Smoking, Physical Activity, and Hypertension Incidence Among Older Adults in Malang, Indonesia

Downloads
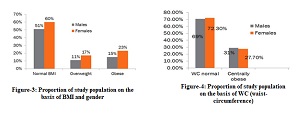
Hypertension is a crucial health concern that requires attention, and it can be influenced by factors such as smoking and physical activity. According to a study conducted at Lawang Health Center, Malang, Indonesia, in 2020, 13.5% of the population in RW 05, Bedali Village, Malang, suffered from hypertension. It was one of the top three prevalent diseases in the village, especially among individuals aged over 69 years. The objective of this research was to examine the relationship between smoking, physical activity, and the occurrence of hypertension among older adults in RW 05, Bedali Village, Lawang, Malang. The study employed a case-control analytic observational method, involving 25 cases and 25 controls within the older adult age group (>45 years). The participants consisted of 50 individuals, including 23 men and 27 women. Among the respondents, 23 were smokers, while 27 were non-smokers. Additionally, 25 respondents engaged in light physical activity, whereas 25 respondents had moderate to vigorous physical activity levels. The analysis indicated a significant correlation between smoking, physical activity, and the prevalence of hypertension among older adults in RW 05, Bedali Village, Lawang, Malang, with a p-value of 0.005 for each factor.
Copyright (c) 2023 Maimanah Zumaro Ummi Faiqoh, Ardiar Rahmananda Laksnadi, Safira Shafa Rachmah Hartawan, Felisita Maritza Abidanovanty, Ikhsanuddin Qoth'i, Karindra Amadea Susetiyo, Anastasia Pearl Angeli, Samsriyaningsih Handayani, Heri Sugeng Widodo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions.
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA).
- The Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA) license allows re-distribution and re-use of a licensed work on the conditions that the creator is appropriately credited and that any derivative work is made available under "the same, similar or a compatible license”. Other than the conditions mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation.