Effects of Anchovy By-Product-Based Diets Supplemented with Soy Lecithin on the Reproductive Performance of Red Claw Crayfish (Cherax quadricarinatus)
Downloads
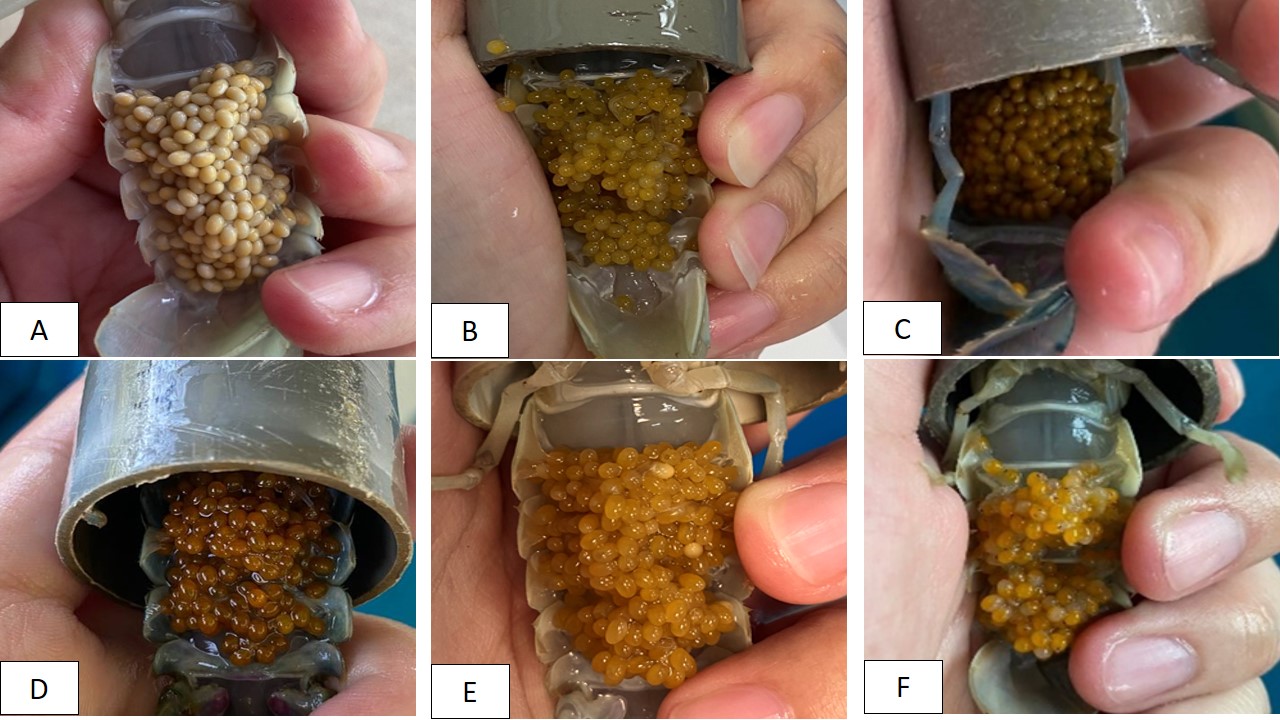
The present study aimed to determine the growth and reproductive performances of red claw crayfish (Cherax quadricarinatus) fed formulated diets based on anchovy by-product meal, supplemented with varying levels of lecithin. The SL0 diet, containing 0% soy lecithin, was used as the control, and four experimental feeds were included with different lecithin levels: SL1: 1% soy lecithin, SL2: 2% soy lecithin, SL3: 3% soy lecithin and SL4: 4% soy lecithin. Five broodstock (four females and one male) were stocked in the square fiberglass tank (105 cm ´ 105 cm ´ 36 cm; 400L) and fed twice daily (0900h and 1600h) until satiation for 11 weeks. The data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test at p < 0.05. Growth and survival rates showed no significant differences among treatments. Notably, SL4 exhibited the highest gonadosomatic index (GSI) at 2.50 ± 1.99%, while SL3 had the highest hepatosomatic index (HSI) at 6.20 ± 1.18%. The spawning rate peaked in SL1 (63.89%), followed by SL0 (47.22%), SL2 (41.67%), SL3 (41.67%), and SL4 (25.00%). SL4 also had the highest fecundity (14.94 eggs/g female), with SL3 (10.72 eggs/g female) and SL0 (9.50 eggs/g female) following. Lipid content in muscle varied from 1.14% (SL4) to 1.46% (SL3), with no significant differences. However, lecithin inclusion notably affected lipid content in hepatopancreas and gonad, with SL1 exhibiting the highest hepatopancreas lipid (61.04%) and SL2 the highest gonad lipid (27.78%). The data suggest that dietary lecithin plays an important role in the reproductive performance of red claw crayfish. Overall, anchovy by-product meal has high potential to serve as a dietary ingredient in the feed formulation for both juvenile and broodstock of red claw crayfish.
Abdu, U. R. I., Yehezkel, G., & Sagi, A. (2000). Oocyte development and polypeptide dynamics during ovarian maturation in the red-claw crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus. Invertebrate Reproduction & Development, 37(1), 75–83.
Alava, V. R. (1993). Effect of dietary phospholipids and n-3 highly unsaturated fatty acids on ovarian development of Kuruma prawn. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi, 59(2), 345–351.
Association of Official Analytical Chemists International (AOAC). (2003). Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International. 17th Ed. AOAC International, Gaithersburg.
Baeza, J. A., Simpson, L., Ambrosio, L. J., Mora, N., Guéron, R., & Childress, M. J. (2016). Active parental care, reproductive performance, and a novel egg predator affecting reproductive investment in the Caribbean spiny lobster, Panulirus argus. BMC Zoology, 1, 1–15.
Bray, W. A., Lawrence, A. L., & Lester, L. J. (1990). Reproduction of eyestalk‐ablated Penaeus stylirostris fed various levels of total dietary lipid. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 21(1), 41–52.
Briggs, M. R. P., Jauncey, K., & Brown, J. H. (1988). The cholesterol and lecithin requirements of juvenile prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) fed semi-purified diets. Aquaculture, 70(1–2), 121–129.
Cahu, C. L., Guillaume, J. C., Stéphan, G., Chim, L. (1994). Influence of phospholipid and highly unsaturated fatty acids on spawning rate and egg tissue composition in Penaeus vannamei fed semi-purified diets. Aquaculture, 126, 159–170.
Carral, J. M., Celada, J. D., González, J., Gaudioso, V. R., Fernández, R., & López-Baissón, C. (1992). Artificial incubation of crayfish eggs (Pacifastacus leniusculus Dana) from early stages of embryonic development. Aquaculture, 104(3–4), 261–269.
Cavalli, R. O., Menschaert, G., Lavens, P., & Sorgeloos, P. (2000). Maturation performance, offspring quality and lipid composition of Macrobrachium rosenbergii females fed increasing levels of dietary phospholipids. Aquaculture International, 8, 41–58.
Celada, J. D., Antolín, J. I., Carral, J. M., Sáez-Royuela, M., & Rodríguez, R. (2005). Successful sex ratio of 1M: 4F in the astacid crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus Dana under captive breeding conditions. Aquaculture, 244(1–4), 89–95.
Chen, J. C., Nan, F. H., Cheng, S. Y., & Sheen, S. S. (1993). Effects of ambient ammonia on ammonia-N and protein concentrations in hemolymph and ammonia-N excretion of Penaeus chinensis. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 98, 203–208.
Chowdhury, R., Angell, C., & Bhattacharjee, H. (1993). A manual for operating a small-scale recirculation freshwater prawn hatchery. Madras: Bay of Bengal Programme. Aquaculture, 151(1–4), 259–267.
Conklin, D. E., D'abramo, L. R., Bordner, C. E., & Baum, N. A. (1980). A successful purified diet for the culture of juvenile lobsters: the effect of lecithin. Aquaculture, 21(3), 243–249.
Corral‐Rosales, D. C., Cruz‐Suárez, L. E., Ricque‐Marie, D., Rodríguez‐Jaramillo, C., & Palacios, E. (2018). Modulation of reproductive exhaustion using Ulva clathrata in Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) broodstock during commercial maturation. Aquaculture Research, 49(12), 3711–3722.
Coutteau, P., Camara, M. R., & Sorgeloos, P. (1996). The effect of different levels and sources of dietary phosphatidylcholine on the growth, survival, stress resistance, and fatty acid composition of postlarval Penaeus vannamei. Aquaculture, 147(3–4), 261–273.
Craig, S. R., & Gatlin III, D. M. (1997). Growth and body composition of juvenile red drum (Sciaenops ocellatus) fed diets containing lecithin and supplemental choline. Aquaculture, 151(1–4), 259–267.
Ding, L. Y., Jin, M., Sun, P., Lu, Y., Ma, H. N., Yuan, Y., & Zhou, Q. C. (2017). Cloning, tissue expression of the fatty acid-binding protein (Pt-FABP1) gene, and effects of dietary phospholipid levels on fabp and vitellogenin gene expression in the female swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus. Aquaculture, 474, 57–65.
Edgerton, B. F., Evans, L. H., Stephens, F. J., & Overstreet, R. M. (2002). Synopsis of freshwater crayfish diseases and commensal organisms. Aquaculture, 206(1–2), 57–135.
Fikri, F., Wardhana, D. K., Purnomo, A., Khairani, S., Chhetri, S., & Purnama, M. T. E. (2022). Aerolysin gene characterization and antimicrobial resistance profile of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from milkfish (Chanos chanos) in Gresik, Indonesia. Veterinary World, 15(7), 1759–1764.
Gong, H., Lawrence, A. L., Jiang, D. H., Castille, F. L., & Gatlin III, D. M. (2000). Lipid nutrition of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei: I. Dietary cholesterol and de-oiled soy lecithin requirements and their interaction. Aquaculture, 190(3–4), 305–324.
Harrison, K. E. (1990). The role of nutrition in maturation, reproduction and embryonic development of decapod crustaceans: a review. Journal of Shellfish Research, 9, 1–28.
Hoa, N. D., Wouters, R., Wille, M., Thanh, V., Dong, T. K., Van Hao, N., & Sorgeloos, P. (2009). A fresh-food maturation diet with an adequate HUFA composition for broodstock nutrition studies in black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon (Fabricius, 1798). Aquaculture, 297(1–4),116–121.
Holme, M. H., Southgate, P. C., Zeng, C. (2007). Assessment of dietary lecithin and cholesterol requirements of mud crab, Scylla serrata, megalopa using semi-purified microbound diets. Aquaculture Nutrition, 13, 413–23.
Hou, S., Zhu, S., Li, J., Huang, J., Li, J., & Cheng, Y. (2022). Effects of dietary phospholipid and cholesterol levels on growth, molting performance, and ovary development in female juvenile crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Aquaculture Nutrition, 2022(1), 4033033.
Hu, Y., Tan, B., Mai, K., Ai, Q., Zhang, L., & Zheng, S. (2011). Effects of dietary menhaden oil, soybean oil and soybean lecithin oil at different ratios on growth, body composition and blood chemistry of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture International, 19, 459–473.
Hung, S. S., Moore, B. J., Bordner, C. E., & Conte, F. S. (1987). Growth of juvenile white sturgeon (Acipenser transmontanas) fed different purified diets. Journal of Nutrition, 117, 328–334.
Jones, C. M. (1995). Production of juvenile redclaw crayfish, Cherax quadricarinatus (von Martens) (Decapoda, Parastacidae) I. Development of hatchery and nursery procedures. Aquaculture, 138(1–4), 221–238.
Kanazawa, A., Teshima, S.I., & Sakamoto, M. (1985). Effects of dietary lipids, fatty acids, and phospholipids on growth and survival of prawn (Penaeus japonicus) larvae. Aquaculture, 50(1–2), 39–49.
Kasper, C. S., & Brown, P. B. (2003). Growth improved in juvenile Nile tilapia fed phosphatidylcholine. North American Journal of Aquaculture, 65, 39–43.
Li, X., Wang, J., Han, T., Hu, S., Jiang, Y., & Wang, C. (2014). Effect of dietary phospholipids levels and sources on growth performance, fatty acid composition of the juvenile swimming crab, Portunus trituberculatus. Aquaculture, 430, 166–172.
Lin, Z., Bu, X., Wang, N., Lei, Y., Liu, S., Wang, X., & Chen, L. (2021). Dietary phospholipid alleviates the adverse effects of high-lipid diet in Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Aquaculture, 531, 735899.
Lin, Z., Han, F., Lu, J., Guo, J., Qi, C., Wang, C., & Chen, L. (2020). Influence of dietary phospholipid on growth performance, body composition, antioxidant capacity and lipid metabolism of Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Aquaculture, 516, 734653.
Liou, C. H., To, V. A., Zhang, Z. F., & Lin, Y. H. (2023). The effect of dietary lecithin and lipid levels on the growth performance, body composition, hemolymph parameters, immune responses, body texture, and gene expression of juvenile white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquaculture, 567, 739260.
Mason, J. C. (1970). Egg-laying in the western north American crayfish, Pacifastacus trowbridgii (Stimpson) (Decapoda, Astacidae). Crustaceana, 19, 37–44.
Poston, H. A. (1990). Response of rainbow trout to soy lecithin, choline, and autoclaved isolated soy protein. The Progressive Fish‐Culturist, 53(2), 85–90.
Poston, H. A. (1991). Response of Atlantic salmon fry to feed-grade lecithin and choline. The Progressive Fish Culturist, 53, 224–228.
Sagi, A., Shoukrun, R., Khalaila, I., & Rise, M. (1996). Gonad maturation, morphological and physiological changes during the first reproductive cycle of the crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus female. Invertebrate Reproduction & Development, 29(3), 235–242.
Sanchez, D. R., Fox, J. M., Gatlin III, D., & Lawrence, A. L. (2011). Dietary effect of squid and fish meals on growth and survival of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei in the presence or absence of phytoplankton in an indoor tank system. Aquaculture Research, 43, 1880–1890.
Saoud, I., Yta, A., & Ghanawi, J. (2012). A review of nutritional biology and dietary requirements of red claw crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus (von Martens 1868). Aquaculture Nutrition, 18, 349–368.
Sato, T., Yoseda, K., Okuzawa, K., & Suzuki, N. (2010). Sperm limitation: possible impacts of large male-selective harvesting on reproduction of the coconut crab Birgus latro. Aquatic Biology, 10(1), 23–32.
Song, D., Shi, B., Ding, L., Jin, M., Sun, P., Jiao, L., & Zhou, Q. (2019). Regulation of dietary phospholipids on growth performance, antioxidant activities, phospholipid metabolism and vitellogenesis in pre reproductive phase of female swimming crabs, Portunus trituberculatus. Aquaculture, 511, 734230.
Sui, L. Y., Wu, X. G., Wille, M., Cheng, Y. X., & Sorgeloos, P. (2009). Effect of dietary soybean lecithin on reproductive performance of Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis (H. Milne-Edwards) Broodstock. Aquaculture International, 17, 45–56.
Tan, P., Zhang, P., Zhang, L., Zhu, W., Wang, L., Chen, R., & Xu, D. (2022). Effects of soybean lecithin on growth performance, intestine morphology, and liver tissue metabolism in rock bream (Oplegnathus fasciatus) larvae. Frontiers in Marine Science, 9, 942259.
Teshima, S., Kanazawa, A., Kakuta, Y. (1986). Effects of dietary phospholipids on growth and body composition of the juvenile prawn. Bulletin Japanese Society for the Science of Fish, 52, 155– 8.
Thanh Hien, T. T., Hai, T. N., Phuong, N. T., Ogata, H. Y., & Wilder, M. N. (2005). The effects of dietary lipid sources and lecithin on the production of giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii larvae in the Mekong Delta region of Vietnam. Fisheries Science, 71, 279–286.
Thompson, K., Muzinic, L., Christian, T., & Webster, C., Rouse, D., Manomaitis, L. (2003). Effect on Growth, Survival, and Fatty Acid Composition of Australian Red claw Crayfish, Cherax quadricarinatus Fed Practical Diets with and Without Supplemental Lecithin and/or Cholesterol. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 34, 1–10.
Thongrod, S., & Boonyaratpalin, M. (1998). Cholesterol and lecithin requirement of juvenile banana shrimp, Penaeus merguiensis. Aquaculture, 161(1–4), 315–321.
Tian, H., Yang, C., Yu, Y., Yang, W., Lu, N., Wang, H., & Xu, X. (2020). Dietary cholesterol level affects growth, molting performance and ecdysteroid signal transduction in Procambarus clarkii. Aquaculture, 523, 735198.
Van Son, T. C., & Thiel, M. (2007). Anthropogenic Stressors and Their Effects on the. Evolutionary Ecology of Social and Sexual Systems: Crustaceans as Model Organisms, 413.
Vazquez, F. J., Tropea, C., & Lopez Greco, L. S. (2008). Development of the female reproductive system in the freshwater crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus (Decapoda, Parastacidae). Invertebrate Biology, 127(4), 433–443.
Vogt, G., Tolley, L., & Scholtz, G. (2004). Life stages and reproductive components of the Marmorkrebs (marbled crayfish), the first parthenogenetic decapod crustacean. Journal of Morphology, 261(3), 286–311.
Wang, J. T., Han, T., Li, X. Y., Hu, S. X., Jiang, Y. D., & Wang, C. L. (2016). Effects of dietary phosphatidylcholine (PC) levels on the growth, molt performance and fatty acid composition of juvenile swimming crab, Portunus trituberculatus. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 216, 225–233.
Wang, L. Q., Li, H. Y., Hu, W., & Jiang, H. (2004). Effect of dietary phospholipids on growth and feed conversion rate of young mitten crab of Eriocheir sinensis. Feed Research, 1, 8–10.
Wang, L., Zuo, D., Lv, W., Li, J., Wang, Q., & Zhao, Y. (2013). Effects of dietary soybean lecithin on gonadal development and vitellogenin mRNA expression in the female red claw crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus (von Martens) at first maturation. Aquaculture Research, 44(8), 1167–1176.
Wu, X., Cheng, Y., Sui, L., Zeng, C., Southgate, P.C., & Yang, X. (2007). Effect of dietary supplementation of phospholipids and highly unsaturated fatty acids on reproductive performance and offspring quality of Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis (H. Milne-Edwards), female broodstock. Aquaculture, 273(4), 602–613.
Yeh, H. S., & Rouse, D. B. (1994). Indoor spawning and egg development of the red claw crayfish, Cherax quadricarinatus. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 25(2), 297–302.
Zhang, F., Ning, Y., Yuan, R., Ding, J., Chang, Y., & Zuo, R. (2022). Effects of soya lecithin addition on the growth, antioxidant capacity, gonad development and nutritional quality of adult sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus intermedius). Aquaculture Reports, 22, 100990.
Copyright (c) 2025 Meccarren Majiun, Rossita Shapawi , Annita Seok Kian Yong, Audrey Daning Tuzan, Leong Seng Lim, Alia Syafiqah Aznan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions;
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions;
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-SA).






11.jpg)




















