Genomic Characterization of Vibrio spp. in Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer, Bloch, 1790) Following Field Vaccination Using a Feed-Based Inactivated Vaccine against Vibriosis
Downloads
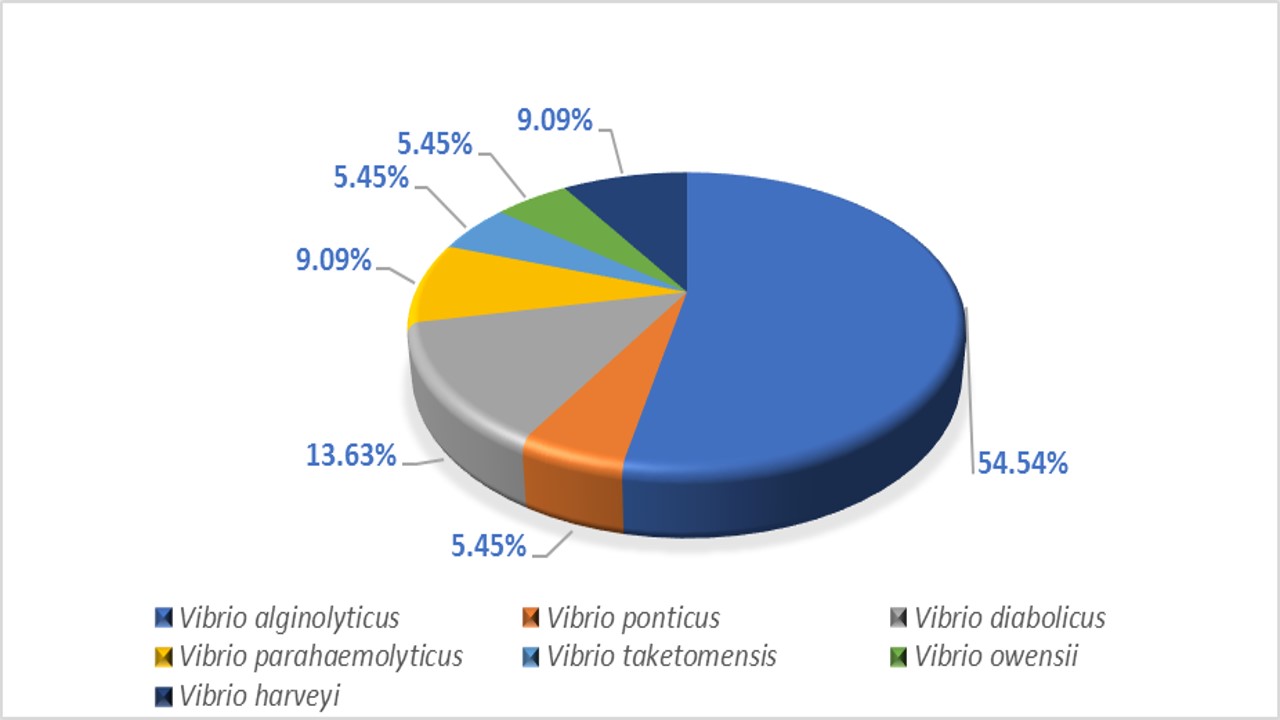
Vibriosis outbreaks pose a significant threat to the productivity of Asian seabass culture, causing substantial losses. Nevertheless, the excessive utilization of antimicrobials exacerbates the issue by fostering the development of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Consequently, exploring alternative disease management strategies, such as the introduction of oral vaccines into Asian seabass culture, has become a subject of ongoing investigation. This study aims to compare the genomic characteristics of different Vibrio species isolated from both orally vaccinated and unvaccinated Asian seabass populations. Archived samples of vaccinated and unvaccinated Asian seabass from one site in Selangor, Malaysia, were utilized in this sample. Briefly, the vaccinated group was administered the feed-based vaccine on week 0 (prime vaccination), 2 (booster), and 6 (second booster) at 4% body weight. At the same time, the non-vaccinated fish were fed with a commercially formulated pellet without the vaccine. Vibrio isolates identified from the gut samples were used in this study. The samples were stored at -80°C before being subjected to genomic DNA extraction, PCR, gel electrophoresis, and sequencing using Illumina and Nanopore platforms. Universal 16s primer and pyrH primer were used to identify Vibrio species. Bioinformatic analysis was done using NCBI BLAST, QUAST, BUSCO 5, CGE, and J Species. The isolates of Vibrio species exhibited smooth, convex, round, and entire colonies on TCBS agar plates, which were yellow and green. Twenty-two isolates were sent for 16s rRNA sequencing and revealed Vibrioalginolyticus (54.54%), followed by V. diabolicus (13.63%) and V. parahaemolyticus and V. harveyi (9.09% respectively). Of the 22 samples, 7 were selected for further Illumina sequencing. The whole genome sequences of the six Vibrio species isolated exhibited good coverage percentage, N50 value, Average Nucleotide Identity (ANIb), single-copy percentage, and GC content, while one sample showed low single-copy percentage and high duplicated percentage, which suggested contamination during DNA extraction. Eight novel alleles were discovered, three from the vaccinated group and five from the unvaccinated group, including the Rec, atpA, gyrB, and pyrH. A virulence factor database analysis search revealed 58 virulent genes from the unvaccinated samples and 39 virulent genes from the vaccinated samples. Overall, this research provides valuable insights into the genomic characteristics between orally vaccinated and unvaccinated cultured Asian seabass in the locality.
Amir-Danial, Z., Zamri-Saad, M., Amal, M.N.A., Annas, S., Mohamad, A., Jumria, S., Manchanayake, T., Arbania, A. and Ina-Salwany, M.Y. (2023). Field Efficacy of a Feed-Based Inactivated Vaccine against Vibriosis in Cage-Cultured Asian Seabass, Lates calcarifer, in Malaysia. Vaccines, 11(1), 9.
Anisimova, M., & Gascuel, O. (2006). Approximate likelihood-ratio test for branches: a fast, accurate, and powerful alternative. Systematic biology, 55(4), 539–552.
Aramaki, T., Blanc-Mathieu, R., Endo, H., Ohkubo, K., Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., & Ogata, H. (2020). KofamKOALA: KEGG Ortholog assignment based on profile HMM and adaptive score threshold. Bioinformatics, 36(7), 2251–2252.
Atkinson, S., & Williams, P. (2016). Yersinia virulence factors-a sophisticated arsenal for combating host defences. F1000Research, 5.
Calder, T., de Souza Santos, M., Attah, V., Klimko, J., Fernandez, J., Salomon, D., & Orth, K. (2014). Structural and regulatory mutations in Vibrio parahaemolyticus type III secretion systems display variable effects on virulence. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 361(2), 107–11.
Cantalapiedra, C. P., Hernández-Plaza, A., Letunic, I., Bork, P., & Huerta-Cepas, J. (2021). eggNOG-mapper v2: functional annotation, orthology assignments, and domain prediction at the metagenomic scale. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 38(12), 5825–5829.
Chen, S., Zhou, Y., Chen, Y., & Gu, J. (2018). fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics, 34, i884–i890.
Chen, Y., Cai, S., & Jian, J. (2019). Protection against Vibrio alginolyticus in pearl gentian grouper (♀ Epinephelus fuscoguttatus×♂ Epinephelus lanceolatus) immunized with an acfA-deletion live attenuated vaccine. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 86, 875–881.
Chevenet, F., Brun, C., Bañuls, A. L., Jacq, B., & Christen, R. (2006). TreeDyn: towards dynamic graphics and annotations for analyses of trees. BMC Bioinformatics, 7, 1–9.
Delamare‐Deboutteville, J., Taengphu, S., Gan, H. M., Kayansamruaj, P., Debnath, P. P., Barnes, A., & Dong, H. T. (2021). Rapid genotyping of tilapia lake virus (TiLV) using Nanopore sequencing. Journal of Fish Diseases, 44(10), 1491–1502.
Deng, Y., Xu, L., Chen, H., Liu, S., Guo, Z., Cheng, C., & Feng, J. (2020). Prevalence, virulence genes, and antimicrobial resistance of Vibrio species isolated from diseased marine fish in South China. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 14329.
Dereeper, A., Audic, S., Claverie, J. M., & Blanc, G. (2010). BLAST-EXPLORER helps you building datasets for phylogenetic analysis. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 10, 8.
