Spatiotemporal Analysis of Interaction of Pollutants on Pneumonia Cases Distribution in Metropolitan Jakarta
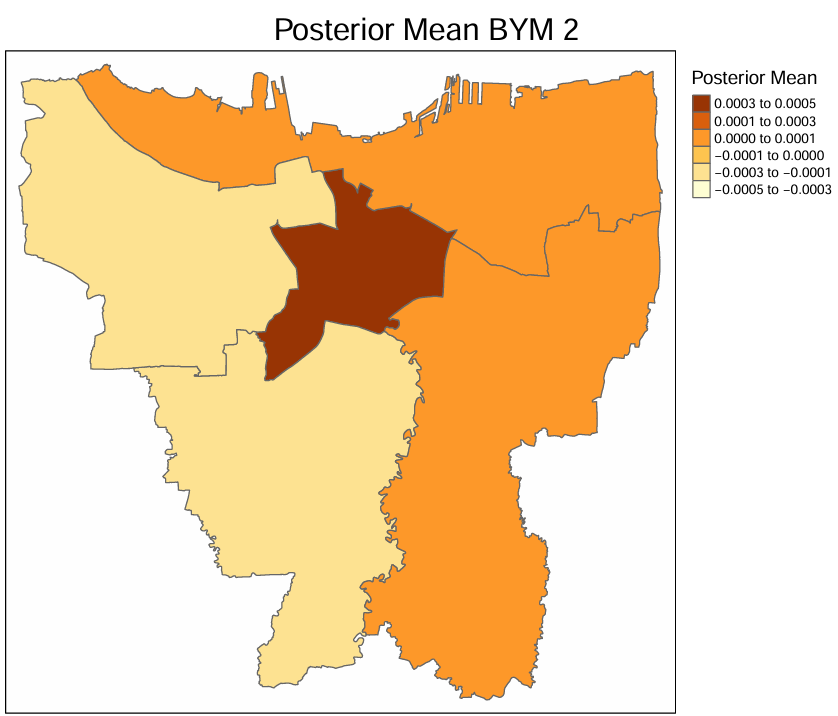
Introduction: Pneumonia is one of the leading causes of death in children under five globally, including in Indonesia. Large metropolitan cities such as Jakarta face a heavier burden due to poor air quality and high population density, further increasing the spread of this disease. This study aims to identify areas with high pneumonia risk and contributing pollutant factors to support more effective interventions and guide policy-making in reducing the impact of pneumonia in urban areas. Methods: This study used the Besag-York-Mollié 2 spatiotemporal model with INLA to analyze the geographic distribution of disease and the influence of pollutant factors. The data comes from Social Security Agency, which has not been used in previous similar studies, and the Jakarta Environmental Agency, thus providing a more accurate description of the actual conditions. Results and Discussion: The effects of pollutants were analyzed based on their credibility intervals, with CO (0.0004, 0.0014); SO2 (-0.0220, 0.0092); and PM10 (-0.0123, 0.0362). Meanwhile, the effect of the time factor (year) has a credibility interval of (0.1669, 0.3464). Spatiotemporal analysis shows an increase in relative risk spread across Jakarta. Conclusion: It was shown through the study that pollutants, particularly CO, positively affected the rising cases of pneumonia, whereas other pollutants discussed under the study had no significant impact. Additionally, time also made a significant impact on the study. The risk ratio for every region of Jakarta rose, and this highlights the importance of air quality management, sustainable urban development, and access to health in an equitable equally.
Long ME, Mallampalli RK, Horowitz JC. Pathogenesis of Pneumonia and Acute Lung Injury. Clinical Science. 2022;136(10):747–769. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20210879
Cilloniz C, Dela Cruz C, Curioso WH, Vidal CH. World Pneumonia Day 2023: The Rising Global Threat of Pneumonia and What We Must Do About It. European Respiratory Journal. 2023;62(5):1-. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01672-2023
Sabbagh WA, Karrar HR, Nouh MI, Alkhaifi NM, Badayyan SY, Shaikh LK, et al. Perspective of Pneumonia in the Health-Care Setting. Journal of Pharmaceutical Research International. 2024;36(7):51–58. https://doi.org/10.9734/jpri/2024/v36i77538
Torres A, Cilloniz C, Niederman MS, Menéndez R, Chalmers JD, Wunderink RG, et al. Pneumonia. Nature Reviews Disease Primers. 2021;7(1): 25. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-021-00259-0
Pahal P, Rajasurya V, Sharma S. Typical Bacterial Pneumonia. StatPearls. 2025;390(1):1-13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.09.099
Lim WS. Pneumonia—Overview. In: Encyclopedia of Respiratory Medicine. Elsevier. 2022;2(1):185–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-801238-3.11636-8
Bassetti M, Magnè F, Giacobbe DR, Bini L, Vena A. New Antibiotics for Gram-negative Pneumonia. European Respiratory Review. 2022;31(166):1-18. https://doi.org/10.1183/16000617.0119-2022
Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia. Indonesia Health Profile 2023. Jakarta: Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia; 2024. https://www.kemkes.go.id/id/profil-kesehatan-indonesia-2023
Lokida D, Farida H, Triasih R, Mardian Y, Kosasih H, Naysilla AM, et al. Epidemiology of Community Acquired Pneumonia Among Hospitalised Children in Indonesia: A Multicentre, Prospective Study. BMJ Open. 2022;12(6):1-13. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2021-057957
Harnofive L, Natalia S, Utami RS. Faktor-Faktor yang Mempengaruhi Kejadian Pneumonia Pada Balita di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Meral Karimun Tahun 2023. An-Najat. 2023;1(4): 91–95. https://doi.org/10.59841/an-najat.v1i4.515
Rolek A. Pneumonia and Asthma Diagnosing and Treatment in Pediatric Medicine. Emergency Medical Service. 2024;11(3):193–197. https://doi.org/10.36740/EmeMS202403108
Selvi, Vaithilingan S. Implementing Community-Based Strategies for Improved Pneumonia Care in Children: Insights From a Pilot Study. Cureus. 2024;6(4):1-15 https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.58159
Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia. National Action Plan for Pneumonia and Diarrhea Control 2023-2030. Directorate General of Disease Prevention and Control. Jakarta: Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia; 2023. https://p2p.kemkes.go.id/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/NAPPD_2023-2030-compressed.pdf
Pratomo AB, Muthmainah HN, Kristiono N, Setyawan GC. Implementation of Internet of Things (IoT) Technology in Air Pollution Monitoring in Jakarta: Quantitative Analysis of the Influence of Air Quality Change and Its Impact on Public Health in Jakarta. West Science Nature and Technology. 2023;1(1):40–47. https://doi.org/10.58812/wsnt.v1i01.225
Soemarko DS, Fadlyana E, Haryanto B, Buftheim S, Hartono B, Wasito E, et al. Linking Jakarta’s Typical Indonesian Urban Context, Air Pollution, and Child Health. The Open Public Health Journal. 2023;16(1):1-6. https://doi.org/10.2174/18749445-v16-e230831-2023-109
Munggaran GA, Kusnoputranto H, Ariyanto J. Korelasi Polusi Udara dengan Insiden Pneumonia Balita di DKI Jakarta pada Tahun 2017-2020. Jurnal Promotif Preventif. 2024;7(1):123–135. https://doi.org/10.47650/jpp.v7i1.1071
Manisalidis I, Stavropoulou E, Stavropoulos A, Bezirtzoglou E. Environmental and Health Impacts of Air Pollution: A Review. Frontiers in Public Health. 2020;8(14):1-13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2020.00014
Shetty SS, D D, S H, Sonkusare S, Naik PB, Kumari N S, et al. Environmental Pollutants and Their Effects on Human Health. Heliyon. 2023;9(9):1-13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19496
Aulia SA. Air Pollution Treatens Health and Climate Change in Jakarta. Human Error and Safety. 2024;1(1): 36–46. https://doi.org/10.61511/hes.v1i1.2024.648
Afifa, Arshad K, Hussain N, Ashraf MH, Saleem MZ. Air Pollution and Climate Change as Grand Challenges to Sustainability. Science of The Total Environment. 2024;928(1):1-16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.172370
Maciejczyk P, Chen LC, Thurston G. The Role of Fossil Fuel Combustion Metals in PM2.5 Air Pollution Health Associations. Atmosphere. 2021;12(9):1-34 https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091086
Azni MA, Md Khalid R, Hasran UA, Kamarudin SK. Review of the Effects of Fossil Fuels and the Need for a Hydrogen Fuel Cell Policy in Malaysia. Sustainability. 2023;15(5):1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054033
Emekwuru N, Ejohwomu O. Temperature, Humidity and Air Pollution Relationships during a Period of Rainy and Dry Seasons in Lagos, West Africa. Climate. 2023;11(5):1-18. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli11050113
Safieh J, Rebwar D, Hamed MH. Investigation of Water Quality in Wet and Dry Seasons Under Climate Change. Ukrainian Journal of Ecology. 2020;10(5):94–104. https://doi.org/10.15421/2020_212
Rosatul Umah, Eva Gusmira. Dampak Pencemaran Udara terhadap Kesehatan Masyarakat di Perkotaan. Profit: Jurnal Manajemen, Bisnis dan Akuntansi. 2024;3(3):103–112. https://doi.org/10.58192/profit.v3i3.2246
Schikowski T, Altuğ H. The Role of Air Pollution in Cognitive Impairment and Decline. Neurochemistry International. 2020;136(1):1-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2020.104708
Tsai MT, Ho YN, Chiang CY, Chuang PC, Pan HY, Chiu IM, et al. Effects of Fine Particulate Matter and Its Components on Emergency Room Visits for Pediatric Pneumonia: A Time-Stratified Case-Crossover Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021;18(20):1-12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182010599
Akbar PNG, Auliya A, Pranita D, Oktadiana H. The Readiness Assessment of Jakarta as a Smart Tourism City. Cogent Social Sciences. 2024;10(1):1-22. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311886.2024.2364386
Nanditho GA, Yola L. Urban Development and Traffic Congestion: Jakarta Study during the Pandemic. Sustainable Development Approaches. 2022;243(1):135–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-99979-7_16
Surya B, Syafri S, Hadijah H, Baharuddin B, Fitriyah AT, Sakti HH. Management of Slum-Based Urban Farming and Economic Empowerment of the Community of Makassar City, South Sulawesi, Indonesia. Sustainability. 2020;12(18):1-42. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187324
Yao J, Xu P, Huang Z. Impact of Urbanization on Ecological Efficiency in China: An Empirical Analysis Based on Provincial Panel Data. Ecological Indicators. 2021;129(1): 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107827
Sasmita NR. Spatial Estimation for Tuberculosis Relative Risk in Aceh Province, Indonesia: A Bayesian Conditional Autoregressive Approach with the Besag-York-Mollie (BYM) Model. Journal of Applied Data Sciences. 2024;5(2):342–356. https://doi.org/10.47738/jads.v5i2.185
Anggrahita H. The Impact of Greening The Narrow Alleys of Densely Populated Settlements on The Reduction of Urban Heat in Jakarta. International Journal of GEOMATE. 2020;18(68):1-8. https://doi.org/10.21660/2020.68.ICGeo33
Wang Y, Chen X, Xue F. A Review of Bayesian Spatiotemporal Models in Spatial Epidemiology. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2024;13(3):1-29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi13030097
Moraga P. Geospatial Health Data. Geospatial Health Data. Boca Raton: Chapman and Hall/CRC; 2019. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780429341823
Blangiardo M, Cameletti M. Spatial and Spatio‐temporal Bayesian Models with R‐INLA. Wiley; 2015. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118950203
Berild MO, Martino S, Gómez-Rubio V, Rue H. Importance Sampling with the Integrated Nested Laplace Approximation. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics. 2022;31(4):1225–1237. https://doi.org/10.1080/10618600.2022.2067551
Martino S, Riebler A. Integrated Nested Laplace Approximations (INLA). Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online. Wiley; 2020:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118445112.stat08212
Van Niekerk J, Krainski E, Rustand D, Rue H. A New Avenue for Bayesian Inference with INLA. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis. 2023;181(1):1-14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csda.2023.107692
Gómez-Rubio V. Bayesian Inference with INLA. Boca Raton, FL: Chapman and Hall/CRC; 2020. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781315175584
Gaedke-Merzhäuser L, Krainski E, Janalik R, Rue H, Schenk O. Integrated Nested Laplace Approximations for Large-Scale Spatiotemporal Bayesian Modeling. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing. 2024;46(4):448–473. https://doi.org/10.1137/23M1561531
