The Effect of Vitamin C Administration on Hemoglobin and Hematocrit of Albino Rats (Rattus norvegicus)
Downloads
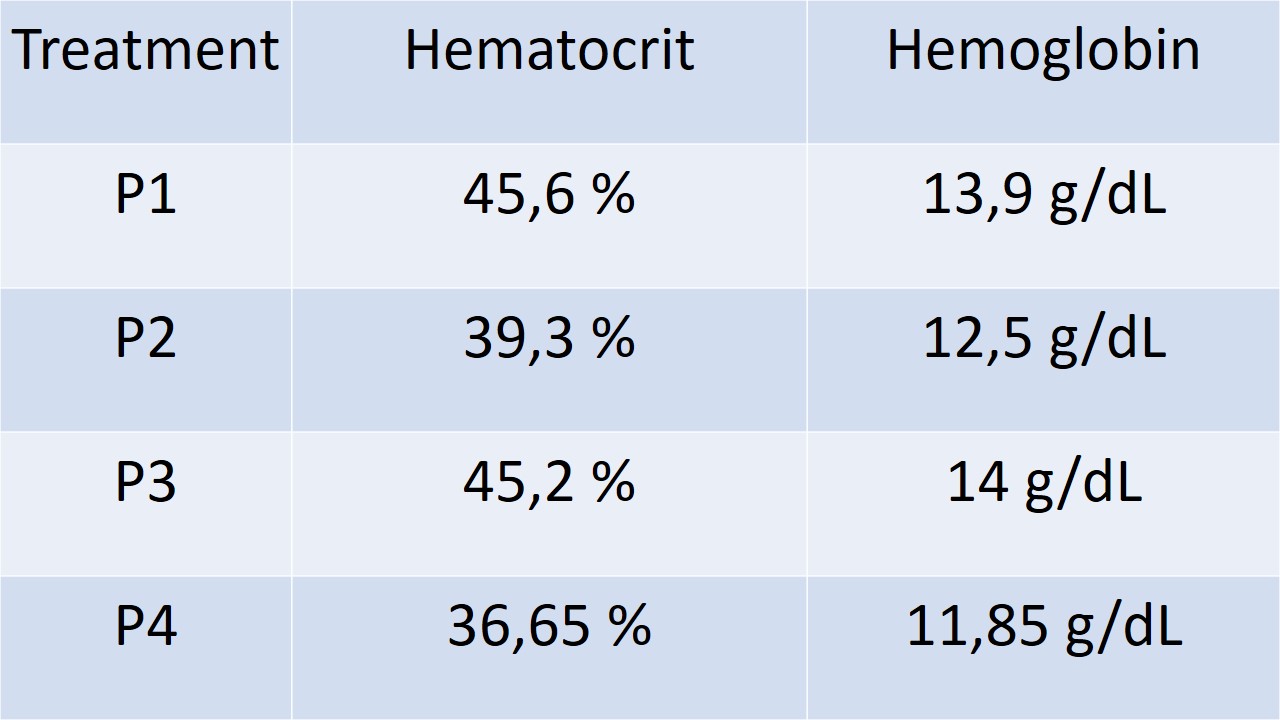
Anemia, a condition characterized by low hemoglobin or red blood cell levels, is a widespread nutritional issue affecting over 2 billion people globally. Iron deficiency, folic acid, and vitamin B12 or C deficiencies are common causes, with vitamin C playing a crucial role in enhancing iron absorption. This study aimed to investigate the impact of various doses of vitamin C supplementation on hematocrit and hemoglobin levels in rats. The experiment employed a True Experimental design with a control group and three treatment groups receiving different doses of vitamin C (1 mg/ml, 3 mg/ml, and 6 mg/ml) over three weeks. Results showed no significant increase in hemoglobin or hematocrit levels across treatment groups compared to the control. Although some variations were observed in the data, particularly with the 6 mg/ml dose showing a slight decrease in hemoglobin levels, the overall effect of vitamin C on these hematological parameters was not substantial. These findings suggest that animal health, feed quality, and vitamin C administration duration influence the outcomes.
Departemen Kesehatan RI. 2001. Program Penanggulangan Anemia Gizi pada Wanita Usia Subur (WUS). Direktorat Gizi Masyarakat. Jakarta: Direktorat Jenderal Bina Kesehatan Masyarakat Depkes.
Inggarsih, R., Purnamasari, S., Diba, M., and Taharu, F. 2022. Analisis Profil Eritrosit Tikus Putih (Rattus norvegicus) Pasca Diet Vegetarian. Sang Pencerah: Jurnal Ilmiah Universitas Muhammadiyah Buton. 8. 107-118.
Kaimudin, N., Lestari, H., and Afa, J. 2017. Skrining Dan Determinan Kejadian Anemia Pada Remaja Putri Sma Negeri 3 Kendari Tahun 2017. Jurnal Ilmiah Mahasiswa Kesehatan Masyarakat Unsyiah, 2 (6), 185793.
Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. 2014. Profil Kesehatan Indonesia. Kemenkes RI. Jakarta.
Krisnanda, R. 2020. Vitamin C helps in the absorption of iron in Iron Deficiency Anemia. Jurnal Penelitian Perawat Profesional, 2(3), 279-286.
Liu, M. C., Wang, X. J., and Xu, W. 2011. The antioxidant effects of vitamin C supplementation on hematological parameters in rodents. Journal of Nutritional Science, 10(2), 89–95.
Muhayati, A., and Ratnawati, D. 2019. Hubungan antara status gizi dan pola makan dengan kejadian anemia pada remaja putri. Jurnal Ilmiah Ilmu Keperawatan Indonesia, 9(01), 563-570.
Pritchard, T., Looney, J., and Smith, R. 2020. The impact of stress and inflammation on hematological parameters in rodent models. Journal of Experimental Animal Science, 67(4), 203–212.
Safnowandi. 2022. Pemanfaatan vitamin C alami sebagai antioksidan pada tubuh manusia. Biocaster: Jurnal Kajian Biologi, 2(1), 6-13. https://e-journal.lp3kamandanu.com/index.php/biocaster/
WHO. 2011. The global prevalence of anaemia in 2011 the global prevalence of anaemia in 2011 ii WHO library cataloguing-in-publication data.
Yulaini, G., Wahyuni, R., Hidayatik, N. 2024. Penuntun praktikum patologi klinik veteriner.
Yunita, V. S., and Maigoda, T. C. 2023. The The Roles of Micro Nutrition Substances (Folic Acid, Vitamin C, Zink) on the Incidence of Anemia in Adolescent Girls. JPK: Jurnal Proteksi Kesehatan, 12(2), 169-176.
Zuhrawati, R., Harjanti, D. W., and Isroli, I. 2010. Analisis kadar hematokrit pada tikus putih akibat perlakuan stres oksidatif. Jurnal Ilmu Ternak dan Veteriner, 15(3), 120–125.
Copyright (c) 2025 Ratna Damayanti, Hasna Firdhausia, Deninda Ainaya, Khansa Kha, Naila Nisrina, Annisa Cahya Reza Pahlevi, Shela Syafira, Alifian Alfarizi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Journal of Basic Medical Veterinary (JBMV) by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions.
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA).
4. The Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA) license allows re-distribution and re-use of a licensed work on the conditions that the creator is appropriately credited and that any derivative work is made available under "the same, similar or a compatible license”. Other than the conditions mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation.







 Perhimpunan Dokter Hewan Indonesia
Perhimpunan Dokter Hewan Indonesia








