Probiotic Potential of Lactic Acid Bacteria on Feed Efficiency, Weight and Carcass Percentage in Ducks
Downloads
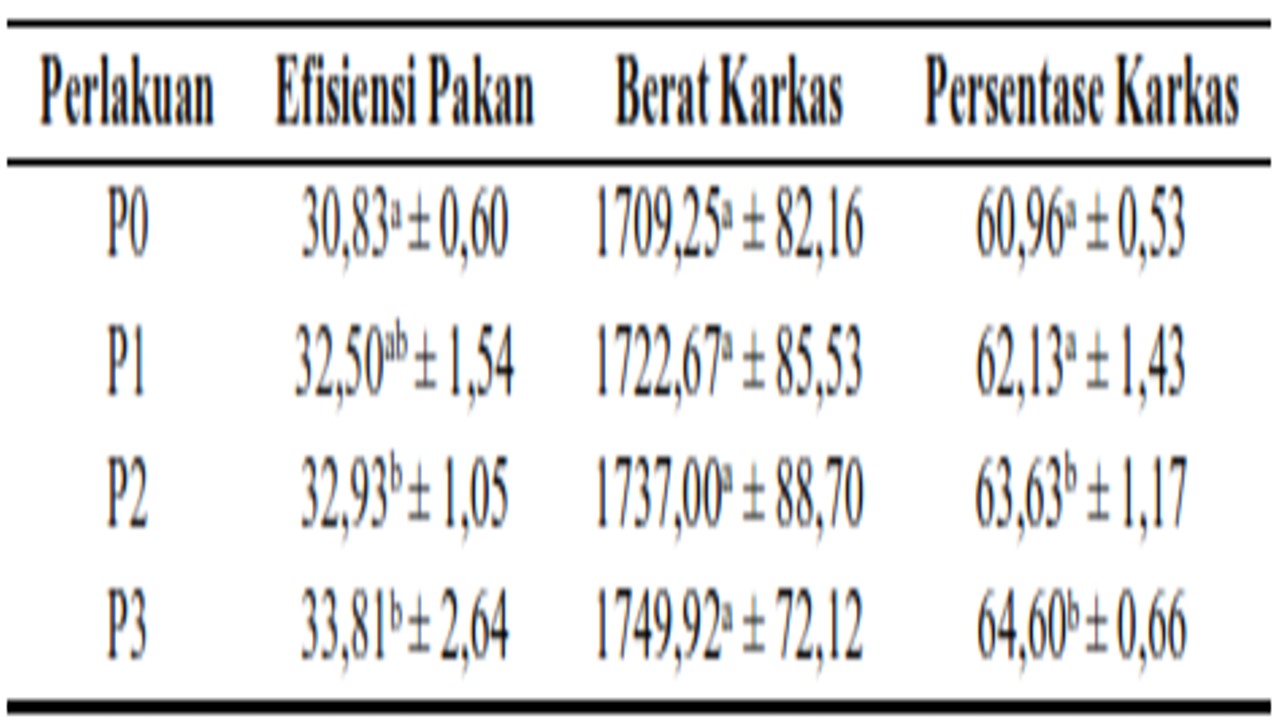
The aim of the study was to determine the effect of the use of probiotic lactic acid bacteria (Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus casei, Lactococcus lactis, and Bifidobacterium sp) on feed efficiency, carcass weight and carcass percentage in broiler ducks. Probiotics lactic acid bacteria produce bacteriocins and organic acids that inhibit the growth of pathogenic microbes in the digestive tract of poultry, so that the intestinal villi of broiler ducks are healthy. Besides that, probiotics are able to reduce cholesterol levels in meat when consumed by humans and can improve health. This study used 48 peking ducks. The probiotics of Lactic Acid Bacteria used were a concentration of 1.2 x 108 CFU/ml. In this study there were four different treatments, namely P0 (without probiotics), P1 (given 1 ml probiotics/liter drinking water), P2 (given 2 ml probiotics/liter drinking water) and P3 (given 3 ml probiotics/liter of drinking water). The results of the feed efficiency study showed that there was a significant difference (p<0.05) in the P0, P1, P2 and P3 treatments. The highest feed efficiency was at P3 (33.81%) while the lowest was P0 (30.84%). The results of the study on carcass weight indicated that the probiotics tended to be higher than those who were not given probiotics but statistically not significantly different (p>0.05). The highest carcass weight was P3 (1749.92 g) and the lowest was P0 (1709.25 g). The results of the study on the percentage of carcass weight showed a significant difference (p<0.05) in both P0, P1, P2 and P3 treatments. The highest percentage of carcass weight was at P3 (64.60%) and the lowest was P0 (60.96%). It can be concluded that the administration of probiotics lactic acid bacteria (Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus casei, Lactococcus lactis, and Bifidobacterium sp) at a dose of 1 ml/liter of drinking water, 2 ml/liter of drinking water and 3 ml/liter of drinking water can affect feed efficiency and the percentage of duck carcasses. but has no effect on the carcass weight of broiler ducks.
Ardhiana, M. Y., Nugroho, B. A., & Hartanto, B. (2014). Efisiensi Pemasaran Telur Ayam Ras di Kecamatan Ringinrejo
Kabupaten Kediri. Jurnal Fakultas Peternakan, 2(1), 1-13.
Bahri, S., Masbulan, E., & Kusumaningsih, A. (2005). Proses praproduksi sebagai faktor penting dalam menghasilkan produk ternak yang aman untuk manusia. Jurnal Litbang Pertanian, 24(1), 27-35.
Brake, J., Havestein, G. B., Scheideler, S. E., Ferket, P. R., & Rives, D. V. (1993). Relationship of sex, age and body weight to broiler carcass yield and offal production. Poultry Science, 72, 1137-1145.
Direktorat Jenderal Peternakan dan Kesehatan Hewan. (2019). Statistik Peternakan dan Kesehatan Hewan. Kementerian Pertanian Republik Indonesia, Jakarta.
Hutabarat M. R. T. (2019). Analysis Usaha Pemberian Probiotik Bakteri Asam Laktat (BAL) Pada Ayam Pedaging Yang Diinfeksi Eschericia Coli Terhadap Persentase Berat Lemak Abdominal dan Berat Karkas. (Tesis). Universitas Airlangga: Surabaya. Hal: 16.
Irawan, P. I. (2020). Potensi Probiotik Bakteri Asam Laktat Terhadap Performa Produksi Dan Analisis Usaha Pada Ayam Petelur. Tesis. Universitas Airlangga: Surabaya. Hal: 20.
Jaelani, A., Gunawan, A., & Syaifuddin, S. (2014). Pengaruh Penambahan Probiotik Starbio Dalam Ransum Terhadap Bobot Potong, Persentase Karkas Dan Persentase Lemak Abdominal Ayam Broiler. Ziraa'ah Majalah Ilmiah Pertanian, 39(2), 85-94.
Liu, J. B., Yan, H. L., Zhang, Y., Hu, Y. D., & Zhang, H. F. (2019). Effects of dietary energy and protein content and lipid source on growth performance and carcass traits in Pekin ducks. Poultry Science, 98(10).
Lokapirnasari, W. P., Sahidu, A. M., Maslachah, L., & Koestanti, E. (2020). Effect of Lactobacillus casei and Lactobacillus acidophilus in Laying Hens Challenged by Escherichia coli Infection. Sains Malaysiana, 49(6), 1237-44.
Lokapirnasari, W. P., Pribadi, T. B., Al Arif, A., Soeharsono, S., Hidanah, S., Harijani, N., Najwan, R., Huda, K., Wardhani, H. C. P., Rahman, N. F. N., & Yulianto, A. B. (2019). Potency of probiotics Bifidobacterium spp. and Lactobacillus casei to improve growth performance and business analysis in organic laying hens. Veterinary World, 12(6), 860.
Mountzouris, K. C., Tsitrsikos, P., Palamidi, I., Arvaniti, A., Mohnl, M., Scgatzmayr, G., & Fegeros, K. (2010). Effect of probiotic inclusion levels in broiler nutrition on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, plasma immunoglobulins and cecal microflora composition. Poultry Science, 89.
Qin, C., Gong, L., Zhang, X. P., Wang, Y. Y., Wang, Y., Wang, B., Li, Y., & Li, W. (2018). Effect of Saccharomyces boulardii and Bacillus subtilis B10 on gut microbiota modulation in broilers. Animal Nutrition, 4.
Rasyaf, M. (1997). Panduan Beternak Ayam Pedaging, Penebar Swadaya Jakarta. Hal: 39.
Soeharsono, L. A., Safitri, R., Sjofjan, O., Abdullah, S., Rostika, R., Lengkey, H. A., & Mushawwir, A. (2010). Probiotik Basis Ilmiah, Aplikasi, dan Aspek Praktis. Penerbit Widya Padjadjaran. Bandung. Hal: 41.
Sujaya, I. N., Ramona, Y., Widarini, N. P., Suariani, N. P., Dwipayanti, N. M. U., Nocianitri, K. A., & Nursini, N. W. (2008). Isolasi dan Karakteristik Bakteri Asam Laktat dari Susu Kuda Sumbawa. Jurnal Veteriner, 9(2), 52-59.
Sukirmansyah, Daud, M., & Latif, H. (2016). Evaluasi produksi dan persentase karkas itik peking dengan pemberian pakan fermentasi probiotik. Jurnal IImiah Mahasiswa Pertanian Unsyiah, 1, 719-730.
Sumarsih, S., & Sulistiyanto, B. (2016). Pengaruh Pemberian Pakan Lengkap Bentuk Pelet Diperkaya Probiotik Lactobacillus Salivarius Terhadap Produktivitas Itik Lokal Periode Finisher. Jurnal Litbang Provinsi Jawa Tengah, 14(2), 181-186.
Tillman, A. D., Hartadi, H., Reksohadiprodjo, S., Prawirokusumo, S., & Lebdosoekojo, S. (1998). Ilmu Makanan Ternak Dasar. Cetakan ke-5. Gadjah Mada University Press, Yogyakarta. Hal: 21.
Wu, Y., Liu, J., Shahid, M. S., Xiao, Z., Dong, X., Yin, D., & Yuan, J. (2019). Effects of dietary energy and protein levels on free force-feed Peking ducks. Journal of Applied Poultry Research, 28(3), 606-615.
Yulianto, A. B., Lokapirnasari, W. P., Najwan, R., Wardhani, H. C. P., Rahman, N. F. N., Huda, K., & Ulfah, N. (2020). Influence of Lactobacillus casei WB 315 and crude fish oil (CFO) on growth performance, EPA, DHA, HDL, LDL, cholesterol of meat broiler chickens. Iranian Journal of Microbiology, 12(2), 148.
Zurmiati, M. E., Mahata, M., Abbas, H., & Wizna. (2014). Aplikasi Probiotik Untuk Temak Itik. Jurnal Petermakan Indonesia, 16(2), 134-144.
Copyright (c) 2022 Evania Haris Chandra, Widya Paramita Lokapirnasari, Sri Hidanah, Muhammad Anam Al-Arif, Wiwik Misaco Yuniarti, Epy Muhammad Luqman

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions;
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions;
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-SA).






11.jpg)




















