Development of Skeletal Ossification in Climbing Perch (Anabas testudineus) from Juvenile to Adulthood
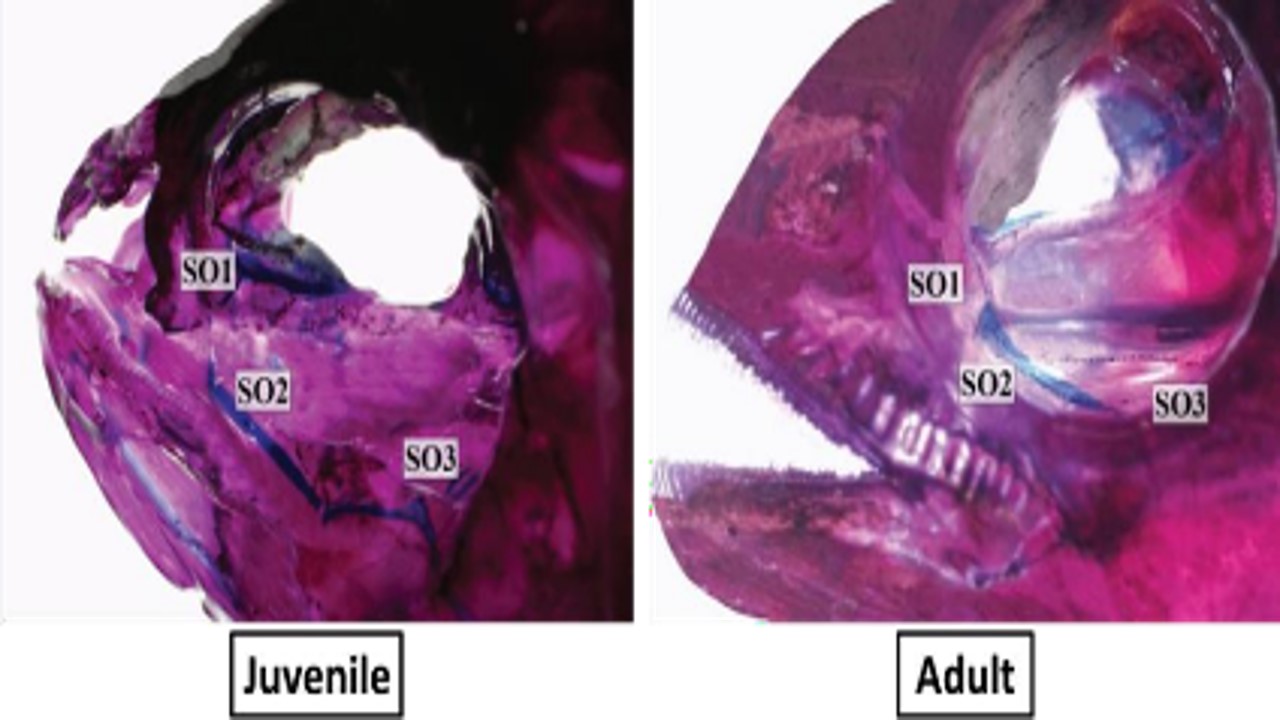
The climbing perch (Anabas testudineus) is a freshwater fish that can withstand highly unfavorable environments and stay out of the water for extended periods. Its anatomical characteristics showed terrestrial adaptation and terrestrial locomotion properties enable the use of climbing perch as an animal model. Moreover, its bone and cartilage profiles at different stages are crucial to improving the anatomical information for the osteogenesis model candidate. The current study aimed to illustrate the skeletal profiles of juvenile and adult climbing perch with the whole staining method. The samples included two adults and two juvenile climbing perch from Daerah Istimewa Yogyakarta, Indonesia. The fish were euthanized using β-hydroxyethyl phenyl ether in a lethal dose. The skeleton was examined using the Alcian blue–Alizarin red whole staining, which revealed the bones and cartilage under the stereomicroscope. The result showed that the bone is the main skeleton. Cartilage was detected in the area surrounding the orbit in the adult climbing perch and in the pterotic, pterosphenoid, prootic, and distal end of the hypural, parhypural, and basal pectoral girdle in the juvenile climbing perch. Endochondral osteogenesis was found in juvenile to adult climbing perch.
Ahammad, A. K. S., Asaduzzaman, M., Uddin Ahmed, M. B., Akter, S., Islam, M. S., Haque, M. M., Ceylan, H., & Wong, L. L. (2021). Muscle cellularity, growth performance and growth-related gene expression of juvenile climbing perch Anabas testudineus in response to different eggs incubation temperature. Journal of Thermal Biology, 96, 1–8.
Benjamin, M. (1990). The cranial cartilages of teleosts and their classification. Journal of Anatomy, 169, 153–172.
Bensimon-Brito, A., Cardeira, J., Dionísio, G., Huysseune, A., Cancela, M. L., & Witten, P. E. (2016). Revisiting in vivo staining with alizarin red S - A valuable approach to analyse zebrafish skeletal mineralization during development and regeneration. BMC Developmental Biology, 16(1), 1–9.
Bergen, D. J. M., Kague, E., & Hammond, C. L. (2019). Zebrafish as an emerging model for osteoporosis: A primary testing platform for screening new osteo-active compounds. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 10(6), 1–20.
Bird, N. C., & Mabee, P. M. (2003). Developmental Morphology of the Axial Skeleton of the Zebrafish, Danio rerio (Ostariophysi: Cyprinidae). Developmental Dynamics, 228(3), 337–357.
Blumer, M. J. F. (2021). Bone tissue and histological and molecular events during development of the long bones. Annals of Anatomy, 235, 1–11.
Breeland, G., Sinkler, M. A., & Menezes, R. G. (2023). Embryology, Bone Ossification. In StatPearls. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30969540
Claeson, K. M., & Dean, M. N. (2011). The skeleton | Cartilaginous Fish Skeletal Anatomy. In Encyclopedia of Fish Physiology, 1, 419–427.
Clarke, B. (2008). Normal bone anatomy and physiology. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology : CJASN, 3(Suppl 3), 131–139.
Davenport, J., & Matin, A. K. M. A. (1990). Terrestrial locomotion in the climbing perch, Anabas testudineus (Bloch) (Anabantidea, Pisces). Journal of Fish Biology, 37(1), 175–184.
Hidayat, R., Carman, O., & Alimuddin, A. (2016). Sexual dimorphism related to growth in climbing perch Anabas testudineus. Jurnal Akuakultur Indonesia, 15(1), 8–14.
Hidayat, R., Carman, O., & Alimuddin, A. (2024). Early Sex Differentiation of Climbing Perch (Anabas testudineus Bloch.): A Pathway to Feminization. Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 7(1), 143–154.
Hidayatulloh, D. R., Dhamayanti, Y., & Purnama, M. T. E. (2021). Species determination based on head scutes, carapace, and plastron of turtle hatchlings at Boom Beach, Banyuwangi. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 718(1), 012047.
Ismarica, I., Setiawati, M., Jusadi, D., & Suprayudi, M. A. (2020). Bone formation and growth of climbing perch Anabas testudinieus larvae fed with Zn enriched Artemia nauplii. Jurnal Akuakultur Indonesia, 19(2), 153–159.
Kader, M. A., Bulbul, M., Ahmed, G. U., Hossain, M. S., Hossain, M. A., & Koshio, S. (2011). Effects of animal proteins in practical diets on growth and economic performance of climbing perch, Anabas testudineus (Bloch). Journal of Applied Aquaculture, 23(2), 166–176.
Khan Manon, M. R., Alam, A., Ullah, M. R., Hossen, M. B., Sufian, M. A., Hossain, M. A., Iqbal, M. M., & Rahman, M. A. (2023). Intraspecific phenotypic differences in climbing perch Anabas testudineus (Bloch, 1792) populations may be linked to habitat adaptations. Heliyon, 9(7).
Khatun, D., Hossain, M. Y., Rahman, M. A., Islam, M. A., Rahman, O., Azad, M. A. K., Sarmin, M. S., Parvin, M. F., Ul Haque, A. T., Mawa, Z., & Hossain, M. A. (2019). Life-History Traits of the Climbing perch Anabas testudineus (Bloch, 1792) in a Wetland Ecosystem. Jordan Journal of Biological Sciences, 12(2), 175–182.
Li, B., Zhang, Y. W., Liu, X., Ma, L., & Yang, J. X. (2021). Molecular mechanisms of intermuscular bone development in fish: A review. Zoological Research, 32(3), 362–376.
Li, W., Ura, K., & Takagi, Y. (2022). Industrial application of fish cartilaginous tissues. Current Research in Food Science, 5(April), 698–709.
Mackie, E. J., Ahmed, Y. A., Tatarczuch, L., Chen, K. S., & Mirams, M. (2008). Endochondral ossification: How cartilage is converted into bone in the developing skeleton. International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, 40(1), 46–62.
Nabi, M. R., & Ara, I. (2018). International Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Studies 2018; 6(4): 484–491 Osteological comparison between local and Thai climbing perch in terms of neurocranium, vertebral column and accessory respiratory organ. Ijfas, 6(4), 484–491.
Prianto, E., Kamal, M. M., Muchsin, I., & Kartamihardja, E. S. (2014). Biologi Reproduksi Ikan Betok (Anabas testudineus) di Paparan Banjiran Lubuk Lampam, Kabupaten Ogan Komering Ilir. BAWAL Widya Riset Perikanan Tangkap, 6(3), 137–146.
Rutkovskiy, A., Stensløkken, K. O., & Vaage, I. J. (2016). Osteoblast Differentiation at a Glance. Medical Science Monitor Basic Research, 22, 95–106.
Sabrina, A. N., Mukti, A. T., Suciyono, Kenconojati, H., Ulkhaq, M. F., Fasya, A. H., Lamadi, A., Imlani, A., & Mariah, S. R. (2023). Color brightness and growth levels of goldfish (Carassius auratus) reared with different light spectrums. Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 6(2), 250–255.
Setiawati, R., & Rahardjo, P. (2019). Bone Development and Growth. Osteogenesis and Bone Regeneration, 1–20.
Shea, C. A., Rolfe, R. A., & Murphy, P. (2015). The importance of foetal movement for co-ordinated cartilage and bone development in utero: clinical consequences and potential for therapy. Bone & joint research, 4(7), 105–116.
Syahbirin, G., Aditianingrum, K. A., & Mohamad, K. (2024). Acute Toxicity of Ethanol Extract of Curcuma zedoaria Rosc (Zingiberaceae) Rhizomes on Brine Shrimp Larvae and Zebrafish Embryos. Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 7(1), 7–18.
Tay, Y. L., Loong, A. M., Hiong, K. C., Lee, S. J., Tng, Y. Y. M., Wee, N. L. J., Lee, S. M. L., Wong, W. P., Chew, S. F., Wilson, J. M., & Ip, Y. K. (2006). Active ammonia transport and excretory nitrogen metabolism in the climbing perch, Anabas testudineus, during 4 days of emersion or 10 minutes of forced exercise on land. Journal of Experimental Biology, 209(22), 4475–4489.
Topczewska, J. M., Shoela, R. A., Tomaszewski, J. P., Mirmira, R. B., & Gosain, A. K. (2016). The morphogenesis of cranial sutures in zebrafish. PLoS ONE, 11(11), 1–23.
Witten, P. E., Owen, M. A. G., Fontanillas, R., Soenens, M., Mcgurk, C., & Obach, A. (2016). A primary phosphorus-deficient skeletal phenotype in juvenile Atlantic salmon Salmo salar: The uncoupling of bone formation and mineralization. Journal of Fish Biology, 88(2), 690–708.
Zhang, W., Xie, H. Q., Li, Y., Jin, T., Li, J., Xu, L., Zhou, Z., Zhang, S., Ma, D., Hahn, M. E., & Zhao, B. (2019). Transcriptomic analysis of Anabas testudineus and its defensive mechanisms in response to persistent organic pollutants exposure. Science of the Total Environment, 669(86), 621–630.
Copyright (c) 2024 Tri Wahyu Pangestiningsih, Woro Danur Wendo, Dwi Liliek Kusindarta

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions;
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions;
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-SA).






11.jpg)




















