Osteogenic Differentiation Potential of Equine Dental Pulp vs. Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells: A Comparative In Vitro Study
Downloads
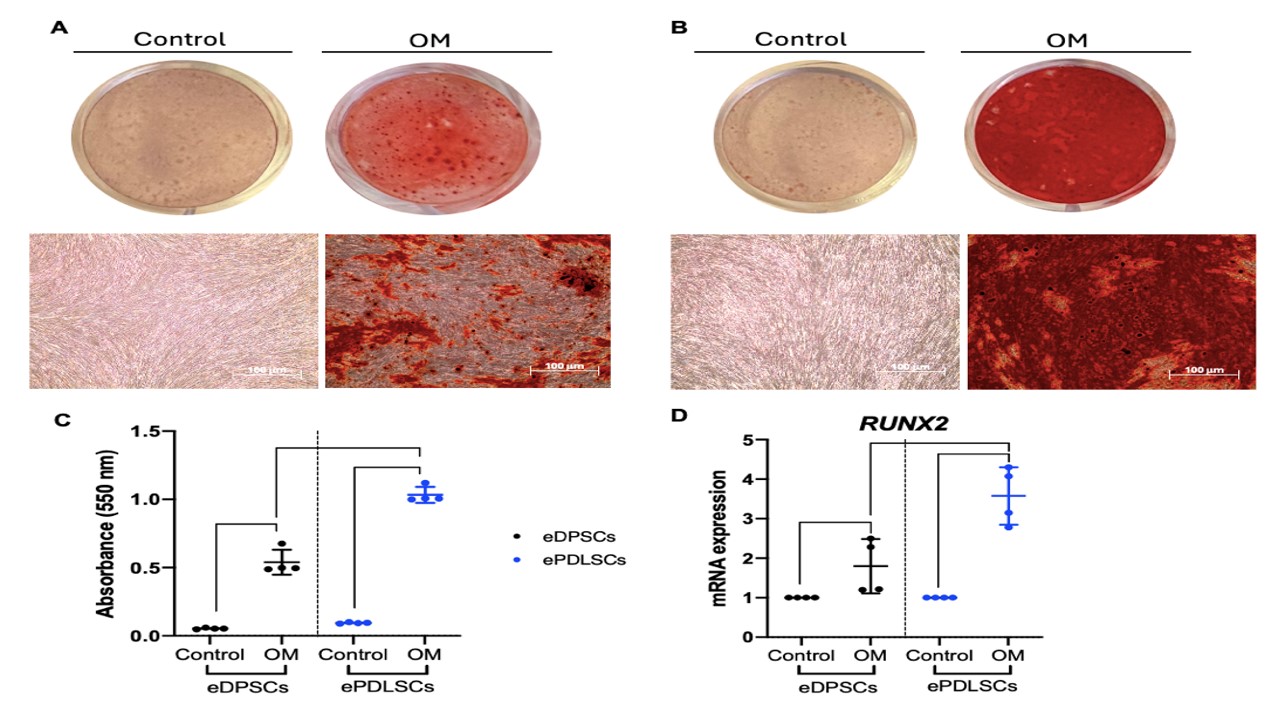
Equine mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are promising for bone tissue engineering (BTE) because of their capabilities of differentiating into osteoblasts. Cell therapy using equine MSCs has been introduced. Recently, dental-derived MSCs have gained significant attention due to their capabilities and ease of collection with minimally invasive collection methods. Dental stem cells show high plasticity, accessibility, and applicability for regenerative medicine and are thus considered alternative sources of MSCs. This study evaluated the characterization, osteogenic differentiation potential, and migration assay of equine dental pulp stem cells (eDPSCs) as compared with equine periodontal ligament stem cells (ePDLSCs). Equine dental stem cells from eDPSCs and ePDLSCs (n = 4) were isolated and expanded to passage 3. The morphology, colony-forming capability, cell proliferation assay, stemness and surface markers, trilineage differentiation potential, and migration assay were investigated in vitro. Both eDPSCs and ePDLSCs exhibited a fibroblast-like morphology; showed a colony-forming capability; were able to proliferate based on the results of the cell proliferation assay; expressed stemness and surface markers (NANOG, CD29, CD44, CD90, CD18); maintained the ability to differentiate into osteocytes, chondrocytes, and adipocytes and demonstrated migration capacity based on the migration assay. Surprisingly, ePDLSCs showed significant differences in matrix mineralization, quantification of Alizarin Red staining by cetylpyridinium chloride, and mRNA expression of the osteogenic marker RUNX2. ePDLSCs and eDPSCs may be better alternative MSCs than dental stem cells for the further design of therapeutic regimens for BTE and wound-healing therapy.
Alipour, F., Parham, A., Mehrjerdi, H. K., & Dehghani, H. (2015). Equine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells: phenotype and growth characteristics, gene expression profile and differentiation potentials. Cell Journal (Yakhteh), 16(4), 456.
Banyatworakul, P., Osathanon, T., Chumprasert, S., Pavasant, P., & Pirarat, N. (2021). Responses of canine periodontal ligament cells to bubaline blood derived platelet rich fibrin in vitro. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 1–13.
Braun, J., Hack, A., Weis-Klemm, M., Conrad, S., Treml, S., Kohler, K., Walliser, U., Skutella, T., & Aicher, W. K. (2010). Evaluation of the osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation capacities of equine adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. American Journal of Veterinary Research, 71(10), 1228–1236.
Bundgaard, L., Stensballe, A., Elbæk, K. J., & Berg, L. C. (2018). Mapping of equine mesenchymal stromal cell surface proteomes for identification of specific markers using proteomics and gene expression analysis: an in vitro cross-sectional study. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 9, 1–10.
Carvalho, A. d. M., Yamada, A. L. M., Golim, M., Álvarez, L., Jorge, L., Conceição, M., Deffune, E., Hussni, C. A., & Alves, A. (2013). Characterization of mesenchymal stem cells derived from equine adipose tissue. Arquivo Brasileiro de Medicina Veterinária e Zootecnia, 65, 939–945.
Delaiah, D., Aswin, A., Susilowati, H., Wijaya, A. Y., Maulana, F. K., Rodprasert, W., Puspitasari, Y., Dhamayanti, Y., & Kuncorojakti, S. (2024). Epidermal growth factor promotes E6 and CCL-81 Vero cells proliferation under serum-free condition. Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 7(1), 1–6.
Egusa, H., Sonoyama, W., Nishimura, M., Atsuta, I., & Akiyama, K. (2012). Stem cells in dentistry–Part II: Clinical applications. Journal of Prosthodontic Research, 56(4), 229–248.
Gugjoo, M. B., & Sharma, G. T. (2019). Equine mesenchymal stem cells: properties, sources, characterization, and potential therapeutic applications. Journal of Equine Veterinary Science, 72, 16–27.
Han, Y. (2021). High concentrations of calcium suppress osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in vitro. Journal of Dental Sciences, 16(3), 817–824.
Ishikawa, S., Horinouchi, C., Murata, D., Matsuzaki, S., Misumi, K., Iwamoto, Y., Korosue, K., & Hobo, S. (2017). Isolation and characterization of equine dental pulp stem cells derived from Thoroughbred wolf teeth. Journal of Veterinary Medical Science, 79(1), 47–51.
Kawamura, M., Yamamoto, T., Yamashiro, K., Kochi, S., Yoshihara‐Hirata, C., Ideguchi, H., Aoyagi, H., Omori, K., & Takashiba, S. (2019). Induction of migration of periodontal ligament cells by selective regulation of integrin subunits. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 23(2), 1211–1223.
Kornicka, K., Geburek, F., Röcken, M., & Marycz, K. (2019). Stem Cells in Equine Veterinary Practice—Current Trends, Risks, and Perspectives. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(5), 675.
Men, Y., Wang, Y., Yi, Y., Jing, D., Luo, W., Shen, B., Stenberg, W., Chai, Y., Ge, W. P., & Feng, J. Q. (2020). Gli1+ periodontium stem cells are regulated by osteocytes and occlusal force. Developmental Cell, 54(5), 639–654.
Mensing, N., Gasse, H., Hambruch, N., Haeger, J.-D., Pfarrer, C., & Staszyk, C. (2011). Isolation and characterization of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells from the gingiva and the periodontal ligament of the horse. BMC Veterinary Research, 7(1), 1–13.
Mukhtar, A. H., & Alqutub, M. N. (2020). Osteogenic Potential of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells Cultured in Osteogenic and Regular Growth Media: Confocal and Scanning Electron Microscope Study. Journal Contemporer Dental Practice, 21, 776–780.
Nantavisai, S., Pisitkun, T., Osathanon, T., Pavasant, P., Kalpravidh, C., Dhitavat, S., Makjaroen, J., & Sawangmake, C. (2020). Systems biology analysis of osteogenic differentiation behavior by canine mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow and dental pulp. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–18.
Nowwarote, N., Manokawinchoke, J., Kanjana, K., Fournier, B. P., Sukarawan, W., & Osathanon, T. (2020). Transcriptome analysis of basic fibroblast growth factor treated stem cells isolated from human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Heliyon, 6(6), e04246.
Nowwarote, N., Sukarawan, W., Kanjana, K., Pavasant, P., Fournier, B. P., & Osathanon, T. (2018). Interleukin 6 promotes an in vitro mineral deposition by stem cells isolated from human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Royal Society Open Science, 5(10), 180864.
Pöschke, A., Krähling, B., Failing, K., & Staszyk, C. (2018). Molecular characteristics of the equine periodontal ligament. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 4, 235.
Purbantoro, S. D., Osathanon, T., Nantavisai, S., & Sawangmake, C. (2022). Osteogenic growth peptide enhances osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells. Heliyon, e09936.
Purbantoro, S. D., Taephatthanasagon, T., Purwaningrum, M., Hirankanokchot, T., Peralta, S., Fiani, N., Sawangmake, C., & Rattanapuchpong, S. (2024). Trends of regenerative tissue engineering for oral and maxillofacial reconstruction in veterinary medicine. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 11, 1325559.
Purwaningrum, M., Giachelli, C. M., Osathanon, T., Rattanapuchpong, S., & Sawangmake, C. (2023a). Dissecting specific Wnt components governing osteogenic differentiation potential by human periodontal ligament stem cells through interleukin-6. Scientific Reports, 13(1), 9055.
Purwaningrum, M., Giachelli, C. M., Osathanon, T., Rattanapuchpong, S., & Sawangmake, C. (2023b). Dissecting specific Wnt components governing osteogenic differentiation potential by human periodontal ligament stem cells through interleukin-6. Scientific Reports, 13(1), 1–19.
Purwaningrum, M., Jamilah, N. S., Purbantoro, S. D., Sawangmake, C., & Nantavisai, S. (2021). Comparative characteristic study from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Journal of Veterinary Science, 22(6), 231.
Radcliffe, C. H., Flaminio, M. J. B., & Fortier, L. A. (2010). Temporal analysis of equine bone marrow aspirate during establishment of putative mesenchymal progenitor cell populations. Stem cells and Development, 19(2), 269–282.
Reed, S. A., & Johnson, S. E. (2008). Equine umbilical cord blood contains a population of stem cells that express Oct4 and differentiate into mesodermal and endodermal cell types. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 215(2), 329–336.
Rodas-Junco, B. A., Canul-Chan, M., Rojas-Herrera, R. A., De-la-Peña, C., & Nic-Can, G. I. (2017). Stem cells from dental pulp: what epigenetics can do with your tooth. Frontiers in Physiology, 8, 999.
Rodprasert, W., Nantavisai, S., Pathanachai, K., Pavasant, P., Osathanon, T., & Sawangmake, C. (2021). Tailored generation of insulin producing cells from canine mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow and adipose tissue. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 1–17.
Safitri, E., Purnobasuki, H., Purnama, M. T. E., & Chhetri, S. (2024). Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells cultured low oxygen tension ameliorates apoptotic inhibitors, viability, and differentiation of ovarian tissue: A study in a rat model with ovarian failure. F1000Research, 12, 24.
Srionrod, N., Bootcha, R., & Petchdee, S. (2016). Foal Deciduous Teeth Stem Cells Enhance Wound Healing in Rabbit Wound Model. The Thai Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 46(1), 155–161.
Tantilertanant, Y., Niyompanich, J., Everts, V., Supaphol, P., Pavasant, P., & Sanchavanakit, N. (2019). Cyclic tensile force-upregulated IL6 increases MMP3 expression by human periodontal ligament cells. Archives of Oral Biology, 107, 104495.
Vidal, M. A., Kilroy, G. E., Lopez, M. J., Johnson, J. R., Moore, R. M., & Gimble, J. M. (2007). Characterization of equine adipose tissue‐derived stromal cells: adipogenic and osteogenic capacity and comparison with bone marrow‐derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Veterinary Surgery, 36(7), 613–622.
Violini, S., Ramelli, P., Pisani, L. F., Gorni, C., & Mariani, P. (2009). Horse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells express embryo stem cell markers and show the ability for tenogenic differentiation by in vitro exposure to BMP-12. BMC Cell Biology, 10, 1–10.
Warhonowicz, M., Staszyk, C., Rohn, K., & Gasse, H. (2006). The equine periodontium as a continuously remodeling system: morphometrical analysis of cell proliferation. Archives of Oral Biology, 51(12), 1141–1149.
Wu, Y., & Gong, P. (2024). Scopolamine regulates the osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells through lactylation modification of RUNX2 protein. Pharmacology Research & Perspectives, 12(1), e1169.
Copyright (c) 2025 Medania Purwaningrum, Aris Haryanto, Yohanna Kayanaveda, Chenphop Sawangmake

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions;
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions;
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-SA).






11.jpg)




















