Drinking Water Quality As A Risk Factor of Stunting : A Systematic Review
Downloads
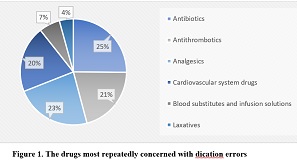
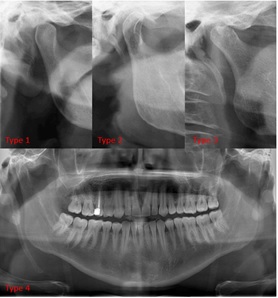
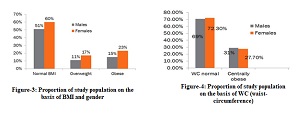
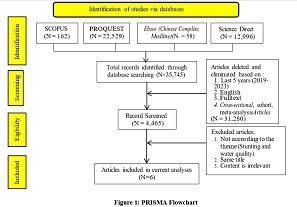
Stunting is a nutritional problem that needs attention because of its risk to future generations. The causes of stunting are related to environmental factors such as sanitation and drinking water quality. Intervention efforts are carried out to improve sanitation and drinking water quality, which is regarded as a risk factor. This article reviewed literature relevant to the topic from Science Direct, Scopus, EBSCO (CINAHL, MEDLINE), and Proquest databases from 2020-2024 publications with the keywords Water Quality and Stunting, then analyzed using a synthesis matrix. The inclusion criteria for this study were articles in English with a correlational design and full text. The results of the journal review found six articles that stated that sanitation factors, especially the quality of drinking water, were the cause of the stunting problem. The quality of drinking water is related to bacterial contamination due to disasters (floods), risk factors for unhealthy behavior, and open toilets. Poor water quality causes infection, which indirectly affects other factors that affect linear growth (weight and height), which are indicators of stunting. Interventions reduce the prevalence of stunting by improving sanitation, especially the quality of proper drinking water, and improving clean living behavior in the community.
Copyright (c) 2023 Ahmad Zaerozi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions.
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA).
- The Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA) license allows re-distribution and re-use of a licensed work on the conditions that the creator is appropriately credited and that any derivative work is made available under "the same, similar or a compatible license”. Other than the conditions mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation.