Protections and Social Support of Exclusive Breastfeeding for Mothers with COVID-19: Message for Health Promotion during The Pandemic
Downloads
Introduction: The COVID-19 pandemic is a concern regarding the potential failure of exclusive breastfeeding in mothers with COVID-19. This study reviews previous research describing the protective and social support practices of exclusive breastfeeding in mothers with COVID-19.
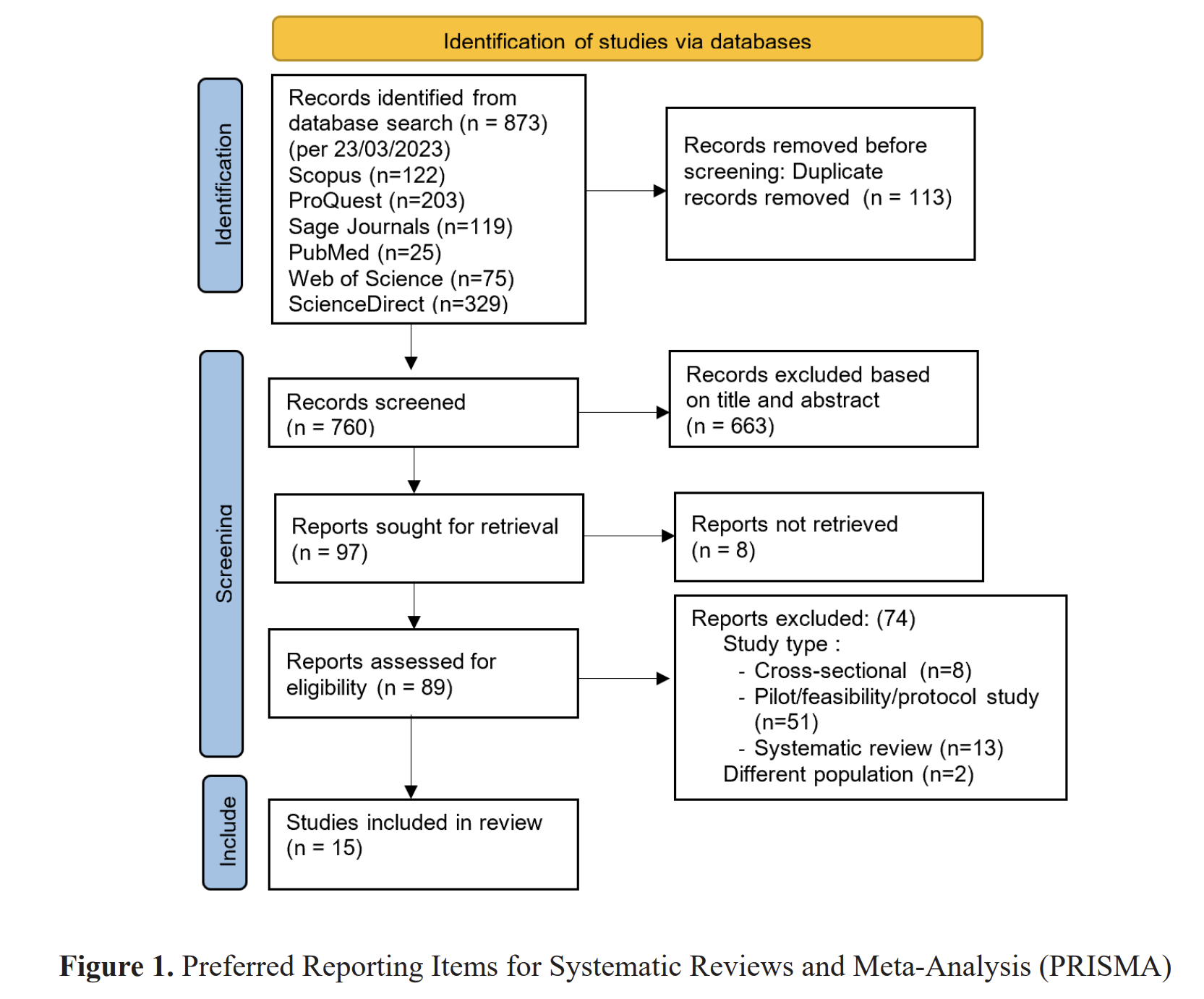
Methods: A systematic search was conducted in March-June 2021 using databases such as Scopus and PubMed with a deadline of 2020-2021 that met the inclusion criteria. 462 articles which were then entered in the elimination stage until the final 16 articles were eligible for a full text review. Study quality was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS).
Results: We identified 16 studies reporting 1,865 cases of maternal infection with COVID-19. An overview of breastfeeding protection practices is carried out through rooming-in and post-delivery skin contact. This practice includes implementing strict precautions such as wearing a mask, social distancing, and maintaining hand and breast hygiene. All babies born to mothers who practice breastfeeding protection are not infected with COVID-19. Social support from health workers, families and health care management cannot be overlooked in ensuring breastfeeding continues and precautions are followed.
Conclusion: In mothers with COVID-19 breastfeeding is still recommended but must be supported by strict health protocols. Social support cannot be neglected to protect exclusive breastfeeding practices and ensure that COVID-19 precautions are adhered to.
WHO. Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports. World Heal Organ. 2020;
Tran HT, Nguyen PTK, Huynh LT, Le CHM, Giang HTN, Nguyen PTT, et al. Appropriate care for neonates born to mothers with COVID"19 disease. Acta Paediatr [Internet]. 2020 Sep 10;109(9):1713–6. Available from: https://search.proquest.com/scholarly-journals/appropriate-care-neonates-born-mothers-with-covid/docview/2414200612/se-2?accountid=17242
WHO. COVID-19 and breastfeeding Position paper. 2020 [Internet]. 2020;1. Available from: https://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0010/437788/breastfeeding-COVID-19.pdf?ua=1
Martín F de la M. Covid-19 and breastfeeding. Rev Cubana Pediatr. 2020;92(May):1–5.
CDC. Maternity Practices in Infant Nutrition and Care (mPINC) Survey. In 2020. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding/data/mpinc/
Wang, Chen, Wu, Shi, Li, Jiang H, et al. Impact of Covid-19 in pregnancy on mother's psychological status and infant's neurobehavioral development: a longitudinal cohort study in China. BMC Med [Internet]. 2020 Dec 4;18(1):347. Available from: https://bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12916-020-01825-1
Tran, Huynh, Le, Nguyen, Nguyen, Nguyen, et al. Early Essential Newborn Care can still be used with mothers who have COVID"19 if effective infection control measures are applied. Acta Paediatr [Internet]. 2021 Mar 23;apa.15837. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/apa.15837
Sánchez-Luna M, Colomer BF, Romero C de A, Allen AA, Souto AB, Longueira FC, et al. Neonates Born to Mothers With COVID-19: Data From the Spanish Society of Neonatology Registry. Vol. 147, Pediatrics. 2021.
Popofsky, Noor, Leavens-Maurer, Quintos-Alagheband, Mock, Vinci, et al. Impact of Maternal Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Detection on Breastfeeding Due to Infant Separation at Birth. J Pediatr [Internet]. 2020 Nov;226:64–70. Available from: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85090113883&origin=inward
Kalamdani P, Kalathingal T, Manerkar S, Mondkar J. Clinical Profile of SARS-CoV-2 Infected Neonates From a Tertiary Government Hospital in Mumbai, India. Indian Pediatr [Internet]. 2020 Dec 12;57(12):1143–6. Available from: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85098531315&origin=inward
Salvatore, Han, Acker, Tiwari, Jin, Brandler, et al. Neonatal management and outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic: an observation cohort study. Lancet Child Adolesc Heal [Internet]. 2020 Oct;4(10):721–7. Available from: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85088938996&origin=inward
García, Gutiérrez, Chamorro, Zamora, Vigil-Vázquez, Rodríguez-Corrales, et al. Epidemiología, manejo y riesgo de transmisión de SARS-CoV-2 en una cohorte de hijos de madres afectas de COVID-19. An Pediatría [Internet]. 2021 Mar;94(3):173–8. Available from: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-85099560106&doi=10.1016%2Fj.anpedi.2020.12.004&partnerID=40&md5=9f8ea1c882d015d91727c491c1d19e20
Ronchi, Pietrasanta, Zavattoni, Saruggia, Schena, Sinelli, et al. Evaluation of Rooming-in Practice for Neonates Born to Mothers With Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection in Italy. JAMA Pediatr [Internet]. 2021 Mar 1;175(3):260. Available from: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/2773311
Cojocaru, Crimmins, Sundararajan, Goetzinger, Elsamadicy, Lankford, et al. An initiative to evaluate the safety of maternal bonding in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. J Matern Neonatal Med [Internet]. 2020 Sep 30;1–7. Available from: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85091876373&origin=inward
Biasucci, Cannalire, Raymond, Capra, Benenati, Vadacca G, et al. Safe Perinatal Management of Neonates Born to SARS-CoV-2 Positive Mothers at the Epicenter of the Italian Epidemic. Front Pediatr [Internet]. 2020 Oct 29;8. Available from: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85095997146&origin=inward
Patil, Maru, Krishnan, Carroll-Bennett, Sanchez, Noble, et al. Newborns of COVID-19 mothers: short-term outcomes of colocating and breastfeeding from the pandemic's epicenter. Vol. 40, Journal of perinatology : official journal of the California Perinatal Association. 2020. p. 1455–8.
Marín Gabriel MA, Cuadrado I, Álvarez Fernández B, González Carrasco E, Alonso Díaz C, Llana Martín I, et al. Multicentre Spanish study found no incidences of viral transmission in infants born to mothers with COVID-19. Acta Paediatr Int J Paediatr [Internet]. 2020;109(11):2302–8. Available from: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-85088582317&doi=10.1111%2Fapa.15474&partnerID=40&md5=408630c15c2faffbd5d47350ddd0de8c
Solís-García G, Gutiérrez-Vélez A, Pescador Chamorro I, Zamora-Flores E, Vigil-Vázquez S, Rodríguez-Corrales E, et al. Epidemiología, manejo y riesgo de transmisión de SARS-CoV-2 en una cohorte de hijos de madres afectas de COVID-19. An Pediatría [Internet]. 2021 Mar;94(3):173–8. Available from: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85099560106&origin=inward
Shlomai, Kasirer, Strauss, Smolkin, Marom, Shinwell, et al. Neonatal SARS-CoV-2 Infections in Breastfeeding Mothers. Vol. 147, Pediatrics. 2021.
Río, Dip Pérez E, Marín Gabriel MÁ. Multi"centre study showed reduced compliance with the World Health Organization recommendations on exclusive breastfeeding during COVID"19. Acta Paediatr [Internet]. 2021 Mar 8;110(3):935–6. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/apa.15642
Gonçalves-Ferri WA, Pereira-Cellini FM, Coca K, Aragon DC, Nader P, Lyra JC, et al. The impact of coronavirus outbreak on breastfeeding guidelines among Brazilian hospitals and maternity services: a cross-sectional study. Int Breastfeed J [Internet]. 2021 Dec 31;16(1):30. Available from: https://api.elsevier.com/content/abstract/scopus_id/85103744115
Oncel, Akın, Kanburoglu, Tayman, Coskun, Narter F, et al. A multicenter study on epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 125 newborns born to women infected with COVID-19 by Turkish Neonatal Society. Eur J Pediatr [Internet]. 2021 Mar 10;180(3):733–42. Available from: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85089254666&origin=inward
Tran HT, Huynh LT, Le CHM, Nguyen VD, Nguyen PTT, Hoang DT, et al. Early Essential Newborn Care can still be used with mothers who have COVID"19 if effective infection control measures are applied. Acta Paediatr [Internet]. 2021 Mar 23;apa.15837. Available from: https://www.proquest.com/scholarly-journals/early-essential-newborn-care-can-still-be-used/docview/2500248148/se-2?accountid=17242
Fadjriah R.N. Model KIE Komprehensif untuk Kesuksesan Perilaku Pemberian ASI Eksklusif Di Kota Palu. Universitas Hasanuddin; 2020.
Ferri, Pereira, Coca, Aragon, Nader P, Lyra JC, et al. The impact of coronavirus outbreak on breastfeeding guidelines among Brazilian hospitals and maternity services: a cross-sectional study. Int Breastfeed J [Internet]. 2021 Dec 31;16(1):30. Available from: https://internationalbreastfeedingjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13006-021-00377-1
Copyright (c) 2022 Khairunnisaa Khairunnisaa, Dian Ayubi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions.
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY).