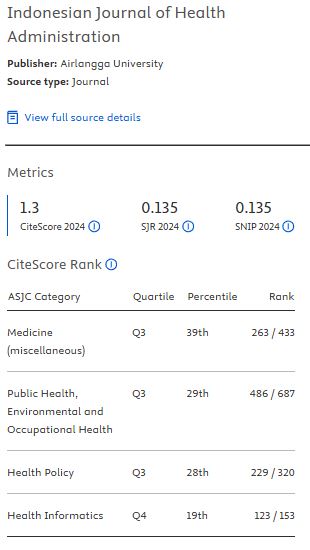
Analisis Fungsi Manajemen Logistik di Badan Pemberdayaan Masyarakat dan Keluarga Berencana Kota Surabaya
Downloads
Board of Community Empowerment and Family Planning has the main task in a family planning and family welfare program.Logistics management was very importance to support that program. There were 17.020 syringes whichexpired but have not been destroyed in 2016. Author wanted to examine the logistics management function in Bapemas and KB. The variables were logistics planning, budgeting, procurement, receiption, storage, distribution, and elimination.The samples were two warehouse logistics officers.Data collection techniqueswere observation and indepth interview.Requirements planning used the formula of average usage per month multiplied by 3 or 24. The procurement process was done by request to BKKBN Province.Budgeting wasderived from two sources. The sources werestate and local fund. Reception and distribution process was appropriate with technical manual book. Storage facilities reached 94.1% of the BBKBN Centerstandard.While the general provisions saving reached 100%. Eliminating logistics had not done since 2012. The recording process used the forms and books that have been standardized by National BKKBN office.Monitoring started from receipt, storage and distribution. That was done by Province BKKBN office.The conclusion of this research was the Implementation of all functions in accordance with the standards.
Keywords: logistics management function, family planning, distribution,procurement
Anwar, SN. (2011). Manajemen Rantai Pasokan (Supply Chain Management) Konsep dan Hakikat.Jurnal Dinamika Informatika, Vol 3 No 2. [e-jurnal]. doi: http://www.unisbank.ac.id/ojs/index.php/fti2/article/view/1315/531
Bapemas dan KB. (2016). Profil Badan Pemberdayaan Masyarakat Kota Surabaya. Surabaya: Bapemas dan KB Kota Surabaya.
BKKBN. (2011). Petunjuk Teknis: Perencanaan Kebutuhan Alat dan Kontrasepsi dan Non Alat Kontrasepsi. Jakarta: Badan Kependudukan dan Keluarga Berencana Nasional.
BKKBN. (2012).Petunjuk Teknis: Penerimaan, Penyimpanan dan Penyaluran Alat/ Obat Kontrasepsi dan Non Alat Kontrasepsi Program KB Nasional. Jakarta: Badan Kependudukan dan Keluarga Berencana Nasional.
Fannya, P. (2011). Evaluasi Pelaksanaan Manajemen Logistik Alat Kesehatan Di Puskesmas Biaro Kabupaten AGAM Tahun 2011.Skripsi. Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Andalas Padang. Retrieved from http://repository.unand.ac.id/17545/1/skripsi_puteri.pdf
Khasanah, U. (2010). Analisis Manajemen Logistik Obat Dalam Perencanaan, Pengendalian Persediaan, Safety Stock, Dan Reorder Point.Skripsi. Fakultas Kesehatan Masyarakat Unair.
Panjaitan, R., Goenawi, L., Lolo, W.. (2014). Pengelolaan Alat dan Obat Kontrasepsi di Badan Kependudukan Keluarga Berencana Nasional (BKKBN) Provinsi Sulawesi Utara.
Jurnal Ilmiah Pharmacon, Vol 3 No 3. [e-journal]:Pp. 230-234. doi: http://ejournal.unsrat.ac.id/index.php/pharmacon/article/viewFile/5423/4930
Rizky, M. A. (2012). Pengukuran Kinerja Supply Chain Management Pada PT. Caraka Purnama Abadi Pasuruan Dengan menggunakan Metode Score. Skripsi.Fakultas Ekonomi dan Bisnis Unair.
Siagian, Y. (2012). Supply Chain Management. [e-book] Grasindo. Retrieved fromhttps://books.google.co.id/books?hl=id&lr=&id=stWD5PwghREC&oi=fnd&pg=PR12&dq=supply+chain+management+adalah&ots=WwO-bjqtL3&sig=vONexbUl-vsAaDWj7OBGb-V7qJk&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=supply%20chain%20management%20adalah&f=false
WHO. (1999). Guidelines For Safe Disposal Of Unwanted Pharmaceuticals In And After Emergencies. Switzerland: World Health Organization. Retrieved fromhttp://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/medicalwaste/unwantpharm.pdf
1. As an author you (or your employer or institution) may do the following:
- make copies (print or electronic) of the article for your own personal use, including for your own classroom teaching use;
- make copies and distribute such copies (including through e-mail) of the article to research colleagues, for the personal use by such colleagues (but not commercially or systematically, e.g. via an e-mail list or list server);
- present the article at a meeting or conference and to distribute copies of the article to the delegates attending such meeting;
- for your employer, if the article is a ‘work for hire', made within the scope of your employment, your employer may use all or part of the information in the article for other intra-company use (e.g. training);
- retain patent and trademark rights and rights to any process, procedure, or article of manufacture described in the article;
- include the article in full or in part in a thesis or dissertation (provided that this is not to be published commercially);
- use the article or any part thereof in a printed compilation of your works, such as collected writings or lecture notes (subsequent to publication of the article in the journal); and prepare other derivative works, to extend the article into book-length form, or to otherwise re-use portions or excerpts in other works, with full acknowledgement of its original publication in the journal;
- may reproduce or authorize others to reproduce the article, material extracted from the article, or derivative works for the author's personal use or for company use, provided that the source and the copyright notice are indicated.
All copies, print or electronic, or other use of the paper or article must include the appropriate bibliographic citation for the article's publication in the journal.
2. Requests from third parties
Although authors are permitted to re-use all or portions of the article in other works, this does not include granting third-party requests for reprinting, republishing, or other types of re-use.
3. Author Online Use
- Personal Servers. Authors and/or their employers shall have the right to post the accepted version of articles pre-print version of the article, or revised personal version of the final text of the article (to reflect changes made in the peer review and editing process) on their own personal servers or the servers of their institutions or employers without permission from JAKI;
- Classroom or Internal Training Use. An author is expressly permitted to post any portion of the accepted version of his/her own articles on the author's personal web site or the servers of the author's institution or company in connection with the author's teaching, training, or work responsibilities, provided that the appropriate copyright, credit, and reuse notices appear prominently with the posted material. Examples of permitted uses are lecture materials, course packs, e-reserves, conference presentations, or in-house training courses;