, P., Kasorndorkbua, C., Lertwatcharasarakul, P., & Salakij, C. (2021). Prevalence and genetic diversity of Haemoproteus and Plasmodium in raptors from Thailand: Data from rehabilitation center. International Journal for Parasitology: Parasites and Wildlife, 16(August), 75–82.
Purnama, M. T. E., Dewi, W. K., Prayoga, S. F., Triana, N. M., Aji, B. S. P., Fikri, F., & Hamid, I. S. (2019). Preslaughter stress in banyuwangi cattle during transport. Indian Veterinary Journal, 96(12), 50–52.
Purnama, M. T. E., Dewi, W. K., Triana, N. M., & Ooi, H. K. (2021). Serum liver enzyme profile in Timor deer (Cervus timorensis) with fascioliasis in Indonesia. Tropical Biomedicine, 38(1), 57–61.
Purnama, M. T. E., Hendrawan, D., Wicaksono, A. P., Fikri, F., Purnomo, A., & Chhetri, S. (2022). Risk factors, hematological and biochemical profile associated with colic in Delman horses in Gresik, Indonesia. F1000Research, 10, 950.
Purnama, M. T. E., Prayoga, S. F., Triana, N. M., Dewi, W. K., Purnomoaji, B. S., Wardhana, D. K., & Fikri, F. (2020). Oxidative stress parameters in landrace pigs slaughtered by the stunning method. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 441(1), 012140.
Putaporntip, C., Jongwutiwes, S., Thongaree, S., Seethamchai, S., Grynberg, P., & Hughes, A. L. (2010). Ecology of malaria parasites infecting Southeast Asian macaques: Evidence from cytochrome b sequences. Molecular Ecology, 19(16), 3466–3476.
Reid, M. J. C., Ursic, R., Cooper, D., Nazzari, H., Griffiths, M., Galdikas, B. M., Garriga, R. M., Skinner, M., & Lowenberger, C. (2006). Transmission of human and macaque Plasmodium spp. to ex-captive orangutans in Kalimantan, Indonesia. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 12(12), 1902–1908.
Rosmanah, L., Nugraha, A. B., & Darusman, H. S. (2022). Leukocyte Differential Study in Macaca nemestrina infected by Plasmodium spp. Indonesian Journal of Primatology, 1(01), 10–14.
Sainawal, T. L., Yuda, I. P., & Zahida, F. (2016). Prevalensi Malaria Pada Burung di Taman Nasional Gunung Merapi Dengan Metode Nested PCR. 6(August).
Saleh Huddin, A., Md Yusuf, N. A., Razak, M. R. M. A., Ogu Salim, N., & Hisam, S. (2019). Genetic diversity of Plasmodium knowlesi among human and long-tailed macaque populations in Peninsular Malaysia: The utility of microsatellite markers. Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 75(July), 103952.
Sanchez, K. L., Greenwood, A. D., Nielsen, A., Nugraha, R. T. P., Prameswari, W., Nurillah, A., Agustina, F., Campbell-Smith, G., Dharmayanthi, A. B., Pratama, R., Exploitasia, I., & Baird, J. K. (2022). Plasmodium pitheci malaria in Bornean orang-utans at a rehabilitation centre in West Kalimantan, Indonesia. Malaria Journal, 21(1), 1–18.
Sanchez, M. S., & Paller, V. G. V. (2022). Prevalence of hemoparasites in avian species of coastal and upland sites of Marinduque Island. Ecosystems and Development Journal, 12(2), 75–84.
Schmidt, L. H., Greenland, R., & Genther, C. S. (1961). The Transmission of Plasmodium cynomolgi to Man *. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 10(5), 679–688.
Scott, J. (2020). Proposed Integrated Control of Zoonotic Plasmodium knowlesi in Southeast Asia Using Themes of One Health. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 5(4), 175.
Seethamchai, S., Putaporntip, C., Malaivijitnond, S., Cui, L., & Jongwutiwes, S. (2008). Malaria and Hepatocystis species in wild macaques, southern Thailand. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 78(4), 646–653.
Silva-Iturriza, A., Ketmaier, V., & Tiedemann, R. (2012). Prevalence of avian haemosporidian parasites and their host fidelity in the central Philippine islands. Parasitology International, 61(4), 650–657.
Singh, B., Sung, L. K., Matusop, A., Radhakrishnan, A., Shamsul, S. S., Cox-Singh, J., Thomas, A., & Conway, D. J. (2004). A large focus of naturally acquired Plasmodium knowlesi infections in human beings. The Lancet, 363(9414), 1017–1024.
Su, X., & Wu, J. (2021). Zoonotic Transmission and Host Switches of Malaria Parasites. Zoonoses, 1(1), 1–18.
Subbarao, S. K. (2011). Centenary celebrations article. Journal of Parasitic Diseases, 35(2), 87–93.
Ta, T. H., Hisam, S., Lanza, M., Jiram, A. I., Ismail, N., & Rubio, J. M. (2014). First case of a naturally acquired human infection with Plasmodium cynomolgi. Malaria Journal, 13(1), 68.
Tan, C. H., Vythilingam, I., Matusop, A., Chan, S. T., & Singh, B. (2008). Bionomics of Anopheles latens in Kapit, Sarawak, Malaysian Borneo in relation to the transmission of zoonotic simian malaria parasite Plasmodium knowlesi. Malaria Journal, 7(1), 52.
Tavinia, T., Fikri, F., Chhetri, S., & Purnama, M. T. (2023). Risk factors of feline lower urinary tract disease in Banten, Indonesia. The Indian Veterinary Journal, 100(6), 24–28.
Telford, S. R., & Wellehan, J. F. X. (2005). Two Plasmodium species of the crocodile skink Tribolonotus gracilis from Irian Jaya, Indonesia. Journal of Parasitology, 91(1), 148–151.
van Rooyen, C. E., & Pile, G. R. (1935). Observations on infection by Plasmodium knowlesi (ape malaria) in the treatment of general paralysis of the insane. BMJ, 2(3901), 662–666.
Vythilingam, I., Tan, C. H., Asmad, M., Chan, S. T., Lee, K. S., & Singh, B. (2006). Natural transmission of Plasmodium knowlesi to humans by Anopheles latens in Sarawak, Malaysia. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 100(11), 1087–1088.
Vythilingam, Indra, Noorazian, Y. M., Huat, T. C., Jiram, A. I., Yusri, Y. M., Azahari, A. H., Norparina, I., Noorrain, A., & Lokmanhakim, S. (2008). Plasmodium knowlesi in humans, macaques and mosquitoes in peninsular Malaysia. Parasites and Vectors, 1(1), 1–10.
World Health Organization (WHO). (2022). World malaria report 2022. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2022, pp: 293.
Wyler, D. J., Miller, L. H., & Schmidt, L. H. (1977). Spleen Function in Quartan Malaria (Due to Plasmodium inui): Evidence for Both Protective and Suppressive Roles in Host Defense. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 135(1), 86–93.
Yuda, P. (2019). Detection of avian malaria in wild birds at Trisik Beach of Yogyakarta, Java (Indonesia). Annals of Parasitology, 65(2), 171–175.
Yusuf, N. M., Zulkefli, J., Jiram, A. I., Vythilingam, I., Hisam, S., Devi, R., Salehhuddin, A., Ali, N. M., Isa, M., Alias, N., Salim, N. O., Aziz, A. A., & Sulaiman, L. H. (2022). Plasmodium spp. in macaques, Macaca fascicularis, in Malaysia, and their potential role in zoonotic malaria transmission. Parasite, 29.
Zhang, X., Kadir, K. A., Quintanilla-Zariñan, L. F., Villano, J., Houghton, P., Du, H., Singh, B., & Smith, D. G. (2016). Distribution and prevalence of malaria parasites among long-tailed macaques (Macaca fascicularis) in regional populations across Southeast Asia. Malaria Journal, 15(1), 1–8.
Copyright (c) 2025 Shafia Khairani, Endang Yuni Setyowati, Ita Krissanti

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions;
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions;
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-SA).






11.jpg)




















