Macroanatomy, Histomorphometry, and Androgen Receptor Expression in the Epididymis of Kacang Goats Aged 4, 8, and 12 Months
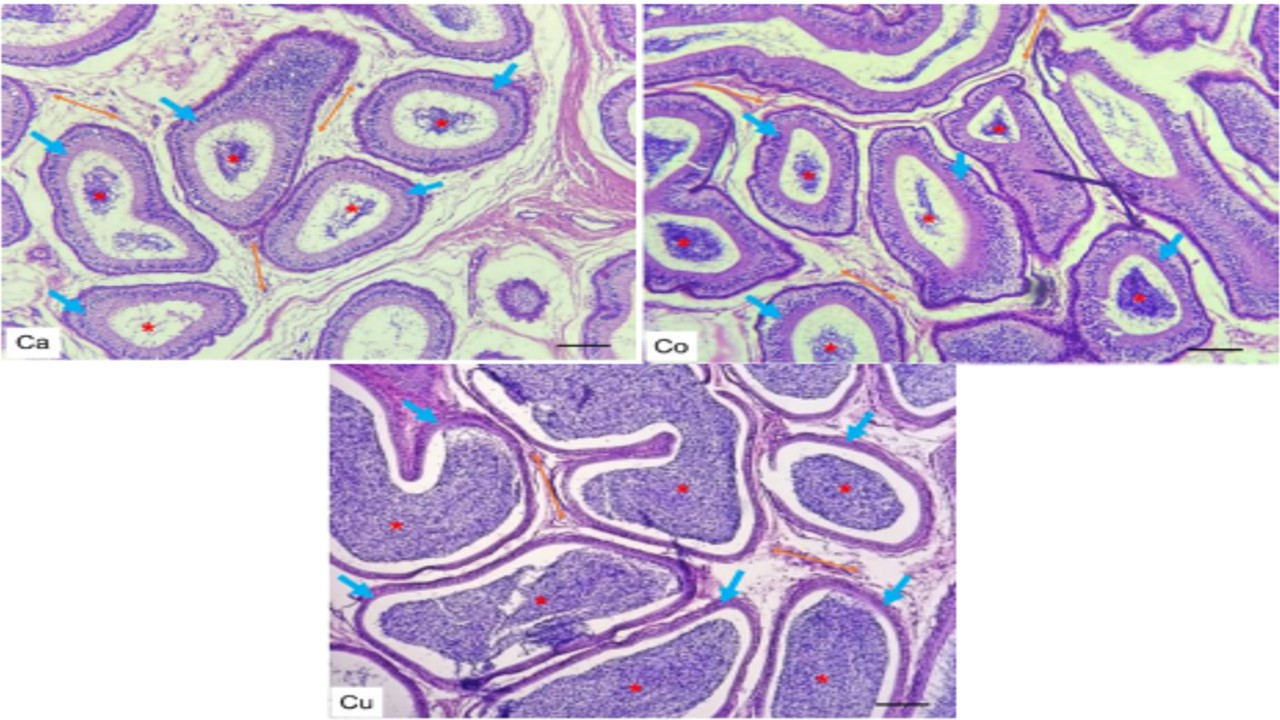
The epididymis is a crucial component of the goat's reproductive structure. The epididymis is responsible for the transportation, concentration, and maturation of sperm. This study aimed to examine the differences in the structure of macro and microanatomy, tissue composition, and the existence of androgen receptors in the epididymis of Kacang goats aged 4, 8, and 12 months. The assessment of macroscopic organ growth was done immediately after sampling, whereas microscopic measurements were carried out following histological preparations using hematoxylin-eosin (HE) and immunohistochemical (IHC) procedures. The results on the macroscopic anatomy of the epididymis indicated a significant association between age with the width of the caput dexter and sinister and the circumference of the right cauda. However, no significant relationship was found between age with the corpus length and the left cauda's circumference. Significant variations were observed in the diameter and concentration of the agglutinated spermatozoa in the lumen during histomorphometry of the epididymis in three age groups of Kacang goats. There were no statistically significant variations in the expression of androgen receptors among the three age groups. This study showed that the correlation coefficient test reveals a positive relationship between age and the caput width and corpus length dimensions, indicating that these measurements tend to grow as age increases. On the other hand, the diameter of the agglutinated spermatozoa in the epididymal lumen exhibits significant variations between the ages of 4 months, with the ages of 8 months and 12 months, suggesting that the sperm becomes fully matured by the age of 8 months.
Abdullahi Mahmud, M., Shehu, S., Danmaigoro, A., Onu, J., Abdullahi Shehu, S., Umaru, A., & Shaibu Atabo, M. (2015). Morphological Studies on Epididymis and Vas Deferens of One-Humped Camel Bull (Camelus dromedarius). Article in Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 3(5), 65–71.
Al-Sadoon, A. A., Al-Yasery, A. J., & Al-Khagani, I. Y. (2019). Comparative morphological and anatomical study to development of testes and epididymis in males of arrabi and awassi sheep. Plant Arch, 19(1), 181–190.
Andaruisworo, S., Tanjungsari, A., Yuniati, E., & Khairullah, A. R. (2023). Diluent and Storage Time Effect on Sperm Abnormality and MDA Level in Muscovy Duck Semen at 27°C. Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 6(3), 390–401.
Archana, Katiyar, R. S., Sharma, D. N., & Farooqui, M. M. (2011).. Gerentological studies on the epididymis of Gaddi goat (Capra hircus). Indian Journal of Veterinary Research, 20(1), 26–32.
Bahari, B. S., Agoeshermadi, H., Fikri, F., Sardjito, T., Purnomo, A., Chhetri, S., Maslamama, S. T., & Purnama, M. T. E. (2023). Efficacy of intra-vulvo submucosal prostaglandins on estrous cycles in goats. The Indian Veterinary Journal, 100(4), 24–27.
Dalimunthe, N. W. Y., Ridlo, M. R., & Budiyanto, A. (2017). Optimalisasi Pembekuan Sperma Limbah Kauda Epididimis Kambing Lokal dengan Metode Bertahap dan Stabilisasi. Jurnal Sain Veteriner, 35(2), 150–158.
Davey, R. A., & Grossmann, M. (2016). Androgen Receptor Structure, Function and Biology: From Bench to Bedside. The Clinical Biochemist Reviews, 37(1), 3.
Fedchenko, N., & Reifenrath, J. (2014). Different approaches for interpretation and reporting of immunohistochemistry analysis results in the bone tissue - a review. Diagnostic Pathology, 9(1), 221.
Fiqih, A. F., Soeharsono, S., Yunita, M. N., Dhamayanti, Y., & Yudhana, A. (2021). Toxic Effect of Robusta Coffee Extract (Coffea canephora) on Bali Cattle Spermatozoa After Equilibration. Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 4(2), 189–192.
Fitria, L., Muyati, M., Tiraya, C. M., & Budi, A. S. (2018). Profil Reproduksi Jantan Tikus (Rattus norvegicus Berkenhout, 1769) Galur Wistar Stadia Muda, Pradewasa, dan Dewasa. Jurnal Biologi Papua, 7(1), 29–36.
Goyal, H. O., Bartol, F. F., Wiley, A. A., & Neff, C. W. (1997). Immunolocalization of receptors for androgen and estrogen in male caprine reproductive tissues: Unique distribution of estrogen receptors in efferent ductule epithelium. Biology of Reproduction, 56(1), 90–101.
Hanifah, N. F., Ratnani, H., Purnama, M. T. E., Restiadi, T. I., Agustono, B., & Prastiya, R. A. (2020). Effect of Glycerol Concentration in Tris Diluents on Spermatozoa Quality of Sapera Goats Before Freezing. Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 3(2), 154–159.
Hejmej, A., Wiszniewska, B., Kosiniak-Kamysz, K., Sadowska, J., & Bilińska, B. (2006). The presence of androgen receptors in the epididymis and prostate of the stallion and cryptorchid horse – A preliminary study. The Veterinary Journal, 171(2), 373–379.
Khan, S. A., Kalhoro, I. B., Gandahi, J. A., Vistro, W. A., Kalwer, Q., Ali, I., Khokhar, T. A., & Mangi, M. H. (2019). Puberty associated micro anatomical modification in testes and epididymis of Teddy goat (Capra hircus). Pesquisa Agropecuaria Brasileira, 8(2), 1281–1286.
Kurniasih, N. N., Fuah, A. M., & Priyanto, R. (2013). Karakteristik Reproduksi dan Perkembangan Populasi Kambing Peranakan Etawah di Lahan Pasca Galian Pasir. Jurnal Ilmu Produksi Dan Teknologi Hasil Peternakan, 1(3), 132–137.
Kuyucu, Y., Coşkun, G., Şaker, D., Karaoğlan, Ö., Ürünsak, İ. F., İzol, V., Arıdoğan, İ. A., Erdoğan, Ş., Özgür, H., & Polat, S. (2021). Immunohistochemical examination of androgen receptor and estrogen receptor alpha expressions in obstructive and non-obstructive azoospermia. Systems Biology in Reproductive Medicine, 67(6), 463–470.
Lestari, T. D., & Ismudiono. (2014). Ilmu Reproduksi Ternak. Airlangga University Press. pp: 34.
Mansour, Y. A., Mosallam, E. S. M. M., Hussein, S., Elleithy, E. M. M., Moussa, I. M., Mubarak, A. S., Dawoud, T. M., Alsubki, R. A., Alhaji, J. H., Hemeg, H. A., & EL-Bargeesy, G. A. H. (2021). Immunolocalization of androgen and vitamin D receptors in the epididymis of mature ram (Ovis aries). Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 28(1), 217.
