Evaluation and Its Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Inactivated Vaccine Candidate in K18-hACE2 Mice
Downloads
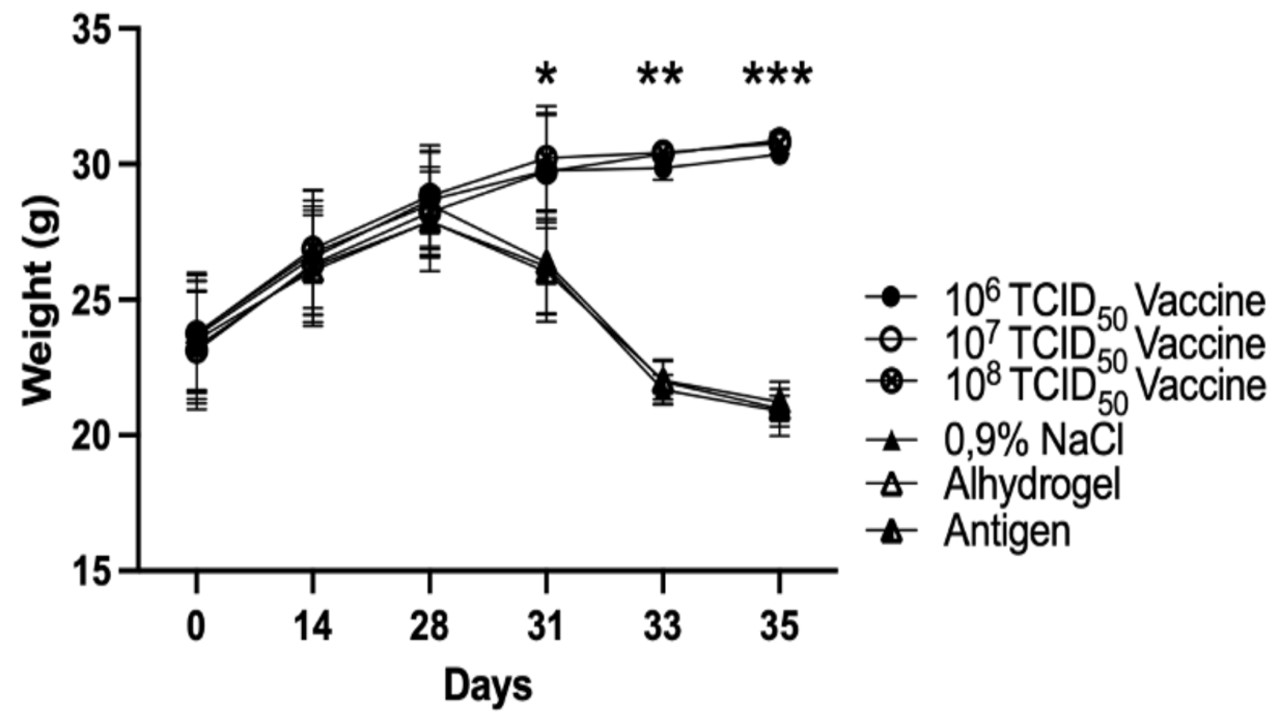
The COVID-19 pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 requires effective vaccines to be developed. This study aimed to assess the impact of a SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine candidate in k18-hACE2 mice by monitoring their body weight, immune activation, and inflammatory cytokines including IL-4, IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-γ. The study utilized k18-hACE2 mice expressing the human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (hACE2) receptor. The mice were administered the inactivated vaccine candidate compared with sham and vehicle. Body weight was monitored, and serum samples were collected to measure IL-4, IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-γ levels using ELISA. Data were evaluated using SPSS statistical analysis software. The administration of the SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine candidate in k18-hACE2 mice did not result in significant changes in body weight compared to the control group. Furthermore, the levels of IL-4, IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-γ were significantly reduced in the vaccinated mice compared to the control group, suggesting a dampening effect on the inflammatory response. This study demonstrates that the SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine candidate has a minimal impact on the body weight of k18-hACE2 mice. Nevertheless, it successfully regulates the levels of IL-4, IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-γ, suggesting its safety and beneficial impact. These findings contribute to understanding the vaccine's efficacy and safety profile in vaccine development.
Arora, P., Sidarovich, A., Krüger, N., Kempf, A., Nehlmeier, I., & Graichen, L. (2021). B.1.617.2 enters and fuses lung cells with increased efficiency and evades antibodies induced by infection and vaccination. Cell Reports, 37(2), 109825.
Dhawan, M., Saied, A. A., Emran, T. B., & Choudhary, O.P. (2022). Emergence of omicron variant’s sublineages BA.4 and BA.5: risks assessment and possible countermeasures. New Microbes New Infection, 48, 100997.
Gao, Q., Bao, L., Mao, H., Wang, L., Xu, K., & Yang, M. (2020). Development of an inactivated vaccine candidate for SARS-CoV-2. Science, 369(6499), 77–81.
Gimenes, L. G., Portilho, A. I., & De Gaspari, E. (2022). Animal Models to Test SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines: Which Ones Are in Use and Future Expectations. Pathogens, 12(1), 20.
Guo, M., Wang, Y., Liu, J., Huang, Z., & Li, X. (2019). Biosafety and data quality considerations for animal experiments with highly infectious agents at ABSL-3 facilities. Journal of Biosafety and Biosecurity, 1(1), 50–5.
Hamid, I. S., Ekowati, J., Solfaine, R., Chhetri, S., & Purnama, M. T. E. (2022). Efficacy of probiotic on duodenal TNF-α expression and the histological findings in the liver and lung in animal model canine coronavirus. Pharmacognosy Journal, 14(3).
