RISK FACTORS AND CHARACTERISTICS OF ACTIVE AND LATENT TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN ≤ 14: ACTIVE CASE FINDING
Faktor Risiko dan Karakteristik Tuberkulosis Aktif dan Laten Pada Anak ≤ 14 Tahun: Penemuan Kasus Aktif
Downloads
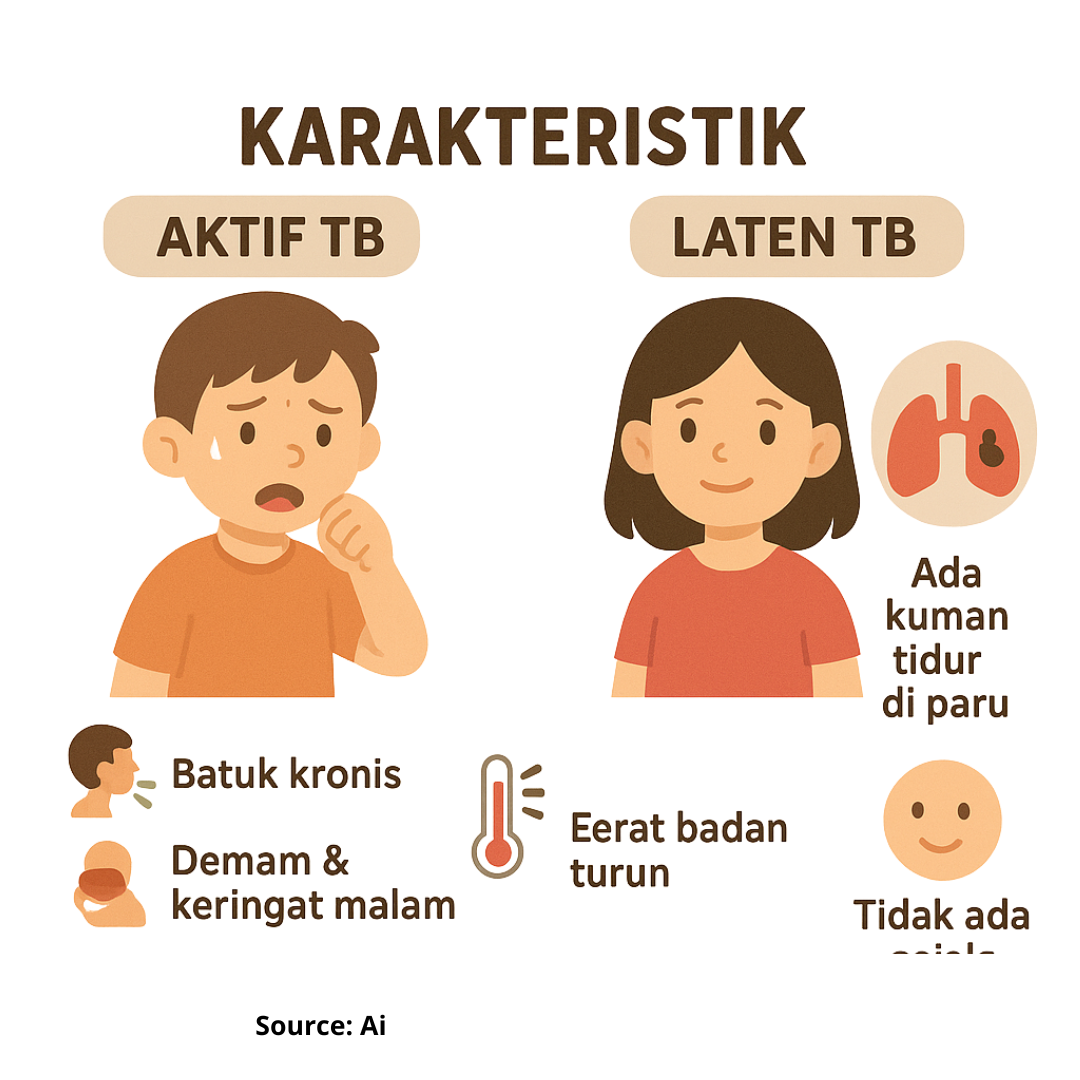
Background: In 2024, 135,000 tuberculosis (TB) cases were reported in Indonesian children, accounting for part of the 885,000 total TB cases nationwide. Pediatric TB remains a concern due to children’s vulnerability from immature immunity, poor nutrition, and close contact with TB patients. Early detection through active case finding (ACF) is crucial for identifying active and latent TB in at-risk populations. Purpose: To determine the prevalence of active and latent TB and analyze associated risk factors among children screened through ACF. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted among 870 children in Sidoarjo Regency using ACF. Active TB was diagnosed through symptom interviews and sputum examination, while latent TB was determined by tuberculin skin test (TST). Nutritional status was assessed using body mass index (BMI). Bivariate analysis was performed to assess associations with active TB. Results: The prevalence of active TB was 4%, and that of latent TB was 4.7%. Among TB cases, 46% were active and 54% latent. Malnutrition was common in active (77%) and latent (46%) TB. Bivariate analysis showed no significant associations with gender, close contact, or passive smoking. Children aged <5 years had a higher risk than those aged 5–14 years (OR = 3.11; 95% CI: 0.99–9.79; p = 0.064). Nutritional status was significantly associated with active TB (χ² = 7.85; p = 0.049). Underweight children had nearly four times higher risk of active TB compared to those with normal nutrition (OR = 3.94; 95% CI: 1.32–11.76; p = 0.018). Conclusion: ACF was effective in detecting active and latent TB among children. Malnutrition was a significant risk factor, suggesting that nutritional interventions should be integrated into pediatric TB control strategies. Patients had close contact with active TB patients.
WHO. Global tuberculosis report 2023. Geneva; 2023.
Simarmata RN, Hartono B, Simamora B. Implementation of Presidential Regulation number 67 of 2021 in the management of pulmonary tuberculosis at Dr. Pirngadi Regional Hospital. Strukt J Ilm Magister Adm Publik. 2024;6(2):233–41.
Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia. Indonesian health profile 2022. Jakarta; 2023.
Moore BK, Graham SM, Nandakumar S, Doyle J, Maloney SA. Pediatric tuberculosis: a review of evidence-based best practices for clinicians and health care providers. pathogens. 2024 Jun 1;13(6):467.
Shakoor S, Mir F. Updates in pediatric tuberculosis in international settings. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2022 Feb;69(1):19–45.
Siddalingaiah N, Chawla K, Nagaraja SB, Hazra D. Risk factors for the development of tuberculosis among the pediatric population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Pediatr. 2023 May 2;182(7):3007–19.
Tristram D, Tobin EH. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-.
Yayan J, Franke KJ, Berger M, Windisch W, Rasche K. Early detection of tuberculosis: a systematic review. Pneumonia. 2024 Jul 5;16(1):11.
Dewi SC, Sunarti, Suryani D, Rokhmayanti. Active tuberculosis case discovery using the adaptation model in the city of Yogyakarta. Jurnal Kesehatan. 2024 May 27;1–11.
Zhou G, Luo S, He J, Chen N, Zhang Y, Cai S, et al. Effectiveness and safety of tuberculosis preventive treatment for contacts of patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 2024 Feb;30(2):189–96.
Tobin EH, Tristam D. Tuberculosis overview. StatPearls Publishing; 2024.
Nolt D, Starke JR. Tuberculosis Infection in children and adolescents: testing and treatment. Pediatrics. 2021 Dec 1;148(6).
Intan Salsabila, Nur Lu’lu Fitriyani, Jaya Maulana. Literature study: risk factors for tuberculosis in children. International Journal of Sustainable Social Science (IJSSS). 2023 Dec 28;1(2):73–82.
Majumdar A, Saraf SK, Sahu C, Verma K, Vishwakarma P. Current perspectives on malnutrition and immunomodulators bridging nutritional deficiencies and immune health. Futur J Pharm Sci. 2025 Apr 24;11(1):50.
Maphalle LNF, Michniak-Kohn BB, Ogunrombi MO, Adeleke OA. Pediatric tuberculosis management: a global challenge or breakthrough? Children. 2022 Jul 27;9(8):1120.
Sagili KD, Muniyandi M, Shringarpure K, Singh K, Kirubakaran R, Rao R, et al. Strategies to detect and manage latent tuberculosis infection among household contacts of pulmonary TB patients in high TB burden countries‐a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Trop Med Int Heal. 2022;27(10):842–63.
Hoffmann J, Horsburgh CR. Addressing gaps in the diagnosis of TB in children. IJTLD OPEN. 2024 Oct 1;1(10):429–30.
Birroudhoh F. Early detection of latent tuberculosis infection (ITB) in household contacts of tuberculosis patients using the Mantoux test method at the Rengel Community Health Center. Action Research Literate. 2024 Oct 28;8(10):2867–70.
Karbito K. Prevalence and risk factors for latent TB infection in household contacts of active TB patients. Jurnal Kesehatan Lingkungan Indonesia. 2023 Oct 1;22(3):351–8.
Ghanaie RM, Karimi A, Azimi L, James S, Nasehi M, Mishkar AP, et al. Diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection among pediatric household contacts of Iranian tuberculosis cases using tuberculin skin test, IFN- γ release assay and IFN-γ-induced protein-10. BMC Pediatr. 2021 Dec 11;21(1):76.
Mafirakureva N, Tchounga BK, Mukherjee S, Tchakounte Youngui B, Ssekyanzi B, Simo L, et al. Cost-effectiveness of community-based household tuberculosis contact management for children in Cameroon and Uganda: a modelling analysis of a cluster-randomised trial. Lancet Glob Health. 2023 Dec;11(12):e1922–30.
Menzies D. Screening for latent tuberculosis infection. JAMA Netw Open. 2023 May 2;6(5):e2312114.
Dowdy DW, Sohn H. Cost-effectiveness of interventions to improve case finding for tuberculosis: developing consensus to motivate investment. BMC Global and Public Health. 2023 Oct 11;1(1):20.
- Every manuscript submitted to must observe the policy and terms set by the Jurnal Berkala Epidemiologi
- Publication rights to manuscript content published by the Jurnal Berkala Epidemiologi is owned by the journal with the consent and approval of the author(s) concerned. (download copyright agreement)
- Complete texts of electronically published manuscripts can be accessed free of charge if used for educational and research purposes according to copyright regulations.

JBE by Universitas Airlangga is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.