Edgar R. C. (2004). MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Research, 32(5), 1792–1797.
Embregts, C. W., & Forlenza, M. (2016). Oral vaccination of fish: Lessons from humans and veterinary species. Developmental & Comparative Immunology, 64, 118–137.
Firdaus‐Nawi, M., Yusoff, S. M., Yusof, H., Abdullah, S. Z., & Zamri‐Saad, M. (2013). Efficacy of feed‐based adjuvant vaccine against Streptococcus agalactiae in Oreochromis spp. in Malaysia. Aquaculture Research, 45(1), 87–96.
Getz, L. J., & Thomas, N. A. (2018). The transcriptional regulator HlyU positively regulates expression of exsA, leading to type III secretion system 1 activation in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Journal of Bacteriology, 200(15), 10–1128.
Grabowski, B., Schmidt, M. A., & Rüter, C. (2017). Immunomodulatory Yersinia outer proteins (Yops)–useful tools for bacteria and humans alike. Virulence, 8(7), 1124–1147.
Guindon, S., & Gascuel, O. (2003). A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Systematic Biology, 52(5), 696–704.
Gurevich, A., Saveliev, V., Vyahhi, N., & Tesler, G. (2013). QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics, 29(8), 1072–1075.
Gutierrez West, C. K., Klein, S. L., & Lovell, C. R. (2013). High frequency of virulence factor genes tdh, trh, and tlh in Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains isolated from a pristine estuary. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 79(7), 2247–2252.
Ina‐Salwany, M. Y., Al‐saari, N., Mohamad, A., Mursidi, F. A., Mohd‐Aris, A., Amal, M. N. A., & Zamri‐Saad, M. (2019). Vibriosis in fish: a review on disease development and prevention. Journal of Aquatic Animal Health, 31(1), 3–22.
Jain, C., Rodriguez-R, L. M., Phillippy, A. M., Konstantinidis, K. T., & Aluru, S. (2018). High throughput ANI analysis of 90K prokaryotic genomes reveals clear species boundaries. Nature Communications, 9(1), 5114.
Jerry, D. R. (Ed.). (2013). Biology and culture of Asian seabass Lates calcarifer. CRC Press.
Kenconojati, H., Ulkhaq, M. F., Azhar, M. H., & Rukmana, N. R. (2023). Vibriocidal Activity of Ethanol Extract of Moringa Leaves and Its Effect on the Growth of Pacific White Shrimp. Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 6(1), 75–81.
Li, L., Meng, H., Gu, D., Li, Y., & Jia, M. (2019). Molecular mechanisms of Vibrio parahaemolyticus pathogenesis. Microbiological Research, 222, 43–51.
Lian, L., Xue, J., Li, W., Ren, J., Tang, F., Liu, Y., & Dai, J. (2021). VscF in T3SS1 Helps to Translocate VPA0226 in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 11, 652432.
Lin, H., Yu, M., Wang, X., & Zhang, X. H. (2018). Comparative genomic analysis reveals the evolution and environmental adaptation strategies of vibrios. BMC Genomics, 19, 1–14.
Mohamad, A., Mursidi, F. A., Zamri-Saad, M., Amal, M. N. A., Annas, S., Monir, M. S., & Ina-Salwany, M. Y. (2022). Laboratory and field assessments of oral Vibrio vaccine indicate the potential for protection against vibriosis in cultured marine fishes. Animals, 12(2), 133.
Mohamad, N., Amal, M. N. A., Saad, M. Z., Yasin, I. S. M., Zulkiply, N. A., Mustafa, M., & Nasruddin, N. S. (2019). Virulence-associated genes and antibiotic resistance patterns of Vibrio spp. isolated from cultured marine fishes in Malaysia. BMC Veterinary Research, 15, 1–13.
Mohamad, N., Mohd Roseli, F. A., Azmai, M. N. A., Saad, M. Z., Md Yasin, I. S., Zulkiply, N. A., & Nasruddin, N. S. (2019). Natural concurrent infection of Vibrio harveyi and V. alginolyticus in cultured hybrid groupers in Malaysia. Journal of Aquatic Animal Health, 31(1), 88–96.
Mursidi, F. (2018). Antigenic Analysis of outer Membrane Protein of Vibrio Species and Development of Versatile Recombinant vhDnaJ Vaccine against Vibriosis. Master Thesis, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang, Malaysia, 2018.
Ottaviani, D., Leoni, F., Talevi, G., Masini, L., Santarelli, S., Rocchegiani, E., Susini, F., Montagna, C., Monno, R., D'Annibale, L., Manso, E., Oliva, M., & Pazzani, C. (2013). Extensive investigation of antimicrobial resistance in Vibrio parahaemolyticus from shellfish and clinical sources, Italy. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 2(42), 191–193.
Parks, D. H., Chuvochina, M., Chaumeil, P. A., Rinke, C., Mussig, A. J., & Hugenholtz, P. (2020). A complete domain-to-species taxonomy for Bacteria and Archaea. Nature Biotechnology, 38(9), 1079–1086.
Pham, T. T. H., Tran, Q. B., Sukasem, C., Nguyen, V. D., Chu, C. H., Do, T. Q. N., & Phung, T. H. (2021). A novel allele-specific pcr protocol for the detection of the hla-c* 03: 02 allele, a pharmacogenetic marker, in vietnamese kinh people. The Application of Clinical Genetics, 27–35.
Raju, T., Manchanayake, T., Danial, A., Zamri-Saad, M., Azmai, M. N. A., Md Yasin, I. S., & Salleh, A. (2023). Evaluating the Intestinal Immunity of Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer, Bloch 1790) following Field Vaccination Using a Feed-Based Oral Vaccine. Vaccines, 11(3), 602.
Simão, F. A., Waterhouse, R. M., Ioannidis, P., Kriventseva, E. V., & Zdobnov, E. M. (2015). BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics, 31(19), 3210–3212.
Solfaine, R., Purnama, M., Maslamama, S., Fikri, F., & Hamid, I. (2024). Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus: A Boost for Hematological and Gut Health in Salmonella enteritidis-Infected Mice. International Journal of Veterinary Science, 13(6).
Waddell, B., Southward, C. M., McKenna, N., & DeVinney, R. (2014). Identification of VPA0451 as the specific chaperone for the Vibrio parahaemolyticus chromosome 1 type III-secreted effector VPA0450. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 353(2), 141–150.
Walker, P. J., & Winton, J. R. (2010). Emerging viral diseases of fish and shrimp. Veterinary Research, 41(6).
Wick, R. R., Judd, L. M., Gorrie, C. L., & Holt, K. E. (2017). Unicycler: resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Computational Biology, 13(6), e1005595.
Zhang, Y., Deng, Y., Feng, J., Guo, Z., Chen, H., Wang, B., Hu, J., Lin, Z., & Su, Y. (2021). Functional characterization of VscCD, an important component of the type III secretion system of Vibrio harveyi. Microbial Pathogenesis, 157, 104965.
Zhang, Y., Osei-Adjei, G., Ni, B., Fang, H., Zhang, L., Zhao, X., Huang, X., Yang, H., Yang, W., Sun, F. (2016). Transcription of exsD is repressed directly by H-NS in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microbial Pathogenesis, 97, 221–225.
Zheng, F., Liu, H., Zhang, Y., Xu, Z., & Wang, B. (2017). Identification and characterization of pathogens associated with fin erubescence and ulceration of cultured Scophthalmus maximus. Aquaculture Research, 48(2), 521–530.
Zheng, H. Y., Yan, L., Yang, C., Wu, Y. R., Qin, J. L., Hao, T. Y., Yang, D. J., Guo, Y. C., Pei, X. Y., Zhao, T. Y., & Cui, Y. J. (2021). Population genomics study of Vibrio alginolyticus. Yi Chuan Hereditas, 43(4), 350–361.
Copyright (c) 2025 Nur Diyana Mohamad Tahir, Sing Yee Yap, Norhariani Mohd. Nor, Ina-Salwany Md. Yasin, Mohammad Noor Amal Azmai, Nurul Izzati Uda Zahli, Han Ming Gan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions;
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions;
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-SA).






11.jpg)




