Nielsen, S. S., Alvarez, J., Bicout, D. J., Calistri, P., Depner, K., Drewe, J. A., Garin-Bastuji, B., Gonzales Rojas, J. L., Schmidt, C. G., Michel, V., Miranda Chueca, M. Á., Roberts, H. C., Sihvonen, L. H., Spoolder, H., Stahl, K., Velarde, A., Viltrop, A., Candiani, D., Van der Stede, Y., & Winckler, C. (2020). Welfare of cattle at slaughter. EFSA Journal, 18(11), e06275.
Noviana, C., Boediono, A., & Wresdiyati, T. (2000). Morphology and Histomorphometry of Testis And Epididymis of Kacang Goat (Capra sp.) and Local Sheep (Ovis sp.). Media Veteriner, 7(2).
Perobelli, J. E., Patrão, M. T. C. C., Fernandez, C. D. B., Sanabria, M., Klinefelter, G. R., Avellar, M. C. W., & Kempinas, W. D. G. (2013). Androgen deprivation from pre-puberty to peripuberty interferes in proteins expression in pubertal and adult rat epididymis. Reproductive Toxicology, 38, 65–71.
Prayogo, D., Susilowati, S., Prastiya, R. A., Safitri, E., & Agustono, B. (2022). Difference Time Effect of Equilibration Before Freezing on The Quality of Spermatozoa Sapera Goats using Egg Yellow Tris. Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 5(2), 188–195.
Purnama, M. T. E., Rahmaningtyas, I. H., Putri, A. S., Lee, A. S. I., Tatimma, F. N., & Masyitoh, H. (2019). Acupuncture could increase spermatogonic cells in albino rats exposed to heat stroke. Indian Veterinary Journal, 96(10), 30–32.
Raji, L. O., Fayemi, O. E., Ameen, S. A., & Jagun, A. T. (2012). The Effects of Aqueous Extract of Allium sativum (Garlic) on Some Aspects of Reproduction in the Female Albino Rat (Wistar Strain). Global Veterinaria, 8(4), 414–420.
Rava, P. C., Sarkar, D., Singha, S., Mondal, M., Mandal, D. K., Das, S. K., Rai, S., Bhakat, C., & Karunakaran, M. (2023). Testicular biometry and semen quality in Bengal kids during pubertal period. Research Square, 2023(3).
Rodriguez-Martinez, H., Roca, J., Alvarez-Rodriguez, M., & Martinez-Serrano, C. A. (2022). How does the boar epididymis regulate the emission of fertile spermatozoa? Animal Reproduction Science, 246, 106829.
Sangen, O. R., Firmawati, A., Marhendra, A. P. W., & Titisari, N. (2021). Spermatogenesis Duration on Adult Javan Langur (Trachypithecus auratus) Based on Testosteron Hormone and Luteinizing Hormone (LH). Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 4(1), 110–117.
Saputro, A. L., Prastiya, R. A., Ulinuha, M. Z., & Widayani, P. (2022). The Effectiveness of Time Equilibration Before Freezing in Sapera Goat Spermatozoa After Electric Separating Sperm. Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 5(1), 1–8.
Tella, A., Chineke, C. A., & Jacob, O. O. (2023). Correlation coefficient of live weight and body measurements of extensively reared West African Dwarf goats in south west zone of Nigeria. Ghana Journal of Agricultural Science, 58(1).
Tmaneak, M. I., Beyleto, V. Y., & Nurwati, M. (2016). Penampilan Produksi Ternak Kambing Kacang Jantan dari Berbagai Kelompok Umur di Kecamatan Insana Utara Kabupataen Timor Tengah Utara. JAS, 1(1), 9–11.
Wajdi, S. A., Utomo, B., Rimayanti, R., Safitri, E., Suprayogi, T. W., & Wurlina, W. (2021). Suppementation of Kelor Leaf (Moringa Oleifera) Aqueous Extract Increase on Post-Thawed Limousin Bull Sperm Quality. Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 4(2), 249–255.
Wijayanti, A., Suprayogi, T. W., Prastiya, R. A., Hernawati, T., Sardjito, T., Saputro, A. L., Amaliya, A., & Sulistyowati, D. (2023). Effect of Addition of Green Tea Extract (Camellia sinensis) in Egg Yolk Tris Diluter on Spermatozoa Quality in Bali Cattle (Bos sondaicus) After Freezing. Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 6(1), 66–74.
Yendraliza, Priyandi, A., Handoko, J., Sianturi, G., Sari, R., & Kusumaningrum, D. A. (2023). The Quality of Buffalo Sperm in Tris Egg Yolk Diluent with Addition of Different Levels of Mangosteen Peel Extract. Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 6(3), 353–358.
Zaya, R., Hennick, C., & Pearl, C. A. (2012). In vitro expression of androgen and estrogen receptors in prepubertal and adult rat epididymis. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 178(3), 573–586.
Copyright (c) 2024 Herlina Pratiwi, Diki Purnama Putra, Wike Andre Septian, Ahmad Furqon, Suyadi Suyadi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions;
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions;
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-SA).






11.jpg)




















