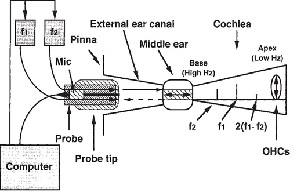
NEWBORNS HEARING SCREENING WITH OTOACOUSTIC EMISSIONS AND AUDITORY BRAINSTEM RESPONSE
Downloads
Hearing loss in newborns is a serious matter, if it is not quickly diagnosed and starts early intervention, a child will experience social, speech, language, cognitive, and academic impairments. There is a method of hearing screening in newborns, which is divided into two types, universal newborn hearing screening, and targeted newborn screening. Both of these methods use OAEs and ABR as objective examination tools. The hearing screening method varies in each country, this difference is based on the test equipment used, age, frequency, professionals involved in screening, referral procedures, funding, and coverage areas. Indonesia uses two stages of screening, while Italy, America, Nigeria, France, India, and Poland use two to five stages of screening. Hearing screening of newborns using OAEs and ABR has a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 99,3%.
Oe B, Ee O, Ediale J. Review article newborn and pre-school hearing screening legislation in Nigeria; Concept, Issues And Suggestions 2018; 3(1): 1–6.
De Kock T, Swanepoel DW, Hall JW. Newborn hearing screening at a community-based obstetric unit: Screening and diagnostic outcomes. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2016;84:124–31.
Olusanya B. Screening for neonatal deafness in resource-poor countries: challenges and solutions. Research and Reports in Neonatology 2015;5:51-64.
Appelbaum EN, Howell JB, Chapman D, Pandya A, Dodson KM. Analysis of risk factors associated with unilateral hearing loss in children who initially passed newborn hearing screening. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2018;106:100–4.
Purnami N, Dipta C, Rahman MA. Characteristics of infants and young children with sensorineural hearing loss in Dr. Soetomo Hospital. ORLI 2018;48(1):11.
Kanji A, Khoza-Shangase K, Moroe N. Newborn hearing screening protocols and their outcomes: A systematic review. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2018;115:104–9.
Suwento R, Semiramis Z, Airlangga T, Suardana W, Anggraeni R, Purnami N, et al. Skrining pendengaran pada bayi baru lahir. Jakarta: Kementrian Kesehatan RI; 2010.p. 5–36.
Kumar A, Gupta SC, Sinha VR. Universal hearing screening in newborns using otoacoustic emissions and brainstem evoked response in eastern uttar pradesh. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2017; 69(3):296–9.
Cianfrone F, Mammarella F, Ralli M, Evetovic V, Pianura CM, Bellocchi G. Universal newborn hearing screening using A-TEOAE and A-ABR: The experience of a large public hospital. J Neonatal Perinatal Med 2018;11(1): 87–92.
Turchetta R, Conti G, Marsella P, Orlando MP, Picciotti PM, Frezza S, et al. Universal newborn hearing screening in the Lazio region, Italy. Ital J Pediatr 2018;44(1):104.
Charaziak KK, Shera CA. Compensating for ear-canal acoustics when measuring otoacoustic emissions. J Acoust Soc Am 2017;141(1):515–31.
Akinpelu O V, Peleva E, Funnell WRJ, Daniel SJ. Otoacoustic emissions in newborn hearing screening: A systematic review of the effects of different protocols on test outcomes. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2014;78(5):711–7.
Szyfter W, DÄ…browski P, Greczka G, Wróbel M. The report of the realization of the universal neonatal hearing screening program in poland between 2003 and 2015. Otolaryngol Pol 2016;70(2):1–5.
James W HH, Patrick J A. Assessment of peripheral and central auditory function. In: Jonas T J, Clark A R, eds. Bailey's head & neck surgery otolaryngology Vol 2. 15th ed. Philadelphia: Lappincot williams & wilkins; 2014. p. 2274–82.
Petersen L, Wilson WJ, Kathard H. A systematic review of stimulus parameters for eliciting distortion product otoacoustic emissions from adult humans. Int J Audiol 2017;56(6):382–91.
Ngui LX, Tang IP, Prepageran N, Lai ZW. Comparison of distortion product otoacoustic emission (DPOAE) and automated auditory brainstem response (AABR) for neonatal hearing screening in a hospital with high delivery rate. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2019; 120:184–8.
Abdala C, Ortmann AJ, Shera CA. Reflection- and distortion-Source otoacoustic emissions: Evidence for increased irregularity in the human cochlea during aging. JARO - J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 2018; 19(5):493–510.
Kileny RP, Zwolan AT. Diagnostic audiology. In: Flint WP, Haughey HB, Lund JV, Niparko KJ, Robbins TK, Thomas RJ, et al. Cummings Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Vol 2. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders elsevier; 2015.p.2051-70.
Sabbag JC, Lacerda A. Rastreamento e monitoramento da triagem auditiva neonatal em unidade de estratégia de saúde da família: estudo-piloto. CoDAS 2017;29(4):1–7.
Zimatore G, Hatzopoulos S, Giuliani A, Martini A, Colosimo A. Comparison of transient otoacoustic emission responses from neonatal and adult ears. J Appl Physiol 2002;92(6):2521–8.
Syamsuddin A, Dewi YA. Gelombang auditory brainstem response (ABR) pada anak di bawah lima tahun. Majalah Kedokteran Bandung 2014; 46(38): 183–8.
Unlu I, Guclu E, Yaman H. When should automatic auditory brainstem response test be used for newborn hearing screening? Auris Nasus Larynx 2015;42(3):199–202.
Lee JW, Bance ML. Hearing loss. Pract Neurol 2019;19(1):28–35.
Yang HC, Sung CM, Shin DJ, Cho YB, Jang CH, Cho HH. Newborn hearing screening in prematurity: fate of screening failures and auditory maturation. Clin Otolaryngol 2017;42(3):661–7.
Bouillot L, Vercherat M, Durand C. Implementing universal newborn hearing screening in the French Rhí´ne-Alpes region. State of affairs in 2016 and the 1st half of 2017. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2019;117:30–6.
Copyright (c) 2020 Kusumagani Hamam, Nyilo Purnami

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions.
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA).
- The Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA) license allows re-distribution and re-use of a licensed work on the conditions that the creator is appropriately credited and that any derivative work is made available under "the same, similar or a compatible license”. Other than the conditions mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation.