The Successful Administration of Steroid in Extrahepatic Cholestasis
Downloads
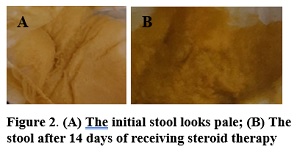
Biliary atresia is the most common cause of liver transplantation in children. Kasai surgery is still a bridging therapy for biliary atresia, but patients are often late for treatment. Based on the currently proposed theory, biliary atresia results from a progressive inflammatory process and progresses to fibrosis of the bile ducts. A case of a 1.5-month-old boy with prolonged jaundice followed by acholic stools and dark urine was presented. He had cholestasis, elevated GGT levels, and a liver biopsy suggesting extrahepatic cholestasis. He was treated with methylprednisolone, ursodeoxycholic acid, and vitamin supplementation was started orally. After steroid therapy, direct bilirubin levels decreased rapidly to 0.55 mg/dl on day 14. Jaundice, acholic stools, cholestasis, and liver function tests were improved. Therapeutic opportunities based on the pathogenesis of inflammation in biliary atresia using steroids may provide new opportunities for non-surgical management of biliary atresia in the early phase of the disease.
Copyright (c) 2023 Anindya Kusuma Winahyu, Rendi Aji Prihaningtyas, Bagus Setyoboedi, Sjamsul Arief

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions.
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA).
- The Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA) license allows re-distribution and re-use of a licensed work on the conditions that the creator is appropriately credited and that any derivative work is made available under "the same, similar or a compatible license”. Other than the conditions mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation.