CAN EDUCATION INCREASE NHI MEMBERSHIP? A CASE STUDY AMONG MADURESE IN INDONESIA
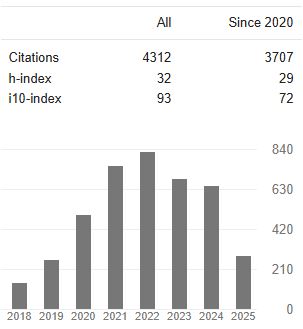
Downloads
Background: Madura Island is often left behind in health development in East Java Province, including in the health sector. Poverty and poor education dominate this region.
Aims: The research examined the role of education in National Health Insurance (NHI) membership among Indonesian Madurese.
Methods: The study employed 791 respondents. We used NHI membership as an outcome variable, education level as an exposure variable, and seven control variables: regency, residence, gender, employment, age, wealth, and marital status. In the last stage, we employed a binary logistic test.
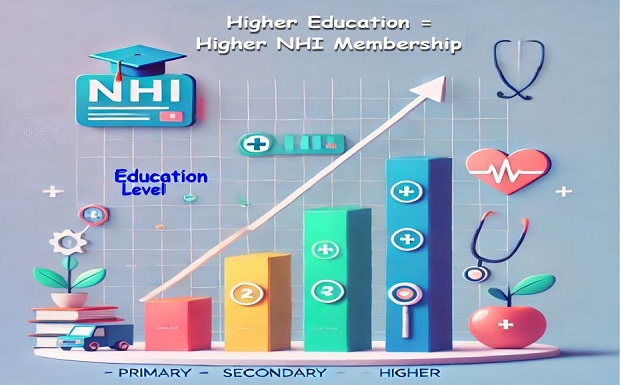
Results: The results showed that 58.2% of Madurese people in Indonesia are members of the NHI. Regarding education level, Madurese with primary education was 1.672 times more likely than those without formal education to be an NHI member (95% CI 1.662-1.683). Meanwhile, Madurese with secondary education was 2.329 times higher than those uneducated to be an NHI member (95% CI 2.306-2.352). Moreover, Madurese with higher education was 4.593 times more likely to be an NHI member than uneducated Madurese (95% CI 4.517-4.669).
Conclusions: Education level was associated with NHI membership among Madurese in Indonesia. The higher the education level, the higher the possibility of being an NHI member.
Keywords: health insurance, National Health Insurance, Madurese, big data, public health
Abiola, A.O. et al. (2019) ‘Knowledge and utilisation of National Health Insurance Scheme among adult patients attending a tertiary health facility in Lagos State, South-Western Nigeria’, African Journal of Primary Health Care & Family Medicine, 11(1). Available at: https://doi.org/10.4102/phcfm.v11i1.2018.
Acharya, D. et al. (2020) ‘Association of information, education, and communication with enrolment in health insurance: a case of Nepal’, Archives of Public Health, 78(1), p. 135. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13690-020-00518-8.
Alo, C.N., Okedo-Alex, I.N. and Akamike, I.C. (2020) ‘Determinants of willingness to participate in health insurance amongst people living with HIV in a tertiary hospital in South-East Nigeria’, The Nigerian postgraduate medical journal, 27(3), pp. 196–201. Available at: https://doi.org/10.4103/npmj.npmj_11_20.
Badu, E. et al. (2018) ‘Households Sociodemographic Profile as Predictors of Health Insurance Uptake and Service Utilization: A Cross-Sectional Study in a Municipality of Ghana’, Advances in Public Health, 2018, pp. 1–13. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7814206.
Bauer, L., Clevenstine, V. and Macklin, M. (2022) ‘Examining the economic status of same-gender relationship households’. Available at: https://www.brookings.edu/articles/examining-the-economic-status-of-same-gender-relationship-households/.
Conde, K.K. et al. (2022) ‘Factors determining membership in community-based health insurance in West Africa: a scoping review’, Global Health Research and Policy, 7(1). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41256-022-00278-8.
Imanhadi, B., Saragih, D.I. and Pranata, S. (2016) Childcare: on the earth of “Adi Poday” Sapudi Island (Pengasuhan Anak di Bumi “Adi Poday”). Surabaya: Unesa University Press.
Ipa, M. et al. (2023) ‘Factors Associated with the Place of Delivery among Urban Poor Societies in Indonesia’, Indian Journal of Community Medicine, 48(6), pp. 888–893. Available at: https://doi.org/10.4103/ijcm.ijcm_798_22.
Kwarteng, A. et al. (2020) ‘The state of enrollment on the National Health Insurance Scheme in rural Ghana after eight years of implementation’, International Journal for Equity in Health, 19(1), p. 4. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12939-019-1113-0.
Laksono, A.D., Nantabah, Z.K., et al. (2022) ‘Barriers to Expanding the National Health Insurance Membership in Indonesia: Who Should the Target?’, Journal of Primary Care and Community Health, 13, pp. 1–7. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1177/21501319221111112.
Laksono, A.D., Rukmini, R., et al. (2022) ‘National Health Insurance Membership among Urban Poor Societies in Indonesia in 2019: Are They Protected?’, Economies, 10(8), p. Article number 196-Article number 196. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/economies10080196.
Laksono, A.D. et al. (2023) ‘The Role of Government-run Insurance in Primary Health Care Utilization: A Cross-Sectional Study in Papua Region, Indonesia, in 2018’, International Journal of Social Determinants of Health and Health Services, 53(1), pp. 85–93. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1177/00207314221129055.
Laksono, A.D., Pranata, S. and Astuti, W.D. (2014) Positioning for Shaman (Positioning Dukun Bayi). Yogyakarta: PT Kanisius.
Laksono, A.D., Wulandari, R.D. and Matahari, R. (2021) ‘The determinant of health insurance ownership among pregnant women in Indonesia’, BMC Public Health, 21(1), pp. 1538–1538. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-11577-z.
Laksono, A.D.A. et al. (2023) ‘The Role of Government-run Insurance in Primary Health Care Utilization: A Cross-Sectional Study in Papua Region, Indonesia, in 2018’, International Journal of Health Services, 53(1), pp. 85–93. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1177/00207314221129055.
Maeda, A. et al. (2014) Universal Health Coverage for Inclusive and Sustainable Development: A Synthesis of 11 Country Case Studies, Universal Health Coverage for Inclusive and Sustainable Development: A Synthesis of 11 Country Case Studies. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1596/978-1-4648-0297-3.
Ministry of State Secretariat of Indonesia (2023) Pursuing the target of 98% UHC by 2024, the Vice President Instructs Four Strategic Steps (Kejar Target 98% UHC pada Tahun 2024, Wapres Instruksikan Empat Langkah Strategis). Available at: https://www.setneg.go.id/baca/index/kejar_target_98_uhc_pada_tahun_2024_wapres_instruksikan_empat_langkah_strategis.
National Institute of Health Research and Development of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia (2014) The 2013 Public Health Development Index. Jakarta, pp. 1–88. Available at: https://repository.badankebijakan.kemkes.go.id/id/eprint/4293/1/IPKM 2014.pdf.
National Institute of Health Research and Development of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia (2019) The 2018 Public Health Development Index. Jakarta. Available at: https://www.litbang.kemkes.go.id/buku-ipkm-2018/.
Oldistra, F. and Machdum, S.V. (2020) ‘Analysis of National Health Insurance Policy Planning From the Aspect of Participation in the Ministry of National Development Planning/Bappenas (Analisis Perencanaan Kebijakan Jaminan Kesehatan Nasional Dari Aspek Kepesertaan Di Kementerian Ppn/Bappenas)’, Jurnal Ilmu Kesejahteraan Sosial, 21(1), pp. 63–86. Available at: https://doi.org/10.7454/jurnalkessos.v21i1.253.
Pratiwi, A.B. et al. (2021) ‘Is Indonesia achieving universal health coverage? Secondary analysis of national data on insurance coverage, health spending and service availability’, BMJ Open, 11(10), p. e050565. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2021-050565.
Putri, N.K., Laksono, A.D. and Rohmah, N. (2023) ‘Predictors of national health insurance membership among the poor with different education levels in Indonesia’, BMC Public Health, 23(1), p. Article number 373-Article number 373. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-023-15292-9.
Rukmini, R. et al. (2022) ‘Non-Communicable Diseases among the Elderly in Indonesia in 2018’, Indian Journal of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology, 16(1), pp. 1026–1036. Available at: https://doi.org/10.37506/ijfmt.v16i1.17631.
Savitha, B. and Banerjee, S. (2020) ‘Education and Experience as Determinants of Micro Health Insurance Enrolment’, International Journal of Health Policy and Management, 10(4), pp. 192–200. Available at: https://doi.org/10.34172/ijhpm.2020.44.
Sukartini, T. et al. (2021) ‘Factors Associated with National Health Insurance Coverage in Indonesia’, F1000Research, 10, p. 563. Available at: https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.53672.1.
Wagstaff, A. and Neelsen, S. (2020) ‘A comprehensive assessment of universal health coverage in 111 countries : a retrospective observational study’, The Lancet Global Health, 8(1), pp. e39–e49. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30463-2.
Wang, Q. et al. (2021) ‘Preferences for long-term care insurance in China: Results from a discrete choice experiment’, Social Science and Medicine, 281, pp. 114104–114104. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2021.114104.
Wiseman, V. et al. (2018) ‘An evaluation of health systems equity in Indonesia: Study protocol’, International Journal for Equity in Health, 17(138), pp. 1–9. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12939-018-0822-0.
Wulandari, R.D. et al. (2019) ‘Socioeconomic Disparities in Hospital Utilization among Elderly People in Indonesia’, Indian Journal of Public Health Research & Development, 10(11), p. 2192. Available at: https://doi.org/10.5958/0976-5506.2019.03885.3.
Wulandari, R.D., Laksono, A.D., Sillehu, S., et al. (2022) ‘Health Insurance Ownership among Moluccans in Indonesia’, Indian Journal of Community Medicine, 47(3), pp. 332–335. Available at: https://doi.org/10.4103/ijcm.ijcm_593_21.
Wulandari, R.D., Laksono, A.D., Nantabah, Z.K., et al. (2022) ‘Hospital utilization in Indonesia in 2018: do urban-rural disparities exist?’, BMC Health Services Research, 2022(22), pp. 491–491. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-022-07896-5.
Wulandari, R.D. et al. (2024) ‘Membership in National Health Insurance Among Workers in Indonesia’, Jurnal Administrasi Kesehatan Indonesia, 12(2), pp. 280–291. Available at: https://doi.org/10.20473/jaki.v12i2.2024.280-291.
Xie, R. (2022) ‘The Influence of Education Level, Gender, Race, Marital Status, Age, and Occupation on the Wage of the General Population’, in 2022 7th International Conference on Social Sciences and Economic Development (ICSSED 2022). Atlantis Press, pp. 926–932. Available at: https://doi.org/10.2991/aebmr.k.220405.155.
Ziegler, S. et al. (2024) ‘A step closer towards achieving universal health coverage: the role of gender in enrolment in health insurance in India’, BMC Health Services Research, 24(1), p. 141. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-023-10473-z.
Copyright (c) 2025 Agung Dwi Laksono, Ratna Dwi Wulandari, Nurhasmadiar Nandini, Maya Weka Santi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. As an author you (or your employer or institution) may do the following:
- make copies (print or electronic) of the article for your own personal use, including for your own classroom teaching use;
- make copies and distribute such copies (including through e-mail) of the article to research colleagues, for the personal use by such colleagues (but not commercially or systematically, e.g. via an e-mail list or list server);
- present the article at a meeting or conference and to distribute copies of the article to the delegates attending such meeting;
- for your employer, if the article is a ‘work for hire', made within the scope of your employment, your employer may use all or part of the information in the article for other intra-company use (e.g. training);
- retain patent and trademark rights and rights to any process, procedure, or article of manufacture described in the article;
- include the article in full or in part in a thesis or dissertation (provided that this is not to be published commercially);
- use the article or any part thereof in a printed compilation of your works, such as collected writings or lecture notes (subsequent to publication of the article in the journal); and prepare other derivative works, to extend the article into book-length form, or to otherwise re-use portions or excerpts in other works, with full acknowledgement of its original publication in the journal;
- may reproduce or authorize others to reproduce the article, material extracted from the article, or derivative works for the author's personal use or for company use, provided that the source and the copyright notice are indicated.
All copies, print or electronic, or other use of the paper or article must include the appropriate bibliographic citation for the article's publication in the journal.
2. Requests from third parties
Although authors are permitted to re-use all or portions of the article in other works, this does not include granting third-party requests for reprinting, republishing, or other types of re-use.
3. Author Online Use
- Personal Servers. Authors and/or their employers shall have the right to post the accepted version of articles pre-print version of the article, or revised personal version of the final text of the article (to reflect changes made in the peer review and editing process) on their own personal servers or the servers of their institutions or employers without permission from JAKI;
- Classroom or Internal Training Use. An author is expressly permitted to post any portion of the accepted version of his/her own articles on the author's personal web site or the servers of the author's institution or company in connection with the author's teaching, training, or work responsibilities, provided that the appropriate copyright, credit, and reuse notices appear prominently with the posted material. Examples of permitted uses are lecture materials, course packs, e-reserves, conference presentations, or in-house training courses;