Dairy Milk Quality After Foot and Mouth Disease in Ternak Sukses Bersama, Kediri Regency

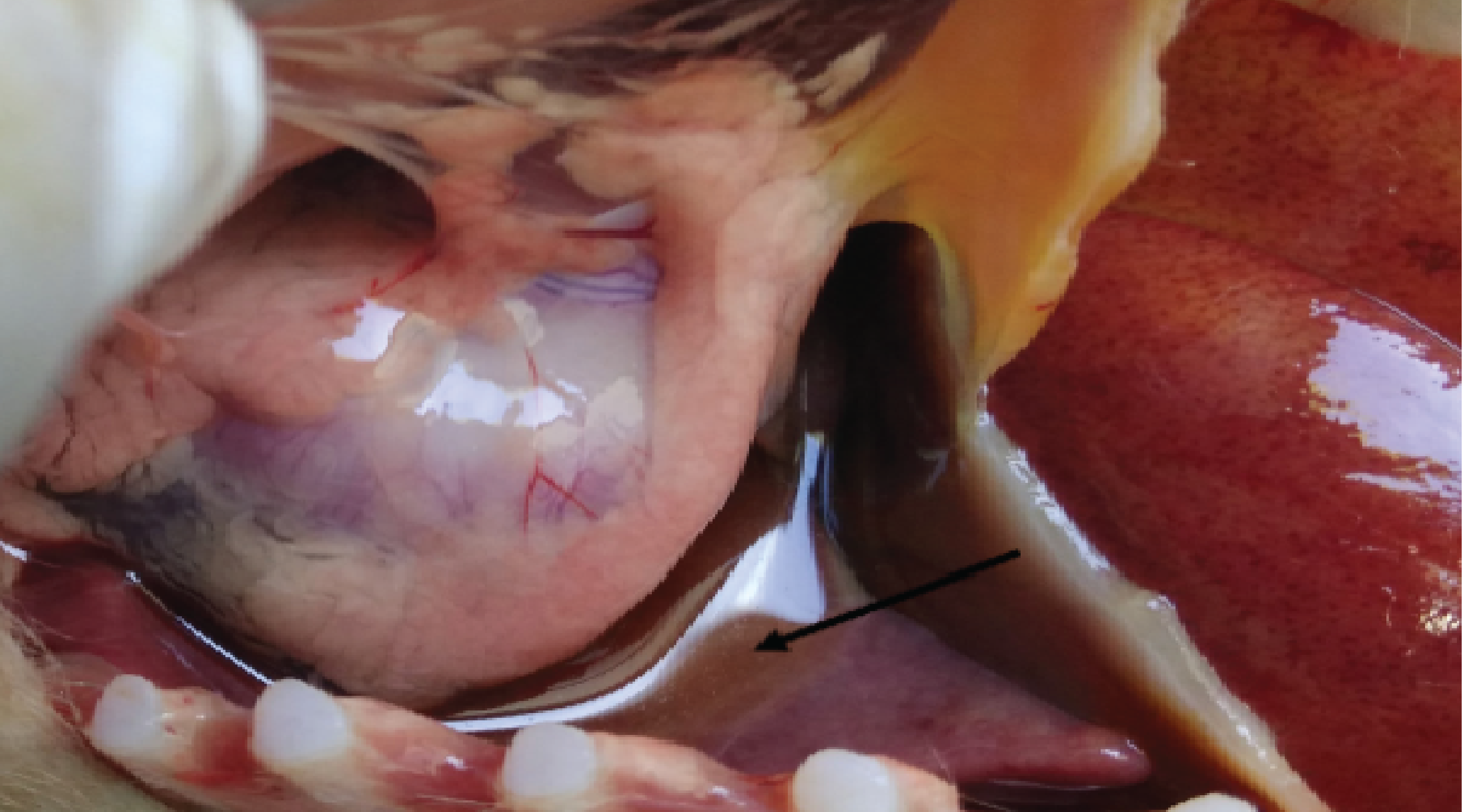
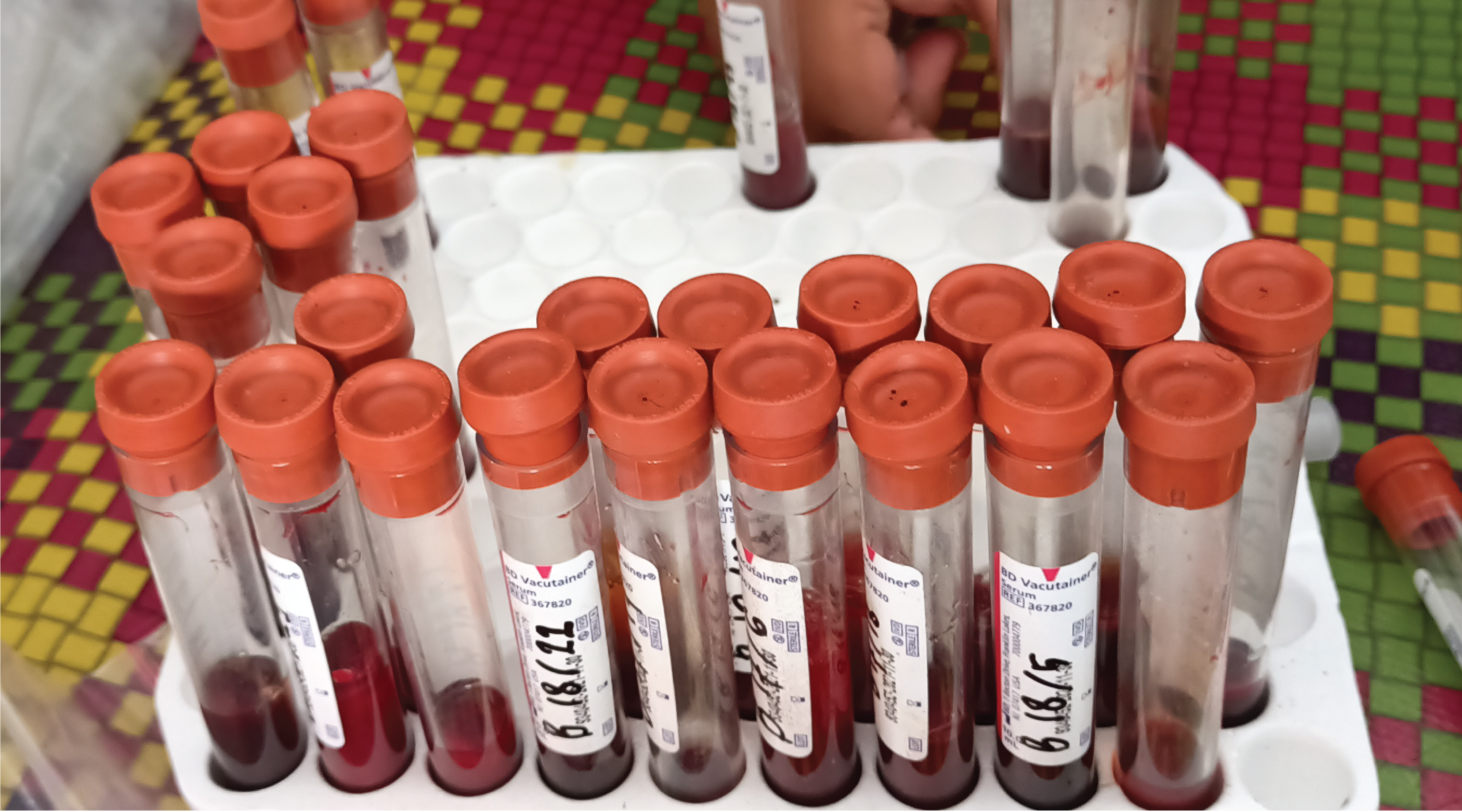
Background: Milk, a nutrient-rich substance obtained from udder secretions, can suffer quality degradation due to factors like disease-causing microorganisms. Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD), an acute viral infection affecting cloven-hoofed animals, can severely impact milk production and quality. Purpose: This study aims to analyze the quality of milk from dairy cattle following the FMD outbreak, as FMD not only reduces milk yield but also alters its composition, affecting consumer preferences and farmer income. Method: Milk quality tests were conducted on cattle following the FMD outbreak with each 50 ml sample stored in an icebox and analyzed using a calibrated Lactoscan tool. The analysis covered fat, solid-non-fat (SNF), density, lactose, salts, protein, temperature, freezing point, added water, total solids, and pH levels. The study received consent from local authorities and breeders. Results: The analysis of cow milk post Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) outbreak reveals significant variability in milk composition, affecting quality and processing, with many falling below or above standard thresholds for fat content, SNFs, protein content, freezing point, and added water, while all samples had a pH level outside the acceptable range. Conclusion: Quality of dairy milk from dairy cattle after FMD outbreaks show decreasing of fat content in five milk samples, four samples in solid non fat, three samples in protein, nine samples in freezing point, eight samples in added water, and all samples fell outside the acceptable pH range.
Adhi, W., 2022. 5 Facts about Foot and Mouth Disease that is Endemic in Indonesia. CNN Indonesia. https://www.cnnindonesia.com/gayalive/ 20220514080653-255- 796669/5-cepat-penyakit-kuku-dan-mulut-yang-sedang-mewabah-di-indonesia. Accessed: July 5, 2022.
Andriawan, T., Harjanti, D. W., and Sambodho, P., 2014. The Relation Between Crude Fiber Intake with Total Milk Production and Milk Fat in Smallholder Dairy Farms in Klaten. Animal Agriculture Journal, 3(3), 383–388.
Ansari-Lari, M., Mohebbi-Fani, M., Lyons, N. A., and Azizi, N., 2017. Impact of FMD Outbreak on Milk Production and Heifers’ Growth on A Dairy Herd in Southern Iran. Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 144, 117–122.
Armson, B., Gubbins, S., Mioulet, V., Qasim, I. A., King, D. P., and Lyons, N. A., 2020. Foot-and-Mouth Disease Surveillance Using Pooled Milk on a Large-Scale Dairy Farm in an Endemic Setting. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 7, 1-11.
Atabany, A., Purwanto, BP., Tohamat, T., and Anggraeni, A., 2011. The Relationship between Vacancies with Productivity in Cow Milk Fresian Holstein in Baturraden, Indonesia. Media Peternakan, 34(2), 70–77.
Ceniti, C., Britti, D., Trimboli, F., Morittu, V. M., Lopreiato, V., and Costanzo, N., 2019. Evaluation of Freezing Point in Milk from Buffalos Reared in Calabria, Italy. Italian Journal of Food Safety, 8(2), 65-68.
Indonesian National Standards Agency., 2011. Fresh Milk- Part 1: Cows. Jakarta: Indonesian National Standards, 3141.
Delvia, J., Nugraha, A. B., Suprayogi, A., and Pisestyani, H., 2023. Case Study: Somatic Cells Count and Milk Composition from Subclinical Mastitis Positive Dairy Cows Owned by PT. Great Giant Livestock. Jurnal Kajian Veteriner, 11(1), 19–27.
Gading, AF., Surwowardojo, P., and Rifa’i., 2023. Correlation of Udder Washing Water Temperature on Production and Milk Fat Content of Post-PMK PFH Cows in Ngantang District, Malang Regency. Journal of Tropical Animal Science, 1(2), 47–53.
Górska-Warsewicz, H., Rejman, K., Laskowski, W., and Czeczotko, M., 2019. Milk and Dairy Products and Their Nutritional Contribution to the Average Polish Diet. Nutrients, 11(8), 1-19.
Hussain, A., Abubakar, M., Shah, H., Arshed, MJ., Hussain, M., and Afzal, M., 2017. Socioeconomic Impact of Foot and Mouth Disease Vaccination in Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Life and Social Sciences, 15(3), 183–191.
Indriani, N., 2020. Evaluasi Konsumsi Bahan Kering, Bobot Badan dan Produksi Susu Induk Sapi Perah Pada Bulan Pertama Laktasi. Jurnal Peternakan Indonesia, 1(2), 2-5.
Janah, AF, Wiyanto, and Hartono., 2018. Penerapan Peta Konsep IPA Terpadu untuk Mengukur Minds-On and Hands-On Activity Siswa Sekolah Menengah Pertama. Unnes Physics Education Journal, 7(2), 9-23.
Kitching, R.P., 2002. Clinical variation in foot and mouth disease: cattle. Revue Scientifique et Technique de l’OIE, 21(3), 499–504.
Lyons, N.A., Alexander, N., Stärk, K.D.C., Dulu, T.D., Sumption, K.J., James, A.D., Rushton, J., and Fine, P.E.M., 2015. Impact of Foot-and-Mouth Disease on Milk Production on A Large-scale Dairy Farm in Kenya. Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 120(2), 177–186.
Muktiani, A., 2017. Correlation Between Consumption Protein, Energy and the Moon Lactation With Cow’s Milk Production Dairy in Semarang Regency. Jurnal Litbang Provinsi Jawa Tengah, 15(2), 153–160.
Namira, N., Cahyadi, A.I., and Windria, S., 2022. Literature Review: Comparison of Subclinical Mastitis Detection Methods. Acta VETERINARIA Indonesiana, 10(1), 39–50.
Oktanella, Y., Cahyani, A.A., Hendrawan, V.F., Nugroho, W., and Agustina, G.C., 2023. Foot and Mouth Disease Impact on Milk Productivity and Quality in KUD Kertajaya, Kediri, Indonesia. Jurnal Medik Veteriner, 6(2), 244–249.
Purwadi, and Prasetyo, A.B., 2024. The Effect of Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) on Milk Production and Income of Smallholder Dairy Farmers in Boyolali. Tropical Animal Science, 6(1), 55–59.
Rabus, T., Oehm, A.W., Knubben-Schweizer, G., Hoedemaker, M., Müller, K., and Zablotski, Y., 2023. Relationship of Body Condition and Milk Parameters during Lactation in Simmental Cows in Bavaria, Germany. Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 220, 1-10.
Riyanto, J., Sunarto, S., Hertanto, B. S., Cahyadi, M., Hidayah, R., and Sejati, W., 2017. Production and Quality of Cow’s Milk Milk Mastitis sufferers who get Treatment Antibiotics. Sains Peternakan, 14(2), 30-41.
Saputra, F.T., 2018. Evaluasi Total Solid Susu Segar Peternak Tawang Argo Berdasarkan Standard Nasional Indonesia. TERNAK TROPIKA Journal of Tropical Animal Production, 19(1), 22–26.
Sarsana, I., and Merdana, I.M., 2022. Vaksinasi Penyakit Mulut dan Kuku Pada Sapi Bali di Desa Sanggalangit Kecamatan Gerokgak Kabupaten Buleleng-Bali. Jurnal Altifani Penelitian Dan Pengabdian Kepada Masyarakat, 2(5), 447–452.
Subagyo, Y., Nugroho, S., Hermawan SW, Syamsi, AN, Ifani, M., and Yusan, R.T., 2022. Total Solids and Specific Gravity of Fresh Milk in Sumbang and Baturraden Districts, Banyumas Regency. In: Opportunities and Challenges for Local Resource-Based Livestock Development to Realize Food Sovereignty. Proceedings of the National Seminar on Livestock Agribusiness Technology IX (STAP IX) 14-15 June 2022, Purwokerto: Faculty of Animal Husbandry, Universitas Jenderal Soedirman, 9: 86-93.
Subagyo, Y., Adzani, A.R., Widodo, H.S., Syamsi, A.N., Ifani, M., and Yusan, R.T., 2023. Relationship Between Total Solids and Fat, Lactose and Fresh Milk Protein in the "Pesat" Cooperative, Banyumas Regency. In: Increasing the Capacity of Livestock Resources and Local Wisdom to Face the Era of Society 5.0. Proceedings of the 10th National Seminar on Animal Husbandry Technology and Agribusiness (STAP X) 20-21 June 2023, Purwokerto: Faculty of Animal Husbandry, Universitas Jenderal Soedirman, 10: 559-566.
Suchowski, M., Eschbaumer, M., Teifke, J.P., and Ulrich, R., 2021. After Nasopharyngeal Infection, Foot and Mouth Disease Virus Serotype A RNA is Shed in Bovine Milk Without Associated Mastitis. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation, 33(5), 997–1001.
Sudarsono, R.P.E., 2022. Epidemiological Study of Suspected Occurrence of Foot and Mouth Disease in Lamongan Regency. Journal of Basic Medical Veterinary, 11(1), 56–63.
Sukoco, H., Wahyuni, S., Utami, S., Cahyani, A. P., Andanawari, S., and Siswanto, F. M., 2023. Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD): Etiology, Pathogenesis, Prevention and Control in Even or Split Hoofed Livestock. Jurnal Sain Peternakan Indonesia, 18(4), 268–273.
Sumartono, W.A.P., Hidanah, S., Sari Yudaniayanti, I., Paramita, W., Anam Al Arif, M., and Mustofa, I., 2023. Milk Production and Business Analysis on Dairy Cattle Affected by PMK In “Kampoeng Ternak” Sidoarjo Livestock: A Literature Review. SIBATIK JOURNAL: Jurnal Ilmiah Bidang Sosial, Ekonomi, Budaya, Teknologi, Dan Pendidikan, 2(5), 1473–1482.
Vergi, M., Suprayogi, T., and Sayuthi, S., 2015. Fat Content, Total Ingredients Dry and Material Dry No Fat Cow’s Milk Milk Consequences of Milking Intervals Different. Animal Agriculture Journal, 5(1), 195–199.
Copyright (c) 2024 Author(s)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions.
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA).

Journal of Applied Veterinary Science and Technology is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License