Han, H., Ma, Q., Li, C., Liu, R., Zhao, L., & Wang, W. (2020). Profiling serum cytokines in COVID-19 patients reveals IL-6 and IL-10 are disease severity predictors. Emerging Microbes Infection, 9(1), 1123–30.
Han, X., Xu, P., & Ye, Q. (2021). Analysis of COVID‐19 vaccines: Types, thoughts, and application. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis, 35(9), e23937.
Johnson, R. M., Ardanuy, J., Hammond, H., Logue, J., Jackson, L., & Baracco, L. (2023). Diet-induced obesity and diabetes enhance mortality and reduce vaccine efficacy for SARS-CoV-2. Journal of Virology, 97(11), e01336–23.
Law, M., Ho, S. S. H., Tsang, G. K. C., Ho, C. M. Y., Kwan, C. M., & Yan, V. K. C. (2023). Efficacy and effectiveness of inactivated vaccines against symptomatic COVID-19, severe COVID-19, and COVID-19 clinical outcomes in the general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Lancet Regional Health-Western Pacific, 37, 100788.
Li, X., Yang, X., & Ning, Z. (2022). Efficacy and safety of COVID-19 inactivated vaccine: A meta-analysis. Frontiers in Medicine, 7(9), 1015184.
Moreau, G. B., Burgess, S. L., Sturek, J. M., Donlan, A. N., Petri, W. A., & Mann, B. J. (2020). Evaluation of K18-hACE2 Mice as a Model of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 103(3), 1215–9.
Natekar, J. P., Pathak, H., Stone, S., Kumari, P., Sharma, S., & Auroni, T. T. (2022). Differential Pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern in Human ACE2-Expressing Mice. Viruses, 14(6), 1139.
Oli, A. N., Oli, U. C., Ejiofor, O. S., Nwoye, C. U., & Esimone, C. O. (2016). An assessment, in mice, of the safety of the childhood immunization vaccines sourced from three south-eastern states of Nigeria. Trials in Vaccinology, 5, 8–14.
Pérez, P., Albericio, G., Astorgano, D., Flores, S., Sánchez-Corzo, C., & Sánchez-Cordón, P. J. (2023). Preclinical immune efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 beta B.1.351 variant by MVA-based vaccine candidates. Frontiers in Immunology, 14, 1264323.
Ruiz, S., Vardon-Bounes, F., Merlet-Dupuy, V., Conil, J. M., Buléon, M., & Fourcade, O. (2016). Sepsis modeling in mice: ligation length is a major severity factor in cecal ligation and puncture. Intensive Care Medicine Experimental, 4(1), 22.
Solfaine, R., Fikri, F., Maslamama, S. T., Purnama, M. T. E., & Hamid, I. (2024a). Exploring the protective efficacy of Lactobacillus acidophilus against interleukin-1beta (IL-1β) expression in mice induced with canine coronavirus vaccine. Advance in Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 12(4), 673–678.
Solfaine, R., Purnama, M., Maslamama, S., Fikri, F., & Hamid, I. (2024b). Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus: A Boost for Hematological and Gut Health in Salmonella enteritidis-Infected Mice. International Journal of Veterinary Science, 13(6), 776–781.
Soto, J. A., Díaz, F. E., Retamal-Díaz, A., Gálvez, N. M. S., Melo-González, F., & Piña-Iturbe, A. (2022). BCG-Based Vaccines Elicit Antigen-Specific Adaptive and Trained Immunity against SARS-CoV-2 and Andes orthohantavirus. Vaccines, 10(5), 721.
Stadlbauer, D., Amanat, F., Chromikova, V., Jiang, K., Strohmeier, S., & Arunkumar, G. A. (2020). SARS‐CoV‐2 Seroconversion in Humans: A Detailed Protocol for a Serological Assay, Antigen Production, and Test Setup. Current Protococal in Microbiology, 57(1), e100.
Turner, P. V., Brabb, T., Pekow, C., & Vasbinder, M. A. (2011). Administration of substances to laboratory animals: routes of administration and factors to consider. Journal of the Amecine Association for Labotaory Animal Science, 50(5), 600–13.
Wang, H., Zhang, Y., Huang, B., Deng, W., Quan, Y., & Wang, W. (2020). Development of an Inactivated Vaccine Candidate, BBIBP-CorV, with Potent Protection against SARS-CoV-2. Cell, 182(3), 713–721.e9.
Wang, S., Li, L., Yan, F., Gao, Y., Yang, S., & Xia, X. (2021). COVID-19 Animal Models and Vaccines: Current Landscape and Future Prospects. Vaccines, 9(10), 1082.
Yadav, P. D., Ella, R., Kumar, S., Patil, D. R., Mohandas, S., & Shete, A. M. (2021). Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidate, BBV152 in rhesus macaques. Nature Communications, 12(1), 1386.
Yeh, K. B., Tabynov, K., Parekh, F. K., Mombo, I., Parker, K., & Tabynov, K. (2021). Significance of High-Containment Biological Laboratories Performing Work During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Biosafety Level-3 and -4 Labs. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 13(9), 720315.
Yinda, C. K., Port, J. R., Bushmaker, T., Offei, O. I., Purushotham, J. N., & Avanzato, V. A. (2021). K18-hACE2 mice develop respiratory disease resembling severe COVID-19. PLoS Pathogens, 17(1), e1009195.
Copyright (c) 2025 Rofiqul A'la, Fedik Abdul Rantam, Andi Yasmin Wijaya, Helen Susilowati, Suryo Kuncorojakti, Diyantoro Diyantoro, Ahmad Aswin, Jola Rahmahani, Lucia Tri Suwanti, Bambang Sektiari Lukiswanto, Ira Sari Yudaniayanti, Boedi Setiawan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions;
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions;
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-SA).






11.jpg)




















