Saltwater Intrusion Effect on Water Supply Project in Sungai Semerak, Pasir Puteh, Kelantan, Malaysia
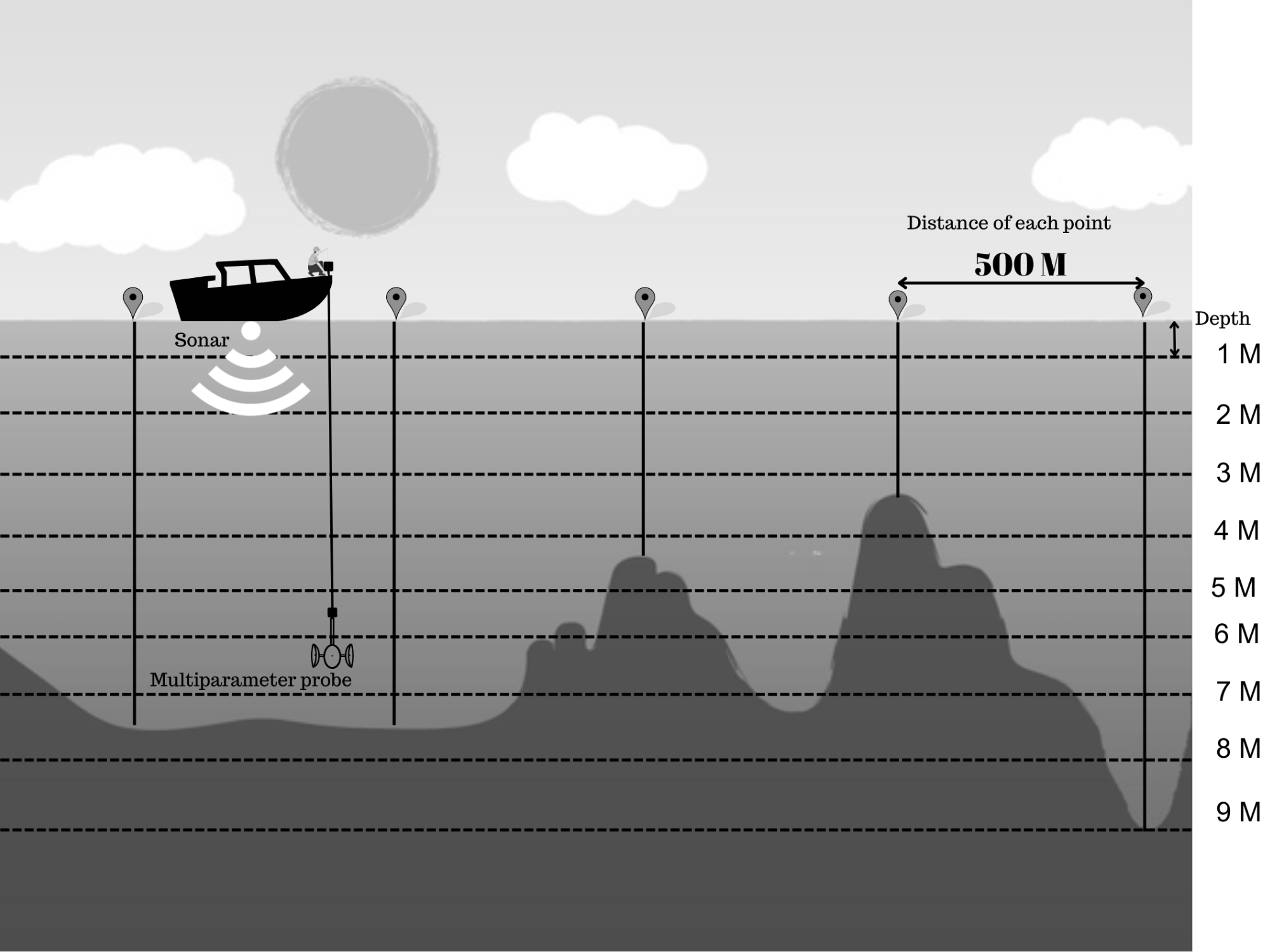
Introduction: In Kelantan, saltwater intrusion was a problem that worsened the water supply, especially groundwater, which was the main source of water supply. This study was conducted to study the suitability of Sungai Semerak as a site for constructing a water intake station in the Pasir Puteh District to provide an alternative water supply source that previously depended on groundwater. Methods: In this study, three approaches were taken to identify the suitable location. The approaches are the Water Quality Index (WQI) by Malaysia Environmental Department includes six water quality parameters of dissolved oxygen (DO), pH, chemical oxygen demand (COD), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), total suspended solids (TSS) and ammoniacal nitrogen (AN) with additional approach of Stratification of saltwater and Groundwater Quality. Result and Discussion: From the data gathered, the freshwater zone shows WQI was in Class III at 52.31, which is higher than 51.9, the lower limit of Class III , which is suitable for water supply with treatment and suitable for irrigation compared to the saline zone, WQI was 47.08, which is in Class IV. Groundwater quality of pH (5.95), Total Dissolve Solids (251.77 mg/L), Conductivity (416.2μS/cm), Turbidity (88.19 NTU), Calcium (14.54mg/L), Magnesium (6.25mg/L), Sodium (36.41mg/L), Bicarbonate (67.11mg/L), Chloride (26.03mg/L), Sulphate (4.67mg/L), Total Hardness (67.12mg/L) also shows acceptable readings for suitability for drinking water. Conclusion: Therefore, Sungai Semerak was suitable for building a water intake station as it was important in a developing state and country.
Song Y, Yang X, Li H, Liu M. Developing an 1. Indicator System and Assessing China’s Progress on Climate Change Adaptation in 2010–2022 from Dual-Dimension. Environmental and Sustainability Indicators. 2025;26(100613):1–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indic.2025.100613
Steinfeld CMM, Sharma A, Mehrotra R, Kingsford 2. RT. The Human Dimension of Water Availability: Influence of Management Rules on Water Supply for Irrigated Agriculture and the Environment. J Hydrol (Amst). 2020;588(125009):1–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125009
He C, Liu Z, Wu J, Pan X, Fang Z, Li J, Bryan BA. 3. Future Global Urban Water Scarcity and Potential Solutions. Nat Commun. 2021;12(25026):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25026-3
De PJMP, Pinto FS, Arantes A, Marques RC. Closing 4. the Loop on Water Supply and Sanitation: the Dynamic Links Between Population, Ecosystems, and Economic Interactions. Sustainable Futures. 2025;9(100434):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sftr.2025.100434
Yilmaz SD, Ben-Nasr S, Mantes A, Ben-Khalifa 5. N, Daghari I. Climate Change, Loss of Agricultural Output and the Macroeconomy: the Case of Tunisia. Ecological Economics. 2025;231(108512):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2024.108512
Jiang F, Chen B, Wang H, Duan C. Mitigating 6. China’s Prefecture-Level Economic Risk of Water Scarcity: the Role of Water Conservation and Carbon Neutrality Policies. Resour Conserv Recycl. 2025;215(108140):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2025.108140
Asmadi AS, Saimy IS, Mohamed YNA, Ba Qutayan 7. S, Salleh SH. The Never-Ending Water Supply Scenario: a Case Study in Kelantan. Springer Nature Singapore. 2023; 75–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7295-9_5
Velmurugan A, Swarnam P, Subramani T, Meena B, Kaledhonkar MJ. Water Demand and Salinity. IntechOpen. 2020;4(876):1-16. https://doi.org/DOI:10.5772/intechopen.88095
Kamal ZA, Khan MMA, Amin M, Mansor HE, Shafiee 9. NS, AI RA, Amin MFM, Hamzah Z, Shah ZA. Assessment of Groundwater Quality in the Coastal Aquifers of Bachok Using Hydrogeochemical Analysis. AIP Conf Proc. 2022; 4(2454):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0078689
Mahmud AY, Birnin-Yauri UA, Muhammad C, Magami 10. IM. Comparative Assessment of Well and Borehole Water Quality Index in Sokoto Metropolis. Caliphate Journal of Science and Technology. 2024;6(3):371–377. https://doi.org/10.4314/cajost.v6i3.14
Samsudin MF, Shau HAT, Amin MMF, Muhammad 11. SMF. The Influence of Tidal on Water Quality in Sungai Semerak, Kelantan. BIO Web Conf EDP Sciences. 2023; 73(05005):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1051/bioconf/20237305005
Nishat MH, Khan MHRB, Ahmed T, Hossain SN, 12. Ahsan A, El-Sergany MM, et al. Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning Models for Predicting Water Quality Index in Dhaka’s Rivers of Bangladesh. Environ Sci Eur. 2025;37(01078):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-025-01078-w
Santos Y, Mosley BA, Nogueira P, Galvão HM, 13. Domingues RB. Growth and Grazing Mortality of Microbial Plankton in a Shallow Temperate Coastal Lagoon (Ria Formosa, SW Iberia). Water (Switzerland). 2024;16(23):1-13. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16233401
Samsudin MS, Azid A, Zaudi MA, Adam MR, Sani 14. MSA, Saharuddin SM, et al. Analyzing Agricultural Land Use with Cellular Automata-MARCOV and Forecasting Future Marine Water Quality Index: A Case Study in East Coast Peninsular Malaysia. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024;235(473):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-07277-0
Man N, Ramli NN, Che’Ya NN. Farmers’ Intention 15. Towards Drone Adoption in Granary Areas of KADA, IADA Kemasin Semerak, Kelantan and IADA KETARA, Terengganu, Malaysia. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci. 2024;1412(012019):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/1412/1/012019
Dawoud MA, Alaswad SO, Ewea HA, Dawoud RM. 16. Towards Sustainable Desalination Industry in Arab Region: Challenges and Opportunities. Desalination Water Treat. 2020;193(25686):1–10. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.25686
Sah SS, Maulud KNA, Sharil S, Karim OA, Nahar 17. NFA. Impact of Saltwater Intrusion on Paddy Growth in Kuala Kedah, Malaysia. J Sustain Sci Manag. 2021;16(6):15–30. https://doi.org/10.46754/jssm.2021.08.004
Florida Department of Environmental Protection18. . Standard Field Procedures for Water Quality Monitoring with Ysi Multi-Parameter Instrument for the Charlotte Harbor Estuaries Volunteer Water Quality Monitoring Network (CHEVWQMN). Charlotte Harbor Aquatic Preserves; 2021. https://floridadep.gov/sites/default/files/YSI-CHEVWQMN-Monitoring-Manual-12-23.pdf
Park YG, Seo S, Kim DG, Noh J, Park HM. Coastal 19. Observation Using a Vertical Profiling System at the Southern Coast of Korea. Front Mar Sci. 2021;8(668733):1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2021.668733
Becker M, Seeger K, Paszkowski A, Marcos 20. M, Papa F, Almar R, et al. Coastal Flooding in Asian Megadeltas: Recent Advances, Persistent Challenges, and Call for Actions Amidst Local and Global Changes. Reviews of Geophysics. 2024;62. https://doi.org/10.1029/2024RG000846
Pakoksung K, Inseeyong N, Chawaloesphonsiya 21. N, Punyapalakul P, Chaiwiwatworakul P, Xu M, Chuenchum P. Seasonal Dynamics of Water Quality in Response to Land Use Changes in the Chi and Mun River Basins Thailand. Sci Rep. 2025;15(7101):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-91820-4
Schlesinger WH, Bernhardt ES. Inland Waters. 22. Biogeochemistry. 2020:12(00008):293–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814608-8.00008-6
Mohamad FSM, Mohd SDN, Mohd AMF, Abdul AH, 23. Mohd KMZ, Zakaria NA, et al. Total Maximum Daily Load Application Using Biological Oxygen Demand, Chemical Oxygen Demand, and Ammoniacal Nitrogen: A Case Study for Water Quality Assessment in the Perai River Basin, Malaysia. Water (Switzerland). 2023;15(6):1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061227
Samsudin MF, Mohd AMF, Syed OSA, Yusoff AH, 24. Sulaiman MS. Water Quality Status of Pergau Reservoir Water Catchment and Lake, Jeli, Kelantan. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci. IOP Publishing Ltd. 2020;549(012009):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/549/1/012009
Hashem AOA, Ahmad WAAW, Yusuf SY. Water quality 25. status of Sungai Petani River, Kedah, Malaysia. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci. 2021;646(012028):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/646/1/012028
Yasmin MN, Mohd RSF, Sharil S, Wan MWHM, 26. Saadon KA. Effectiveness of Tidal Control Gates in Flood-Prone Areas During High Tide Appearances. Front Environ Sci. 2022;10(919704):1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.919704
Rose L, Bhaskaran PK. Tidal Variations Associated 27. with Sea Level Changes in the Northern Bay of bengal. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci. 2022;272(107881):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECSS.2022.107881
Wu Y, Zhao E, Li X, Zhang S. Application of 28. Wave–Current Coupled Sediment Transport Models with Variable Grain Properties for Coastal Morphodynamics: A Case Study of the Changhua River, Hainan. Ocean Science. 2025;21(1):473–495. https://doi.org/10.5194/os-21-473-2025
Arevalo FM, Álvarez-Silva Ó, Caceres-Euse A, 29. Cardona Y. Mixing Mechanisms at the Strongly-Stratified Magdalena River’s Estuary and Plume. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci. 2022;277(108077):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2022.108077
Colina AA, Van MDS, Van WRJA, Huismans Y, 30. Wang ZB. Morphodynamic Modeling of Tidal Basins: The Role of Sand-Mud Interaction. J Geophys Res Earth Surf. 2023;128(9):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1029/2023JF007391
Khakhim N, Kurniawan A, Pranowo WS. 31. Morphodynamic Cartography Visualization of Wulan River Estuary Systems from Space to NumericalApproach Based on Multi-Season Analysis. Geomatics and Environmental Engineering. 2024;18(5):91–112. https://doi.org/10.7494/geom.2024.18.5.91
Nguyen HT, Kawanishi K, Xiao C. Transverse Salinity 32. Dynamic in A Shallow Tidal Channel. International Journal of GEOMATE. 2022;22(91):113–121. https://doi.org/10.21660/2022.91.j2387
Ledoux E, Hertz E, Robinet JC, Combes P. Reflections 33. on the Role of Chemical Osmosis Mechanisms on the Long-term Behavior of a Collapsed Salt Cavity. Comptes Rendus - Geoscience. 2023;355(153):637–645. https://doi.org/10.5802/crgeos.153
Nascimento Â, Biguino B, Borges C, Cereja R, Cruz 34. JPC, Sousa F, et al. Tidal Variability of Water Quality Parameters in a Mesotidal Estuary (Sado Estuary, Portugal). Sci Rep. 2021;11(23112):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-02603-6
Alao JO, Bello A, Lawal H, Abdullahi D. Assessment 35. of Groundwater Challenge and the Sustainable Management Strategies. Results in Earth Sciences. 2024;2(100049):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rines.2024.100049
Liu B, Peng S, Liao Y, Wang H. The Characteristics 36. and Causes of Increasingly Severe Saltwater Intrusion in Pearl River Estuary. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci. 2019;220(45):54–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2019.02.041
Siddique MI. Sustainable Water Management in 37. Urban Areas: Integrating Innovative Technologies and Practices to Address Water Scarcity and Pollution. The Pharmaceutical and Chemical Journal. 2021;8(1):172–178. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.11523688
Fonseca SLM, Magalhães AADJ, Campos VP, 38. Medeiros YDP. Effect of the Reduction of the Outflow Restriction Discharge from the Xingó Water Salinity in the Lower Stretch of The São Francisco River. Revista Brasileira de Recursos Hidricos. 2020;25(4):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1590/2318-0331.252020180093
Wegman TM, Pietrzak JD, Horner-Devine AR, 39. Dijkstra HA, Ralston DK. Observations of Estuarine Salt Intrusion Dynamics During a Prolonged Drought Event in the Rhine-Meuse Delta. J Geophys Res Oceans. 2025;130(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1029/2024JC021655
Pan D, Li Y, Pan C. Short-Term Morphological 40. Responses of Adjacent Intertidal Flats to the Construction of Tidal Gates in an Estuarine Tributary. J Mar Sci Eng. 2022;10(7):1–20. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10070882
Adhikari MP, Rawal NB, Pradhananga AR, Adhikari 41. NB. Assessment of Water Quality Index and Role of Tributaries on Degradation of Bagmati River Water. J Water Environ Technol. 2024;22(6):255–270. https://doi.org/10.2965/jwet.23-118
Abu SH, Yuzir MA, Azman S. Water Quality 42. Assessment using Selected Macroinvertebrate Based Indices and Water Quality Index of Sungai Air Hitam Selangor. Tropical Aquatic and Soil Pollution. 2024;4(2):143–156. https://doi.org/10.53623/tasp.v4i2.505
Olorunsaye O, Heiss JW. Stability of 43. Saltwater-Freshwater Mixing Zones in Beach Aquifers with Geologic Heterogeneity. Water Resour Res. 2024;60(8):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1029/2023WR036056
Hagage M, Abdulaziz AM, Elbeih SF, Hewaidy AGA. 44. Monitoring Soil Salinization and Waterlogging in the Northeastern Nile Delta Linked to Shallow Saline Groundwater and Irrigation Water Quality. Sci Rep. 2024;14(27838):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-77954-x
Gopaiah M, Iswar CD, Vazeer M. Modelling the 45. Spatial Distribution and Future Trends of Seawater Intrusion due to Aquaculture Activities in Coastal Aquifers of Nizampatnam, Andhra Pradesh. Disaster Advances. 2023;16(10):1–10. https://doi.org/10.25303/1610da01010
Lovrinović I, Srzić V, Aljinović I. Characterization of 46. Seawater Intrusion Dynamics Under the Influence of Hydro-Meteorological Conditions, Tidal Oscillations and Melioration System Operative Regimes to Groundwater in Neretva Valley Coastal Aquifer System. J Hydrol Reg Stud. 2023;46(101363):1–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2023.101363
Saccò M, Mammola S, Altermatt F, Alther R, Bolpagni 47. R, Brancelj A, et al. Groundwater is a Hidden Global Keystone Ecosystem. Glob Chang Biol. 2024;30(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.17066
Zainudin AM, Isa NM, Husin NH, Looi LJ, Aris AZ, 48. Sefie A, et al. Groundwater Potability Assessment Through Integration of Pollution Index of Groundwater (Pig) and Groundwater Quality Index (Gwqi) in Linggi River Basin, Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia. Groundw Sustain Dev. 2024;26(101225):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2024.101225

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. Copyright of all journal manuscripts is held by the Jurnal Kesehatan Lingkungan.2. Formal legal provisions to access digital articles of electronic journal are subject to the provision of the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike license (CC BY-NC-SA), which means that Jurnal Kesehatan Lingkungan is rightful to keep, transfer media/format, manage in the form of databases, maintain, and publish articles.
3. Published manuscripts both printed and electronic are open access for educational, research, and library purposes. Additionally, the editorial board is not responsible for any violations of copyright law.
JKESLING by UNAIR is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.







































