Stigmatization, life satisfaction, and its associated factors of childfree women: A scoping review
Downloads
Introduction: Having children during marriage is a way to preserve the family lineage. To be childfree leads to negative stigma from society and even one's own family. However, not all couples want to have children, some of them choose to be childfree. Objective: This study aimed to review literature about the perspective of women who choose to be childfree.
Methods: The literature search about being childfree used electronic databases, namely Scopus and PubMed, with the keywords “childfree," "quality of life" and “life satisfaction.” The studies included discuss the factors, impacts and satisfaction of a childfree life. This search was restricted to articles published in 2018-2023 and were analyzed by qualitative synthesis.
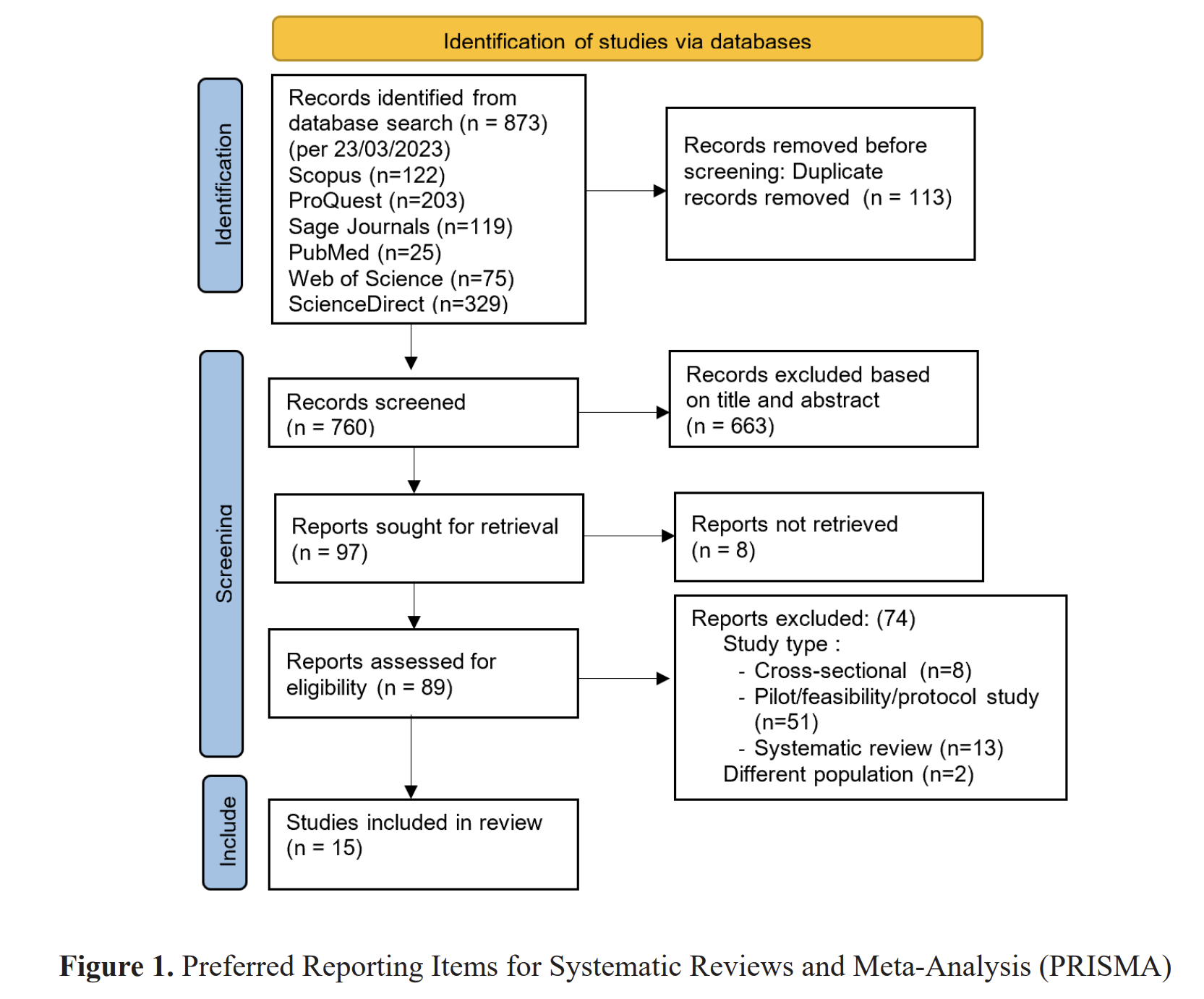
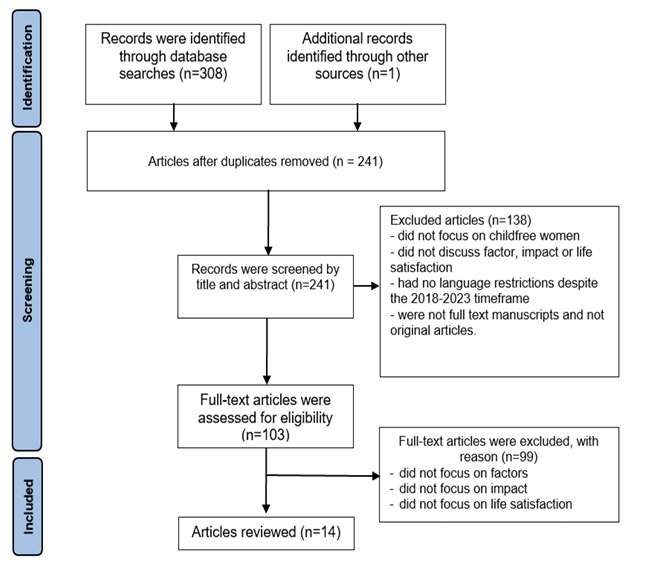
Results: There were 309 articles from both electronic databases, which were then sorted according to the PRISMA diagram, so that there were 14 articles that met the criteria. The articles were grouped into 12 qualitative articles and two quantitative articles. There are five main factors that cause women to be childfree, including individual, health, economic, family and environmental factors. Most women reported experiencing societal stigmatization, social pressure and pressure from the family. Even though they experience the negative impacts of childfree, they still feel satisfaction with life.
Conclusion: The perspectives of childfree women are diverse, ranging from the reasons for choosing to be childless, the social and emotional impacts and the level of life satisfaction.
Keywords: childfree; factors; impact; life satiscation; women
Copyright (c) 2025 Suhariyati Suhariyati, Shinta Alifiana Rahmawati, Masunatul Ubudiyah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions.
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY).