Developing nursing care protocols for hypertensive pregnancies using the delphi method and a cultural belief framework
Downloads
Introduction: The failure of hypertension therapy during pregnancy and the absence of standardized nursing interventions that incorporate cultural beliefs highlight the need for expert consensus. Objective: This study aims to develop a nursing care framework for hypertensive pregnancy based on a cultural belief approach using the Delphi Method.
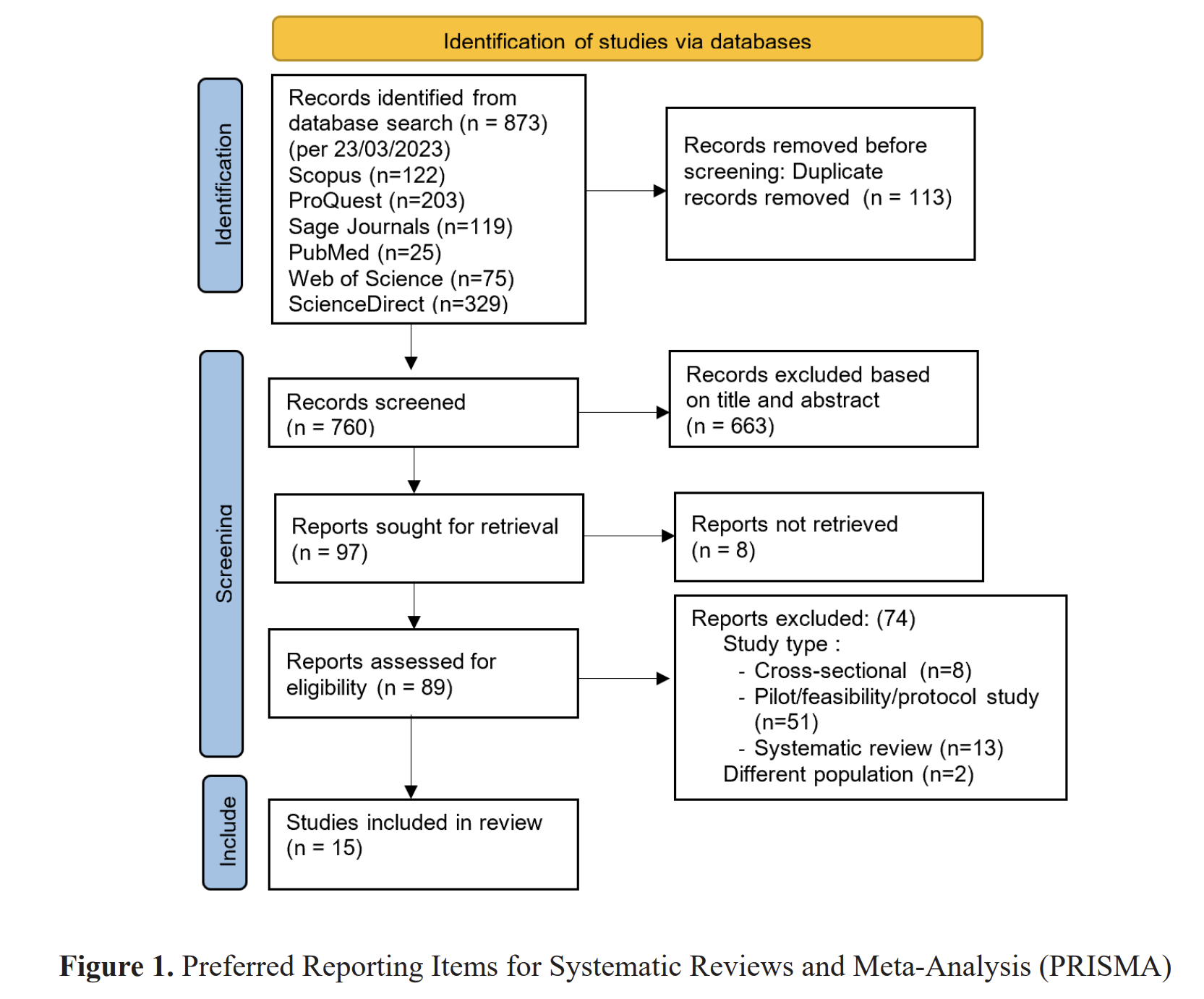
Methods: The Delphi Method was employed to gather expert opinions on hypertensive pregnancy care. Ten senior maternity nurse managers from Maternity and Children's Hospitals in Bandung, Indonesia, participated in two rounds of interviews. Data were analyzed for validity and reliability.
Results: A nursing intervention instrument was developed based on the NANDA-NOC-NIC Standard. The first round identified seven nursing diagnoses: (1) Readiness for enhanced self-management, (2) Imbalanced nutrition influenced by cultural beliefs, (3) Fatigue, (4) Readiness for enhanced hope, (5) Ineffective role performance due to inadequate resources and psychosocial support, (6) Ineffective coping resulting from poor adaptation and limited social support, and (7) Impaired comfort due to restricted environmental control and adaptation challenges. The second round refined the instrument, leading to the development of a nursing intervention checklist.
Conclusion: Standardizing hypertension care in pregnancy through a cultural belief approach may improve adaptation and coping. Nurses should integrate cultural beliefs into discharge planning, empowering pregnant women to independently implement nursing interventions as part of their daily care.
Keywords: cultural belief; hypertensive pregnancy care; nursing intervention
Copyright (c) 2025 Kusila Devia Rahayu, Liwayway T Vallesteros

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions.
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY).