Prevalence of Camel Mange and Associated Risk Factors in The Banadir Region, Somalia

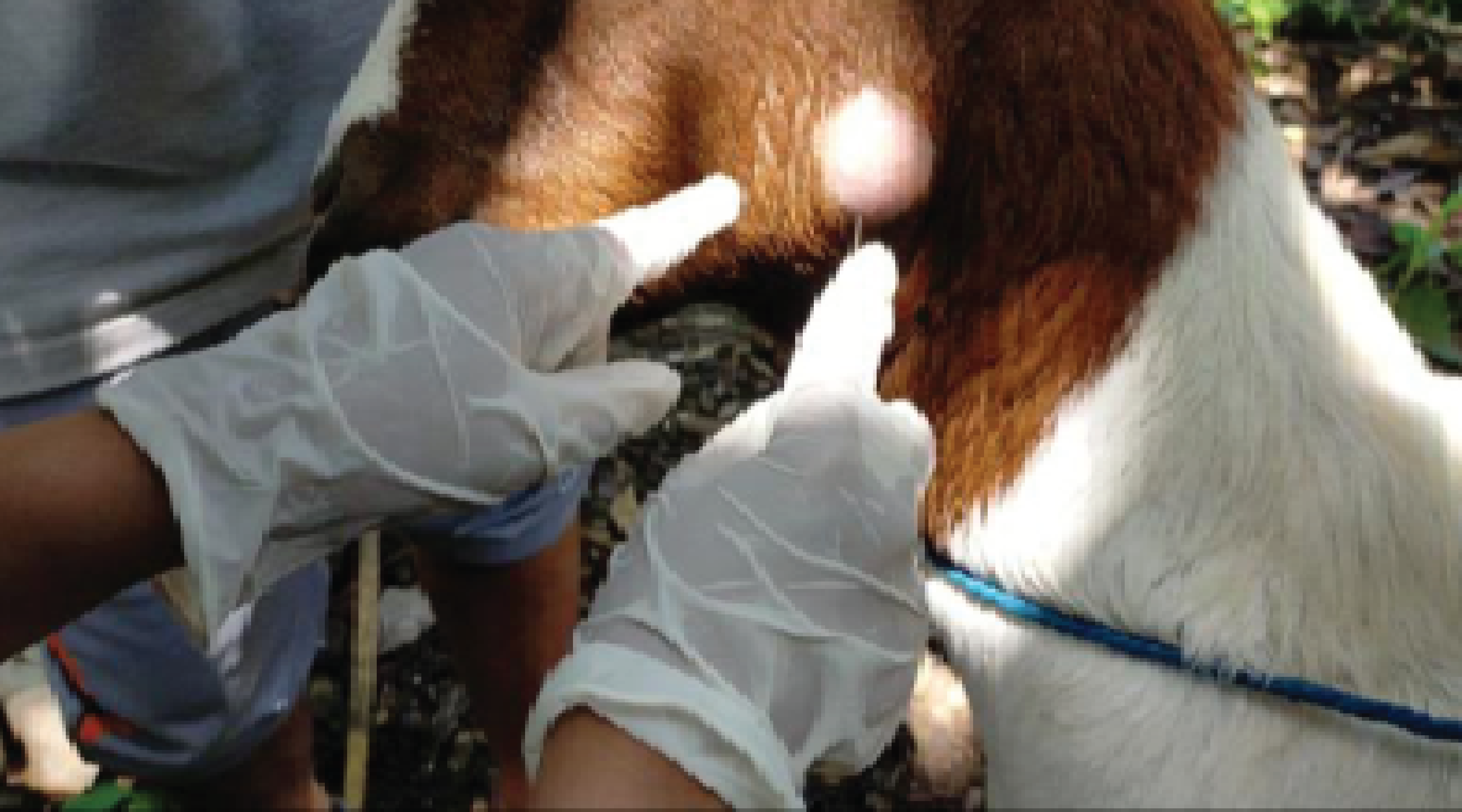
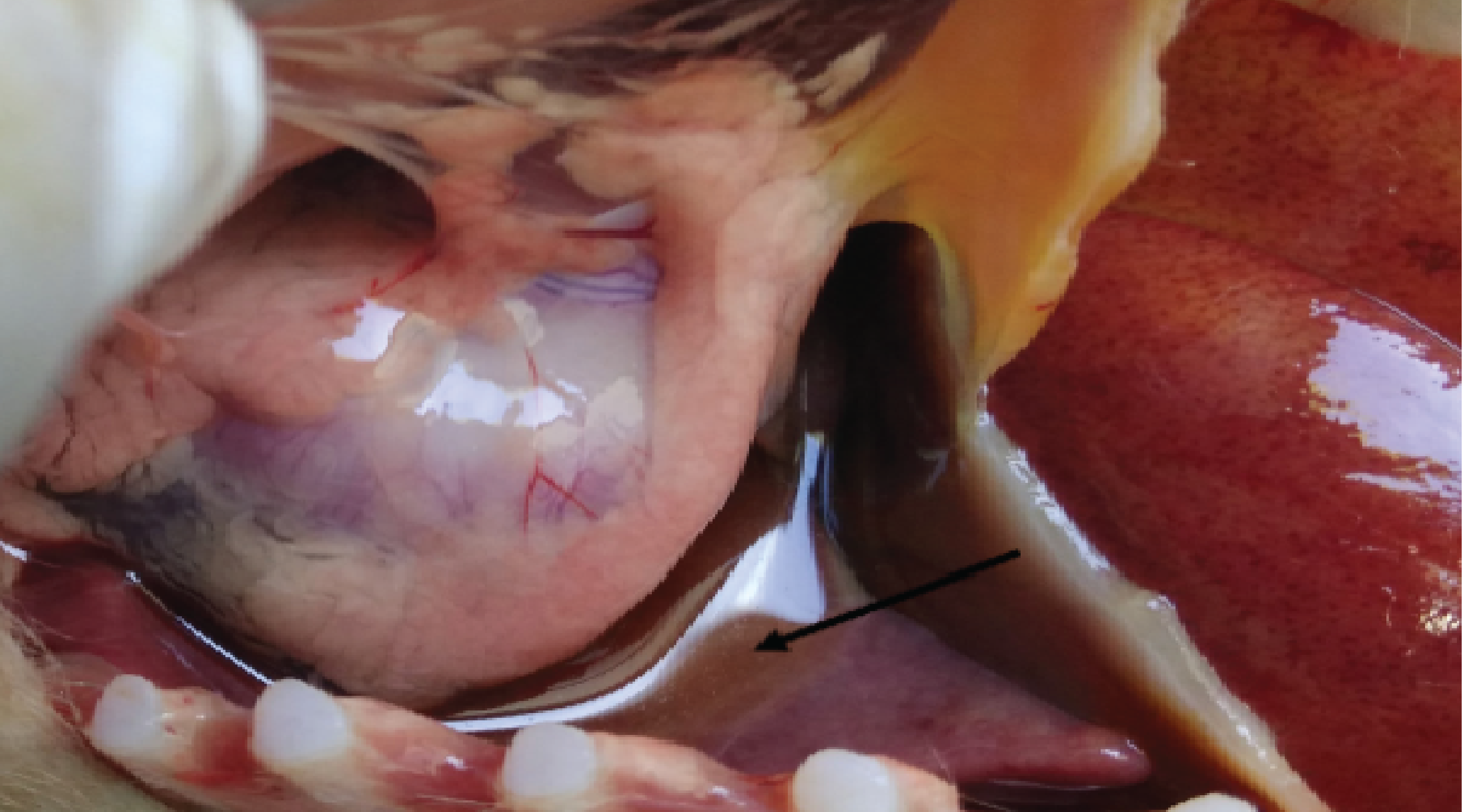
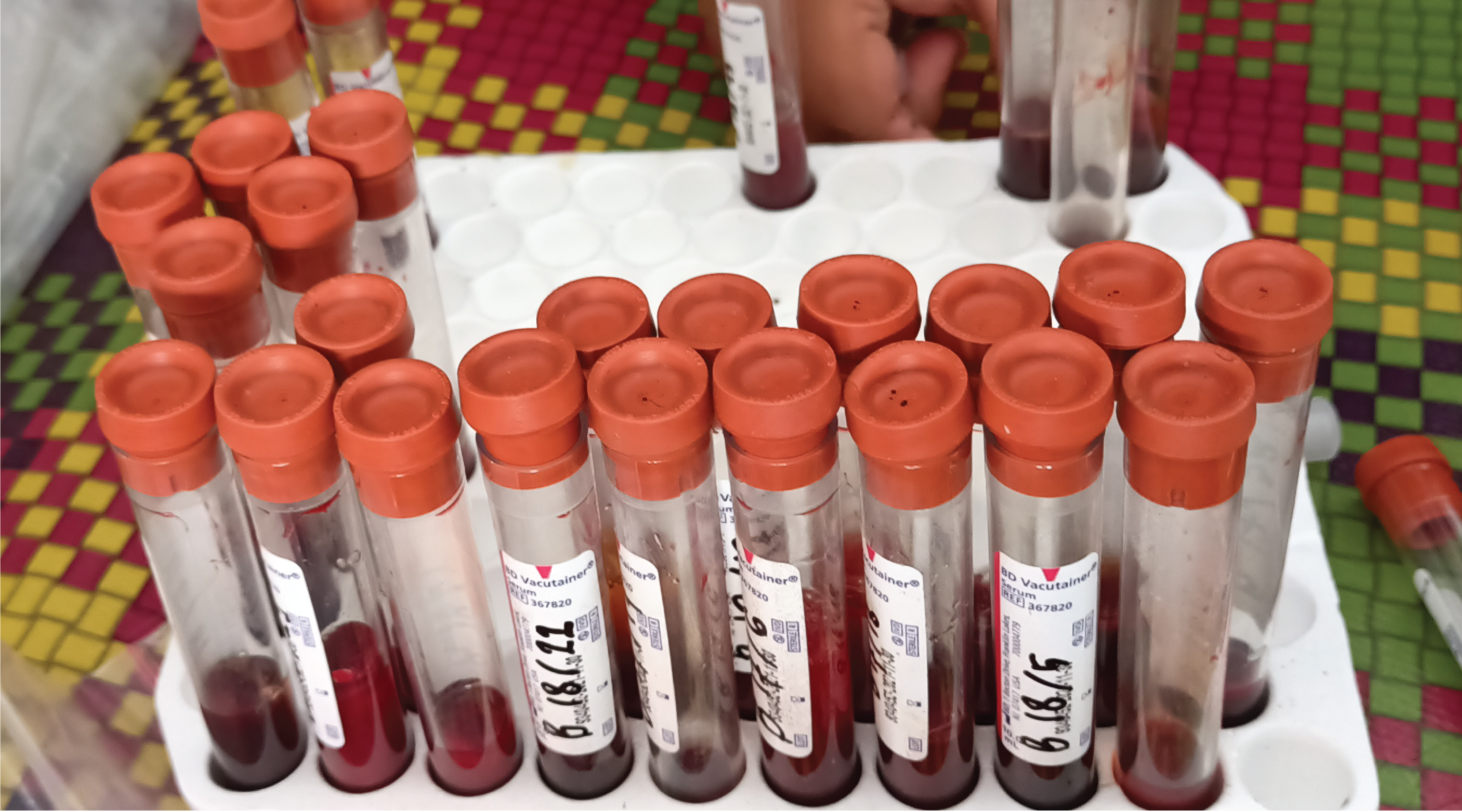
Background: Camel mange, a highly infectious and itchy condition brought on by Sarcoptes scabiei var. cameli, can be spread through direct and indirect contact. It is one of the most significant parasitic diseases affecting camels, severely impacting their productivity and health, with substantial economic consequences. Purpose: Assessing the prevalence of camel mange mites and identifying potential risk factors. Method: This cross-sectional study was carried out between June 2023 and February 2024 in the Benadir region of Somalia. A total of 384 camels were randomly selected for skin scrapings, with samples from suspected lesions being microscopically examined. Results: Of these, 82 camels (21%) were infested with mange mites, with Sarcoptes scabiei var. cameli identified as the only mite species. The research uncovered that the condition of the body, the size of the herd, and age substantially influenced the prevalence of mange mites (p<0.05), while district, sex, and age had no significant effect on infestation rate (p>0.05). Conclusion: The results suggest that mange mite infestations in the camel populations in the Benadir region negatively affect their health and productivity. Therefore, there is an urgent need to improve management practices and conduct further research and control measures to mitigate the effects of mange mite infestations on camel husbandry.
Ahmed, M., Ibrahim, M., and Mahamed, S., 2023. Study on Prevalence of One Humped Camel Mange and Its Associated Risk Factors in Selected Kebeles of Kebribeyah District of Fafan Zone, Somali Regional State, Ethiopia. Research Square, 1, 1-12.
Ahmed, M.A., Ibrahim, A.S., Bashir, B.M., and Mahamed, S.A., 2024. Prevalence of One Humped Camel Mange and Its Associated Risk Factors in Selected Kebeles of Kebri-Beyah District of Fafan Zone, Somali Regional State, Ethiopia. International Journal of Tropical Disease & Health, 45(1), 40-47.
Al-Owaimer, A.N., Suliman, G.M., Sami, A.S., Picard, B., and Hocquette, J.F., 2014. Chemical Composition and Structural Characteristics of Arabian camel (Camelus dromedarius) m. Longissimus Thoracis. Meat Science, 96(3), 1233-1241.
Ame, M.K.M., Mohamed, K., Usman, M., and Aliyi, A., 2023. Assessment of Camel Mange Mite Prevalence in Kumbi Woreda, Eastern Harergae, Ethiopia. Pesticide Science, 2(1), 1-12.
Ashraf, S., Chaudhry, H.R., Chaudhry, M., Iqbal, Z., Ali, M., Jamil, T., Sial, N., Shahzad, M.I., Basheer, F., Akhter, S., Ur Rehman, S.H., and Yasin, A., 2014. Prevalence of Common Diseases in Camels of Cholistan Desert, Pakistan. Journal of Infection and Molecular Biology, 2(4), 49-52.
Awol, N., Kiros, S., Tsegaye, Y., Ali, M., and Hadush, B., 2014. Study on Mange Mite of Camel In Raya-Azebo District, Northern Ethiopia. Veterinary Research Forum, 5(1), 61-64.
Dinka, A., Eyerusalem, B., and Yacob, H.T., 2010. A Study On Major Ectoparasites of Camel In and Around Dire Dawa, Eastern Ethiopia. Revue de Médecine Vétérinaire, 161(11), 498-501.
Elias, M., Yacob, H., and Jio, K., 2020. Prevalence, Risk Factors and Species Diversity of Ixodid Ticks that Parasitize Dromedary Camel in Yabello District of Borana Zone, Southern Ethiopia. Journal of Parasitology and Vector Biology, 12(2), 52-59.
Farah, K., Nyariki, D.M., Ngugi, R.K., Noor, I.M., and Giluye, A.Y., 2004. The Somali and the Camel: Ecology, management and economics. The Anthropologist, 6(1), 45-55.
Feyera, T., Admasu, P., Abdilahi, Z., and Mummed, B., 2015. Epidemiological and Therapeutic Studies of Camel Mange in Fafan zone, Eastern Ethiopia. Parasites & Vectors, 8(1), 1-6.
Feyera, T., Kebeta, M.M., Maalin, K., and Gizaw, Y., 2017. Major ectoparasites Infesting Camelus dromedarius in Three Districts of Somali Regional State, Eastern Ethiopia. World Applied Sciences Journal, 35(1), 96-103.
Frumkin, M., 2019. Camel Leasing: Impacting Somali Lives. https://agrilinks.org/post/camel-leasing-impacting-somali-lives . Accessed: 5 July 2024.
Giro, A., and Jilo, K., 2020. Prevalence of Camel Trypanosomosis and Associated Risk Factors in Arero district, Borena Zone, Southern Ethiopia. International Journal of Veterinary Science and Research, 6(1), 14-22.
Jarso, D., Birhanu, S., Wubishet, Z., 2018. Review on Epidemiology of Camel Mange Mites. Biomedical Journal of Scientific & Technical Research, 8(1), 6313-6316.
Jilo, K., 2016. Medicinal Values Of Camel Milk. International Journal of Veterinary Science and Research, 2(1), 18-25.
Lawal, M. D., Ameh, I.G., and Ahmed, A., 2007. Some Ectoparasites of Camelus dromedarius in Sokoto, Nigeria. Journal of Entomology, 4(2), 143-148.
Lioyd, S., 1983. Effect of Pregnancy and Lactation Up on Infection. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology, 4(2), 153-176.
Madalcho, A. B., Tadesse, B.A., Gebeyew, K., and Gebresilassie, G., 2019. Camel Feed Characterization Of Ethiopian Somali Region Rangelands Through Traditional Knowledge. Journal of Agriculture and Ecology Research International, 19(3), 1-15.
Megersa, B., Demena, A., Bekele, A., and Sgeferaw, D., 2012. Ticks and Mange Mites Infesting Camels of Boran Pastoral Areas and The Associated Risk Factors, Southern Ethiopia. Journal of Veterinary Medicine and Animal Health, 4(5), 71-77.
Mume, J.A., 2020. Study on The Prevalence of Camel Mange Mite in Kumbi Woreda, Eastern Harergae, Ethiopia. [Thesis]. Jimma University. Ethiopia
Prior, J., 1994. Pastoral Development Planning. Oxam Library, 12-54.
Rabana, J.L., Kumshe, H.A., Kamani, J., Hafsat, G., Turaki, U.A., and Dilli, H.K., 2011. Effects of Parasitic Infections on Erythrocyte Indices of Camels in Nigeria. Veterinary Research Forum, 2(1), 59-63.
Schwartz, H.J., and Dioli, M., 1992. The One-Humped Camel In Eastern Africa. A Pictorial Guide To Diseases, Health Care And Management. Berlin: Verlag Joseph Margraf.
Teshome, Y., Jilo, K., Kararsa, N., Zegeye, Z., Guyo, Z., and Duba, T., 2021. Prevalence of Camel Mange Mite and Associated Risk Factors in Gomole district, Borana zone, Southern Ethiopia. Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 9(4), 88-92.
Wosene, A., 1991. Traditional Husbandry Practices and Major Health Problems of Camels in The Ogaden (Ethiopia). Nomadic Peoples, 29, 21-30.
Yifat, D., Menna, Y., and Sheferaw, D., 2013. Mange Mite Infestation of Small Ruminants and Associated Factors, School of Veterinary Medicine, Hawassa Ethiopia. World Journal of Zoology, 8(3), 299-302.
Zahid, M., Maqbool, A., Anjum, S., and Ashraf, K., 2015. Prevalence of Sarcoptic Mange in Camels in Punjab, Pakistan. The Journal Of Animal and Plant Sciences, 25(5), 1259-1263.
Copyright (c) 2024 Author(s)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions.
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA).

Journal of Applied Veterinary Science and Technology is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License