Alfarisi S, Christina A, Naqiya SY, Rachmawati RN, Machmud A, Palupi EK. Bayesian Spatial Modeling of Landslide Events Using Integrated Nested Laplace Approximation (INLA): A Study Case on Natural Conditions and Community Actions in East Java, Indonesia. International Journal of Hydrological and Environmental for Sustainability. 2023;2(3):157–166. https://doi.org/10.58524/ijhes.v2i3.354
Gómez-Rubio V, Bivand RS, Rue H. Estimating Spatial Econometrics Models with Integrated Nested Laplace Approximation. Mathematics. 2021;9(17):1-23. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9172044
Zhu B, Xing X, Kim J, Rha H, Liu C, Zhang Q, et al. Endogenous CO Imaging in Bacterial Pneumonia with a NIR Fluorescent Probe. Biomaterials. 2024;304(1):1-12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122419
Song J, Qiu W, Huang X, Guo Y, Chen W, Wang D, et al. Association of Ambient Carbon Monoxide Exposure with Hospitalization Risk for Respiratory Diseases: A Time Series Study in Ganzhou, China. Frontiers in Public Health. 2023;11(1):1-10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2023.1106336
Kwas H, Rangareddy H, Rajhi HH. Impact of Outdoor Air Pollutants Exposure on the Severity and Outcomes of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Gabes Region, Tunisia. Cureus. 2024;16(8): https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.66578
Zhou X, Guo M, Li Z, Yu X, Huang G, Li Z, et al. Associations Between Air Pollutant and Pneumonia and Asthma Requiring Hospitalization Among Children Aged Under 5 Years in Ningbo, 2015–2017. Frontiers in Public Health. 2023;10(1):1-10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.1017105
David JF, Iyaniwura SA. Effect of Human Mobility on the Spatial Spread of Airborne Diseases: An Epidemic Model with Indirect Transmission. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology. 2022;84(6):1-24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-022-01020-8
Beentjes D, Shears RK, French N, Neill DR, Kadioglu A. Mechanistic Insights into the Impact of Air Pollution on Pneumococcal Pathogenesis and Transmission. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2022;206(9):1070–1080. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.202112-2668TR
Yee J, Cho YA, Yoo HJ, Yun H, Gwak HS. Short-term Exposure to Air Pollution and Hospital Admission for Pneumonia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Environmental Health. 2021;20(1):1-10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-020-00687-7
Syuhada G, Akbar A, Hardiawan D, Pun V, Darmawan A, Heryati SHA, et al. Impacts of Air Pollution on Health and Cost of Illness in Jakarta, Indonesia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023;20(4):1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20042916
Hairunnisa H, Hadijati M, Fitriyani N. Geographically Weighted Lasso Method in Modeling the Gross Regional Domestic Product of the Bali-Nusra Region. Jurnal Aplikasi Statistika & Komputasi Statistik. 2024;16(1):58–66. https://doi.org/10.34123/jurnalasks.v16i1.576
Shrestha N. Detecting Multicollinearity in Regression Analysis. American Journal of Applied Mathematics and Statistics. 2020;8(2):39–42. https://doi.org/10.12691/ajams-8-2-1
Yee TC, Szemen Y, Yi-Xiu Ch. Unusual Delayed Pulmonary Presentation of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: A Case Report. Clinical Case Reports Journal. 2022;3(2):1-4. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14911322
Sohn CH, Huh JW, Seo DW, Oh BJ, Lim KS, Kim WY. Aspiration Pneumonia in Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Patients with Loss of Consciousness: Prevalence, Outcomes, and Risk Factors. The American Journal of Medicine. 2017;130(12):21-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.06.038
Ji W, Park YR, Kim HR, Kim HC, Choi CM. Prolonged Effect of Air Pollution on Pneumonia: a Nationwide Cohort Study. European Respiratory Society. 2017;50(61):OA467. https://doi.org/10.1183/1393003.congress-2017.OA467

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. Copyright of all journal manuscripts is held by the Jurnal Kesehatan Lingkungan.2. Formal legal provisions to access digital articles of electronic journal are subject to the provision of the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike license (CC BY-NC-SA), which means that Jurnal Kesehatan Lingkungan is rightful to keep, transfer media/format, manage in the form of databases, maintain, and publish articles.
3. Published manuscripts both printed and electronic are open access for educational, research, and library purposes. Additionally, the editorial board is not responsible for any violations of copyright law.
JKESLING by UNAIR is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.







































