The effectiveness of normal birth e-module on increasing nursing students' learning satisfaction
Downloads
Introduction: E-modules are information technology-based modifications of conventional modules. Students learning satisfaction can be used to gauge learning success. Learning satisfaction is the value of comparing the level of reality with the level of expectation in learning. This study aims to determine the effectiveness of the normal birth e-module in increasing nursing student learning satisfaction.
Methods: Pre-experimental with a one-shot case study design with data from online survey results using the E-Module Satisfaction Questionnaire instrument. The population of this study was 244 active students of the Faculty of Nursing, Universitas Padjadjaran, who had completed the maternity course using the normal birth e-module. As many as 46 people were willing to be respondents and fill out the level of learning satisfaction questionnaire. The study samples were determined by G-Power and data analysis using the Pearson Correlation test and the R square test or the Coefficient of Determination.
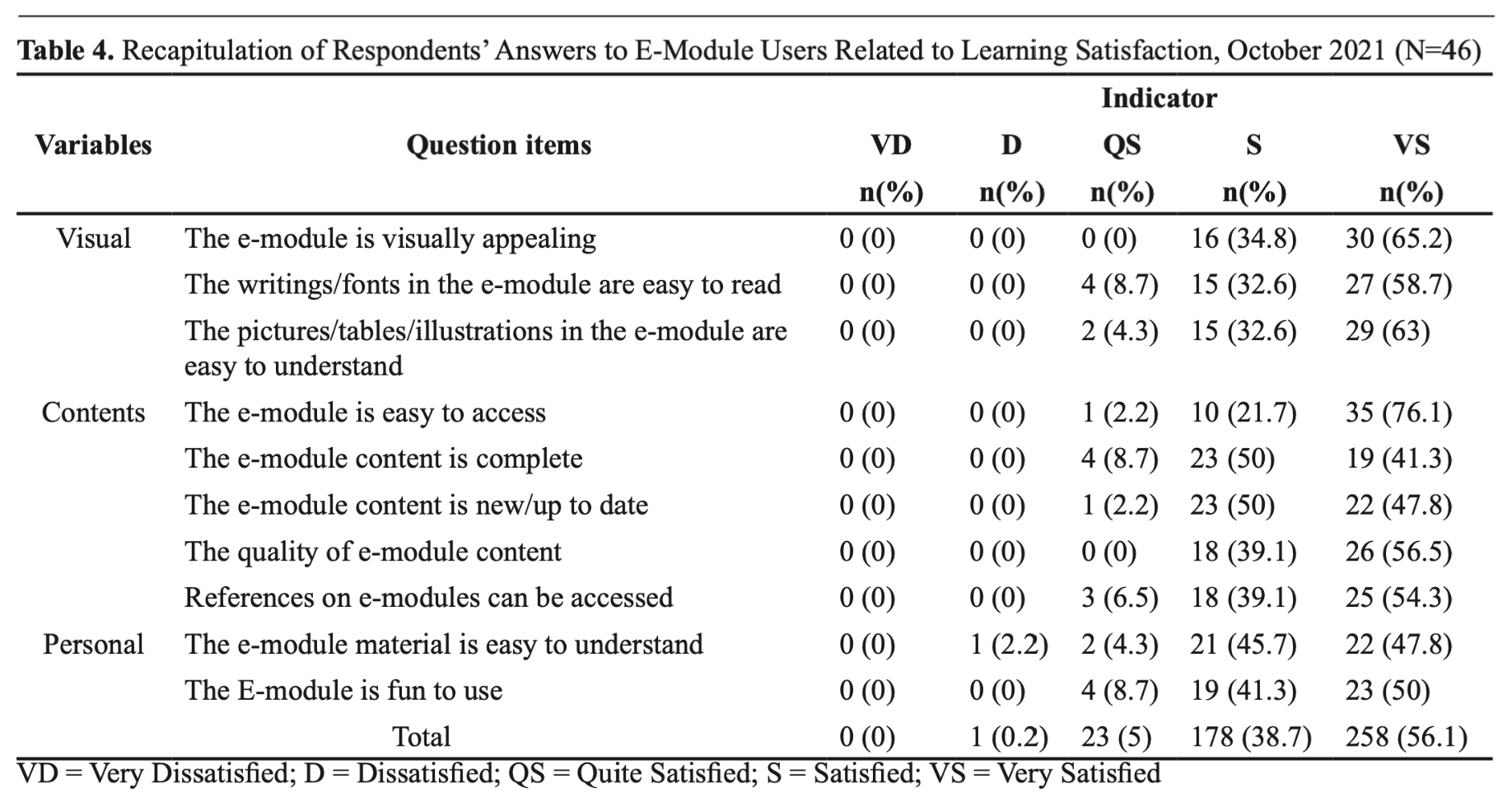
Results: Overall, the level of learning satisfaction of nursing students who use the normal birth e-module is very satisfactory/high, with an average of 4.51% in the range of 4.5 - 5.0. The percentage of the results of the assessment of all respondents was dissatisfied (0.2%), quite satisfied (5%), satisfied (38.7%), and very satisfied (56.1%). However, 2.2% or 1 out of 46 participants reported dissatisfaction with the respondent's understanding. The coefficient of determination or R square test of 0.876 or 87.6% is in the 0.8 – 0.99 (very effective).
Conclusions: The use of the Normal Birth E-Module is very effective as a learning method that can increase the level of learning satisfaction of nursing students.
Keywords: e-module; learning satisfaction; normal birth; nursing students
Abbasi, M. S., Ahmed, N., Sajjad, B., Alshahrani, A., Saeed, S., Sarfaraz, S., Alhamdan, R. S., Vohra, F., & Abduljabbar, T. (2020). E-Learning perception and satisfaction among health sciences students amid the COVID-19 pandemic. Work, 67(3), 549–556. https://doi.org/10.3233/wor-203308
Agung, N. (2020). Lakukan Praktikum Online, Mahasiswa: Kurang Efektif dan Merepotkan. SCIENTIARUM. http://scientiarum.com/2020/11/06/lakukan-praktikum-online-mahasiswa-kurang-efektif-dan-merepotkan/
Al Munawar, A., & Fuadaturrahmah, F. (2021). Tingkat Kepuasan Mahasiswa Terhadap Penggunaan Media E-learning Di Era Pandemi Covid-19. CHEDS: Journal of Chemistry, Education, and Science, 5(1), 1–5.
Alabdulkarim, L. (2021). University health sciences students rating for a blended learning course framework: University health sciences students rating. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 28(9), 5379–5385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.05.059
Alqhtani, A., Alswedan, N., Almulhim, A., Aladwan, R., Alessa, Y., Alqhtani, K., Albogami, M., Altwairqi, K., Alotaibi, F., Alhadlaq, A., & Aldhafian, O. (2021). Online versus classroom teaching for medical students during COVID-19 : measuring effectiveness and satisfaction. 1–7. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-021-02888-1
Budhianto, B. (2020). Analisis perkembangan dan faktor yang mempengaruhi keberhasilan pembelajaran daring (e-learning ). Jurnal AgriWidya, 1(1), 11–29.
Disdik. (2019). Revolusi Industri 4.0, Apakah Itu? Dan Pengaruhnya Terhadap Dunia Pendidikan. DinasPendidikan Kabupaten Bandung Barat. https://disdikkbb.org/news/revolusi-industri-4-0-apakah-itu-dan-pengaruhnya-terhadap-dunia-pendidikan/
Elshami, W., Taha, M. H., Abuzaid, M., Saravanan, C., Al Kawas, S., & Abdalla, M. E. (2021). Satisfaction with online learning in the new normal: perspective of students and faculty at medical and health sciences colleges. Medical Education Online, 26(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/10872981.2021.1920090
Fitri, E. N. (2021). Keterampilan Mengajar Dosen secara Daring Terhadap Kepuasan Belajar Mahasiswa pada Mata Kuliah Pengantar Akuntansi. Jurnal Riset Teknologi Dan Inovasi Pendidikan (JARTIKA), 4(1), 163–172.
Isnayni, M. Y., & Hermansyah, W. (2020). Pengaruh Pembelajaran Sistem Daring terhadap Mahasiswa Tadris Biologi dalam Memahami Materi Mata Kuliah Biokimia. ALVEOLI: Jurnal Pendidikan Biologi, 1(1), 22–28. https://doi.org/10.35719/alveoli.v1i1.3
Juniarti, N., & Trisyani, M. (2017). Pedoman Program Studi Pendidikan Sarjana Keperawatan Universitas Padjadjaran. Fakultas Keperawatan Universitas Padjadjaran.
Mahyanti, I. G. A. K., & Sriathi, A. A. (2017). Pengaruh Karakteristik Individu, Karakteristik Pekerjaan, dan Karakteristik Situasi Kerja terhadap Kepuasan Kerja Karyawan. E-Jurnal Manajemen Unud, 6(4), 2253–2279.
Manurung, E., Siagian, N., Indonesia, U. A., Kolonel, J., No, M., & Barat, K. B. (2020). Hubungan Pengetahuan dengan Kecemasan Siswa SMA Swasta Terhadap Pandemi Covid-19. Nursing Inside Community, 3, 8–14.
Nurhayati, N., & Zuhra, F. (2020). Analisis Tingkat Kepuasan Mahasiswa Fkip Matematika Universitas Almuslim Terhadap Pemanfaatan E-Learning Di Era Pandemi Covid 19. Jurnal Ilmiah Pendidikan Matematika Al Qalasadi, 4(2), 83–90. https://doi.org/10.32505/qalasadi.v4i2.2184
Partono. (2019). Pemanfaatan Emodul Dalam Pembelajaran. SMAN 1 Pegandon. https://sma1pegandon.sch.id/read/107/pemanfaatan-emodul-dalam-pembelajaran
Philip, G. C., & Moon, S.-Y. (2013). An Investigation of Student Expectation, Perceived Performance and Satisfaction of E-textbooks. Journal of Information Technology Education: Innovations in Practice, 12, 287–298. https://doi.org/10.28945/1903
Rahmawati, D. (2013). Analisis Faktor-Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi Kepuasan Mahasiswa. Jurnal Economia, 9(1), 52–65. https://doi.org/10.21831/economia.v9i1.1376
Rajeh, M. T., Abduljabbar, F. H., Alqahtani, S. M., Waly, F. J., Alnaami, I., Aljurayyan, A., & Alzaman, N. (2021). Students' satisfaction and continued intention toward e-learning: a theory-based study. Medical Education Online, 26(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/10872981.2021.1961348
Rokhani, S., & Marlianingrum, P. R. (2021). Pengaruh Kualitas Pelayanan dan Kualitas Pembelajaran Daring Terhadap Kepuasan Mahasiswa Dimasa Pandemi COVID-19. Journal of Management (SME's), 14(3), 291–310.
Satgas Penanganan COVID-19. (2021). Peta Sebaran COVID-19. https://covid19.go.id/peta-sebaran-covid19
Simaremare, D. A., & Junaidi, A. (2020). Analisis Tingkat Kepuasan Mahasiswa Pengguna E-Learning Menggunakan End User Computing Satisfication. Jurnal Infortech, 2(2), 250–257. https://doi.org/10.31294/infortech.v2i2.9257
Sugiharni, G. A. D. (2017). Validitas Isi Instrumen Pengujian Modul Digital Matematika Diskrit Berbasis Open Source di STIKOM Bali. E-Proceedings KNS&I STIKOM Bali, 678–684. http://knsi.stikom-bali.ac.id/index.php/eproceedings/article/view/123/118%0Ahttp://knsi.stikom-bali.ac.id/index.php/eproceedings/article/view/123
WHO. (2020). Novel Coronavirus. Situation Report – 205. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200121-sitrep-1-2019-ncov.pdf
Yusmiono, B. A. (2018). Media Pembelajaran Visual Terhadap Hasil Belajar Mahasiswa Program Studi Pendidikan Geografi Di Universitas PGRI Palembang. Faktor Jurnal Ilmiah Kependidikan, 5(1), 1–8.
Zahra, B. I. A. (2020). Apa Benar Indonesia Siap Menggunakan E-Learning Secara Permanen? Media Mahasiswa Indonesia. https://mahasiswaindonesia.id/apa-benar-indonesia-siap-menggunakan-e-learning-secara-permanen/
Copyright (c) 2023 Hasna Nurul Naafiah Jamaludin, Raini Diah Susanti, Habsyah Saparidah Agustina, Aep Maulid Mulyana

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions.
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY).