Prevalence of Gastrointestinal Nematodes in Silvery Mole-Rats in Morogoro Region, Tanzania
Downloads
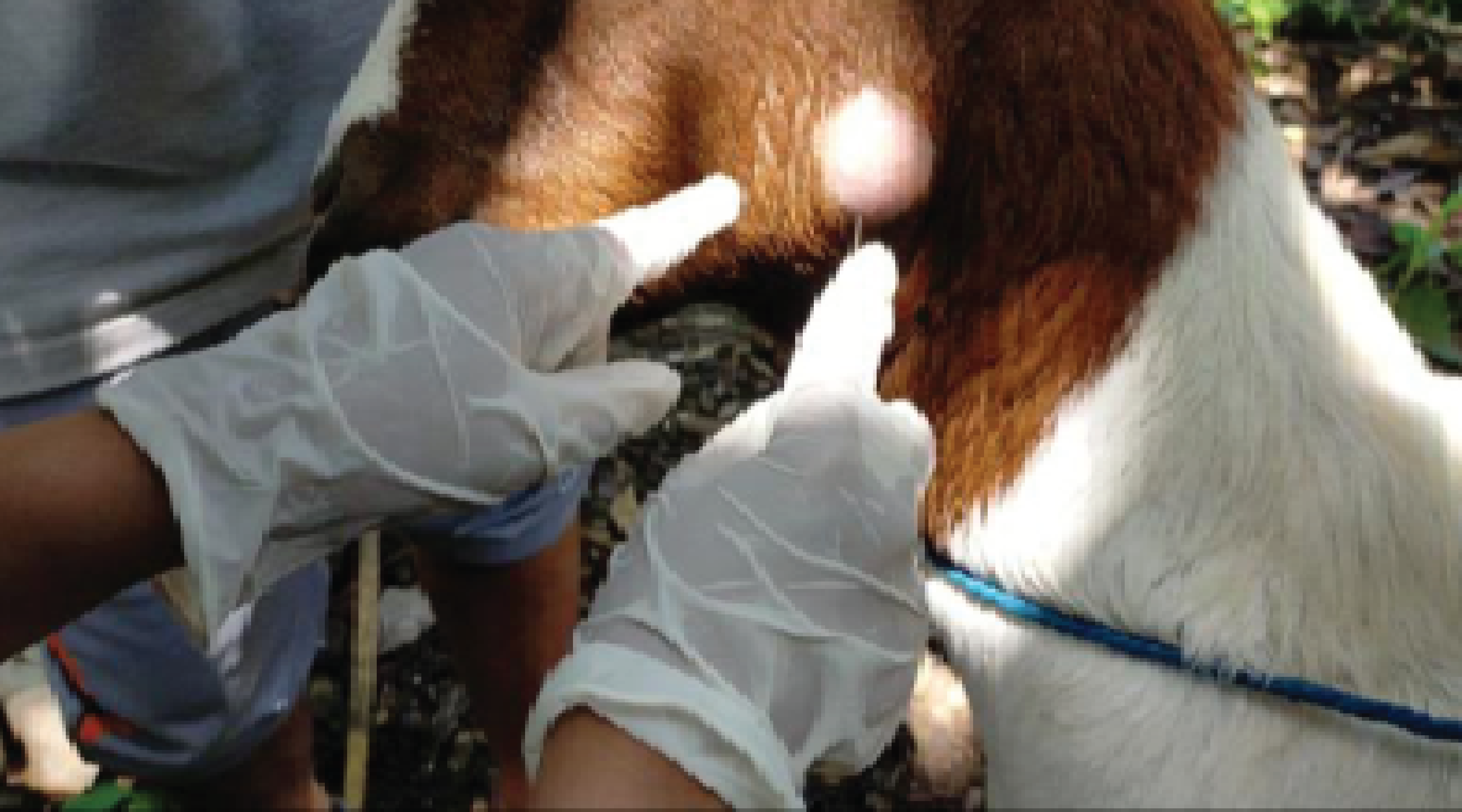
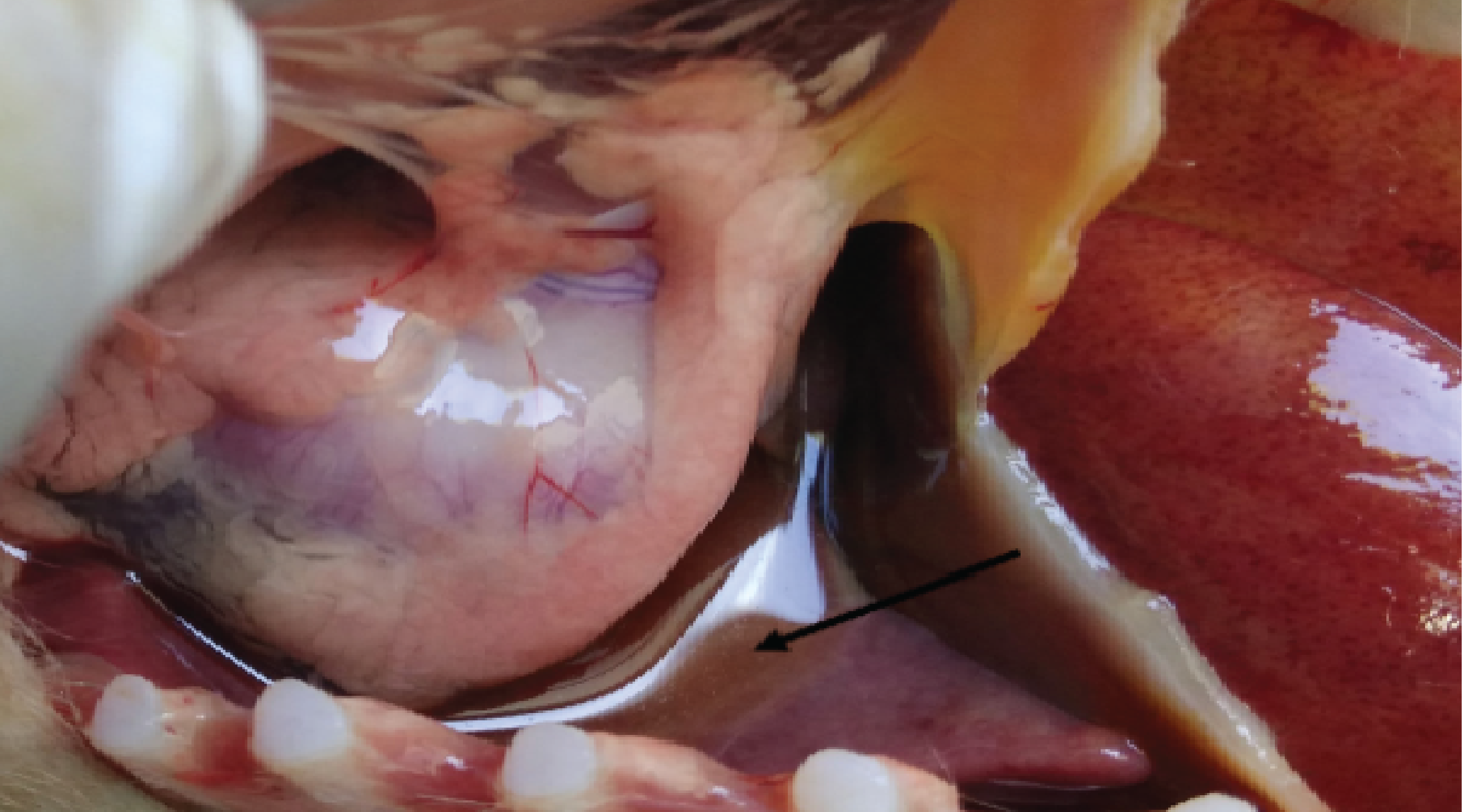
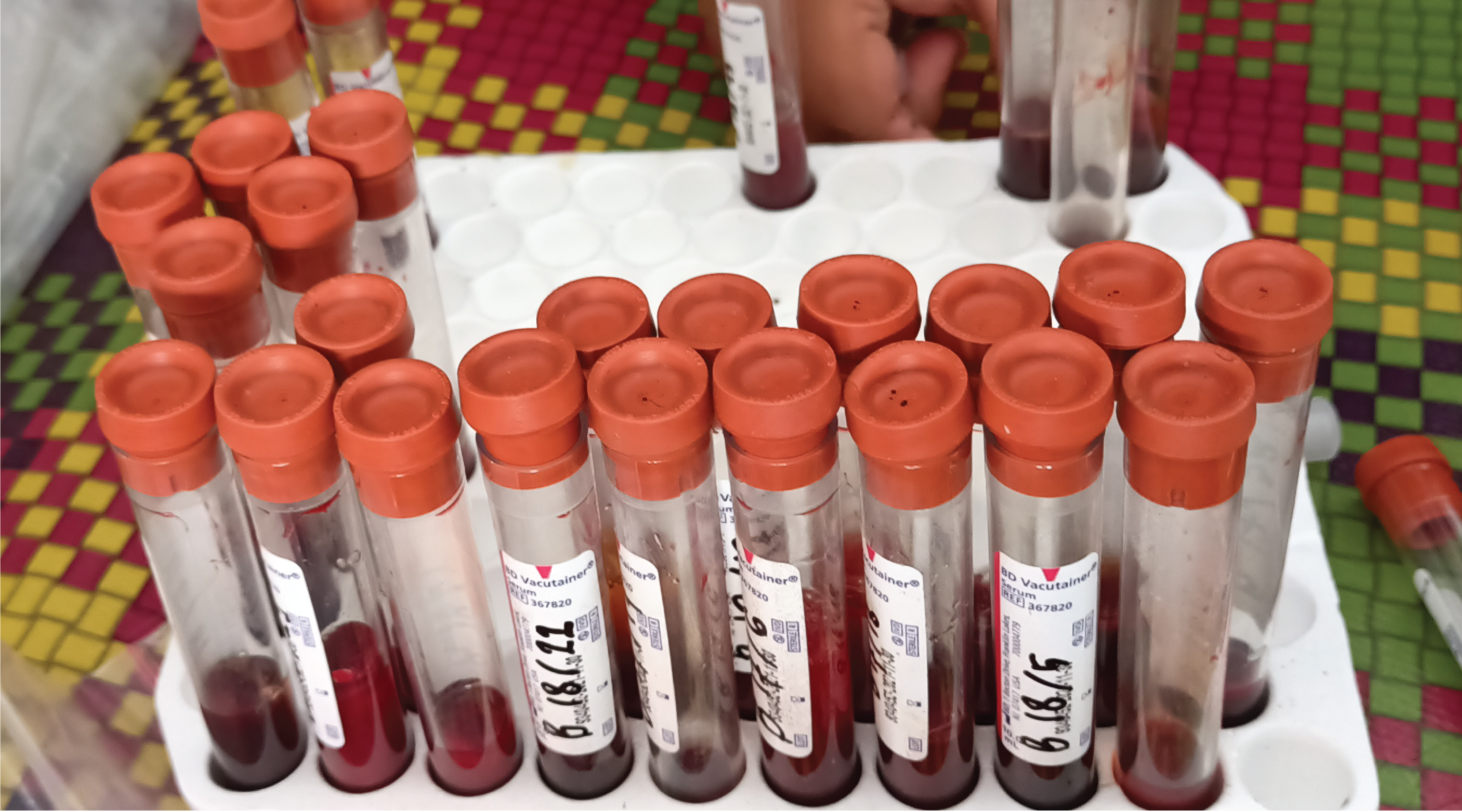
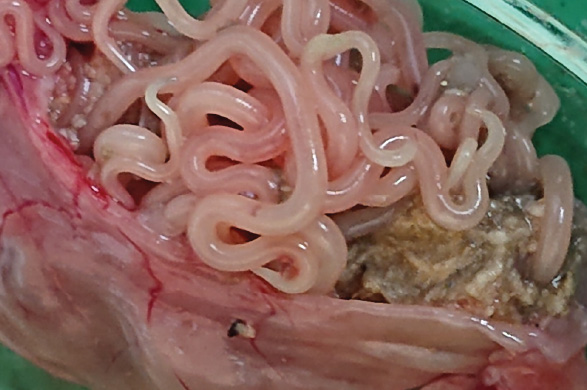
Background: Exploring the nematode diversity in silvery mole rats opens up a fascinating avenue for understanding the intricate relationships between underground-dwelling mammals and their parasites. It is intriguing to consider the potential transmission of parasitic zoonotic between humans, livestock, and silvery mole rats due to the notable interactions of these animals. Purpose: This study aims to acquire crucial information about the nematode fauna in silvery mole rats in the Morogoro region, Tanzania. Method: A survey of nematode parasites in silvery mole rats was conducted in the Morogoro region, from March to June 2023. Collected rats were euthanized using Diethyl Ether, and dissected to remove the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). Adult worms were collected and preserved in 70% ethanol. A flotation method and lactophenol mounting techniques were employed to process gastrointestinal contents and adult roundworms. The prevalence of nematodes was computed, and a chi-square test was applied to assess the relationship, a p-value< 0.05 was considered significant. Results: The examination of the gastrointestinal tract contents revealed two nematode taxa; Physaloptera spp and Strongyloides spp. The overall prevalence of nematode infection was 38.69% (53/137), with Physaloptera species being the most prevalent (37.22%). Adult rats had a lower infection risk than sub-adult rats. Female silvery mole rats were at higher risk of being infected compared to males. Conclusion: The study established two nematodes in silvery mole rats of Morogoro region, Tanzania, which are Physaloptera spp and Strongyloides spp.
Adelman, J.S., 2010. Immune Systems and Sickness Behavior. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Animal Care and Use Committee., 1998. Guidelines for The Capture, Handling, and Care of Mammals As Approved By The American Society of Mammalogists. Journal of Mammalogy, 79(4), 1416–1431.
Archer, E.K., Bennett, N.C., Junker, K., Faulkes, C.G., and Lutermann, H., 2017. The Distribution of Gastrointestinal Parasites in Two Populations of Common Mole-Rats (Cryptomys hottentotus hottentotus). Journal of Parasitology, 103(6), 786–790.
Barelli, C., Pafčo, B., Manica, M., Rovero, F., Rosà, R., Modrý, D., and Hauffe, H.C., 2020. Loss of Protozoan and Metazoan Intestinal Symbiont Biodiversity In Wild Primates Living In Unprotected Forests.. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–12.
Bartel, M.H. and Gardner, S.L., 2000. Arthropod and helminth parasites from the Plains Pocket Gopher, Geomys bursarius bursarius from The Hosts’ Northern Boundary Range in Minnesota. Journal of Parasitology, 86(1), 153–156.
Baruš, V., Tenora, F., and Šumbera, R., 2003. Relative concentration of Four Heavy Metals in The Parasites Protospirura muricola (Nemtaoda) and Inermicapsifer arvicanthidis (Cestoda) in Their Definitive Host Silvery Mole-Rat (Heliophobius argenteocinereus: Rodentia). Helminthologia, 40(4), 227–232.
Ben-Batalla, I., Vargas-Delgado, M.E., von Amsberg, G., Janning, M., and Loges, S., 2020. Influence of Androgens on Immunity to Self and Foreign: Effects on Immunity and Cancer. Frontiers in Immunology, 11(1), 1–20.
Bennett, N. and Faulkes, C., 2000. African Mole-Rats: Ecology and Eusociality. Cambridge University Press.
Burda, H., 2001. Determinants of the Distribution and Radiation of African Mole-Rats (Bathyergidae, Rodentia) Ecology or geography?. 254-277.
Castillo, G.N., Acosta, J.C., Rivas, C.J.G.-, and Ramallo, G., 2020. Parasitic Nematodes of Reptiles (Lizards and Snakes) in The Monte Desert of Argentina. Acta Zoologica Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae, 66(4), 319–327.
Catalano, S., Symeou, A., Marsh, K.J., Borlase, A., Léger, E., Fall, C.B., Sène, M., Diouf, N.D., Ianniello, D., Cringoli, G., Rinaldi, L., Bâ, K., and Webster, J.P., 2019. Mini-FLOTAC as An Alternative, Non-Invasive Diagnostic Tool for Schistosoma Mansoni and Other Trematode Infections In Wildlife Reservoirs. Parasites and Vectors, 12(1), 1–9.
Dryden, M., Payne, P., Ridley, R., and Smith, V., 2005. Comparison of Common Fecal Flotation Techniques for the Recovery of Parasite Eggs and Oocysts. Spring, 6(1), 15–28.
Dursahinhan, A.T., Kenkel, D.A., and Gardner, S.L., 2023. Helminth and Protozoan Parasites of Subterranean Rodents (Chordata, Mammalia, Rodentia) of The World. ZooKeys, 1151, 159–203.
Esrony, K., Kambarage, D.M., Mtambo, M.M.A., Muhairwa, A.P., and Kusiluka, L.J.M., 1997. Helminthosis in local and cross-bred pigs in the Morogoro region of Tanzania. Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 32(1–2), 41–46.
Fagir, D.M., Bennett, N.C., Ueckermann, E.A., Howard, A., and Hart, D.W., 2021. Ectoparasitic Community of the Mahali Mole-Rat, Cryptomys hottentotus mahali: Potential Host for Vectors of Medical Importance in South Africa. Parasites and Vectors, 14(24), 2-9.
Faulkes, C.G., Bennett, N.C., Cotterill, F.P.D., Stanley, W., Mgode, G.F., and Verheyen, E., 2011. Phylogeography and Cryptic Diversity of The Solitary-Dwelling Silvery Mole-Rat, Genus Heliophobius (family: Bathyergidae). Journal of Zoology, 285(4), 324–338.
Fisher, M.C. and Viney, M.E., 1998. The Population Genetic Structure of The Facultatively Sexual Parasitic Nematode Strongyloides Ratti In Wild Rats. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 265(1397), 703–709.
Greives, T.J., McGlothlin, J.W., Jawor, J.M., Demas, G.E., and Ketterson, E.D., 2006. Testosterone and iInnate Immune Function Inversely Covary In A Wild Population of Breeding Dark-Eyed Juncos (Junco hyemalis). Functional Ecology, 20(5), 812–818.
Hart, L., O’Riain, M.J., Jarvis, J.U.M., and Bennett, N.C., 2006. Is the Cape dune Mole-Rat, Bathyergus suillus (Rodentia: Bathyergidae), A Seasonal or Aseasonal Breeder?. Journal of Mammalogy, 87(6), 1078–1085.
Hodder, S.A.M. and Chapman, C.A., 2012. Do Nematode Infections of Red Colobus (Procolobus rufomitratus) and Black-and-White Colobus (Colobus guereza) on Humanized Forest Edges Differ from Those on Nonhumanized Forest Edges?. International Journal of Primatology, 33(4), 845–859.
Horáková, S., Šumbera, R., Sovová, J., and Robovský, J., 2019. The Penial and Bacular Morphology Of The Solitary Silvery Mole-Rat (Heliophobius Argenteocinereus, Bathyergidae) From Malawi and Evolutionary Patterns Across The African Mole-Rat Family. Mammalian Biology, 99, 54–62.
Jarvis, J.U.M., O’Riain, M.J., Bennett, N.C., and Sherman, P.W., 1994. Mammalian Eusociality: A Family Affair. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 9(2), 47–51.
Junker, K., Lutermann, H., and Mutafchiev, Y., 2017. A New Ascaridid Nematode, Mammalakis zambiensis n. sp. (Heterakoidea: Kiwinematidae), From The Mole Rat Fukomys anselli (Burda, Zima, Scharff, Macholán & Kawalika)(Rodentia: Bathyergidae) in Zambia. Systematic Parasitology, 94(5), 557–566.
Katandukila, J. V., Chimimba, C.T., Bennett, N.C., Makundi, R.H., Le Comber, S.C., and Faulkes, C.G., 2014. Sweeping the House Clean: Burrow Architecture and Seasonal Digging Activity in The East African Root Rat from Tanzania. Journal of Zoology, 293(4), 271–280.
Keyyu, J.D., Kassuku, A.A., Msalilwa, L.P., Monrad, J., and Kyvsgaard, N.C., 2006. Cross-Sectional Prevalence of Helminth Infections In Cattle on Traditional, Small-Scale and Large-Scale Dairy Farms In Iringa District, Tanzania. Veterinary Research Communications, 30(1), 45–55.
Klein, S.L., 2000. The effects of hormones on sex differences in infection: From genes to behavior. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 24(6), 627–638.
Lutermann, H., 2022. Socializing in an Infectious World: The Role of Parasites in Social Evolution of a Unique Rodent Family. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 10 (May), 1–22.
Lutermann, H. and Bennett, N.C., 2012. Determinants of Helminth Infection in a Subterranean Rodent, the Cape Dune Determinants of Helminth Infection in a Subterranean Rodent, the Cape Dune Mole-Rat. Journal of Parasitology, 98(3), 686–689.
Lutermann, H., Bennett, N.C., Speakman, J.R., and Scantlebury, M., 2013. Energetic Benefits of Sociality Offset the Costs of Parasitism in a Cooperative Mammal. PLoS ONE, 8(2), 1–8.
Lutermann, H., Butler, K.B., and Bennett, N.C., 2022. Parasite-Mediated Mate Preferences in a Cooperatively Breeding Rodent. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 10(1), 1–10.
Lutermann, H., Haukisalmi, V., Junker, K., and Journal, S., 2018. First Report of Gastrointestinal Parasites from Ansell’s Mole-Rat (Fukomys anselli) in Zambia First Report of Gastrointestinal Parasites from Ansell’s Mole-Rat (Fukomys anselli). Journal of Parasitology, 104(5), 566–570.
Manz, K.M., Clowes, P., Kroidl, I., Kowuor, D.O., Geldmacher, C., Ntinginya, N.E., Maboko, L., Hoelscher, M., and Saathoff, E., 2017. Trichuris trichiura Infection and Its Relation to Environmental Factors in Mbeya Region, Tanzania: A cross-sectional, population- based study. PLoS ONE, 12(4), 1–16.
Modrý, A.D., Jirk, M., and Šumbera, R., 2005. Three New Species of Eimeria (apicomplexa: eimeriidae) From the Silvery Mole-Rat (Heliophobius argenteocinereus Peters 1846) (rodentia: bathyergidae) from Malawi. Journal of Parasitology, 1846(5), 1200–1203.
MRP, 2022. Morogoro Region Social-Economic Profile, 2020. Morogoro Region Social-Economic Profile, 2020.
Nzalawahe, J., Kassuku, A.A., Stothard, J.R., Coles, G.C., and Eisler, M.C., 2015. Associations Between Trematode Infections in Cattle and Freshwater Snails in Highland and Lowland Areas of Iringa Rural District, Tanzania. Parasitology, 142(11), 1430–1439.
Ortlepp, R.J., 1937. Some Undescribed Species of The Nematode Genus Physaloptera Rud., Together With a Key to The Sufficiently Known Forms. Science and Animal Industry, 9(1).
Rossin, A. and Malizia, A.I., 2002. Relationship Between Helminth Parasites and Demographic Attributes of a Population of the Subterranean Rodent Ctenomys talarum (Rodentia: Octodontidae). Journal of Parasitology, 88(6), 1268–1270.
Rossin, M.A., 2010. Zoootaxa, An Endemic Taenia from South America: validation of T. talicei Dollfus, 1960. Zootaxa, 58, 49–58.
Rossin, M.A., Malizia, A.I., Timi, J.T., and Poulin, R., 2010. Parasitism Underground: Determinants of Helminth Infections in Two Species of Subterranean Rodents (Octodontidae). Parasitology, 137(10), 1569–1575.
Rossin, M.A., Varela, G., and Timi, J.T., 2009. Strongyloides myopotami in Ctenomyid Rodents: Transition from Semi-Aquatic to Subterranean Life cycle. Acta Parasitologica, 54(3), 257–262.
Scharff, A., Burda, H., Tenora, F., Kawalika, M., and Barus, V., 1997. Parasites in Social Subterranean Zambian Mole-Rats (Cryptomys spp., Bathyergidae, Rodentia). Journal of Zoology, 241(3), 571–577.
Soulsby, E.J.L., 1982. Helminths, Arthropods and Protozoa of Domesticated Animals. 7th ed. Baillière Tindall, London, 1982, 329.
Sumbera, R., Burda, H., and Chitaukali, W.N., 2003. Reproductive Biology of a Solitary Subterranean Bathyergid Rodent, the Silvery Mole-Rat (Heliophobius argenteocinereus). Journal of Mammalogy, 84(1), 278–287.
Šumbera, R., Chitaukali, W.N., and Burda, H., 2007. Why Study a Neglected Subterranean Rodent Species? In:Begall, S., Burda, H, and Schleich, C.E. (Eds.), Subterranean Rodents: News from Underground, pp. 221–236. Springer.
Taylor, M.A., Coop, R.L., and Wall, R.L., 2016. Veterinary Parasitology. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Tenora, F., Baruš, V., M.P., Šumbera, R., and Koubková, B., 2003. Helminths Parasitizing the Silvery Mole-Rat (Heliophobius argenteocinereus) from Malawi. Helminthologia, 40(3), 227–232.
Viljoen, H., Bennett, N.C., Ueckermann, E.A., and Lutermann, H., 2011. The Role of Host Traits, Season and Group Size on Parasite Burdens in a Cooperative Mammal. PLoS ONE, 6(11), e27003.
Wells, K., Smales, L.R., Kalko, E.K.V., and Pfeiffer, M., 2007. Impact of Rain-Forest Logging on Helminth Assemblages in Small Mammals (Muridae, Tupaiidae) from Borneo. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 23(1), 35–43.
Zajac, A.M., Conboy, G.A., Little, S.E., and Reichard, M.V., 2012. Veterinary Clinical Parasitology. Wiley-Blackwell, 3-368.
Copyright (c) 2025 Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions.
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA).

Journal of Applied Veterinary Science and Technology is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License