Factors related to pap smear test among female health workers based on the health belief model
Downloads
Introduction: A Pap smear test is crucial for cervical cancer. However, in Indonesia, the awareness of women to perform cervical screening is still low, including among female health workers. This study aimed to analyze the factors correlating with the Pap smear test among female health workers by using the Health Belief Model.
Methods: This study used a descriptive-analytic design with a cross-sectional approach. The population was 184 female health workers and the samples were 125 female health workers from the selected Public Health Centre (PHC) recruited using simple random sampling. The dependent variable was the Pap smear test while the independent variables were perceived susceptibility, perceived seriousness, perceived benefit, perceived barrier, cues to action, and self-efficacy. Data were collected by using a structured questionnaire and analyzed by using a chi-square test with a level significance of α≤ 0.05.
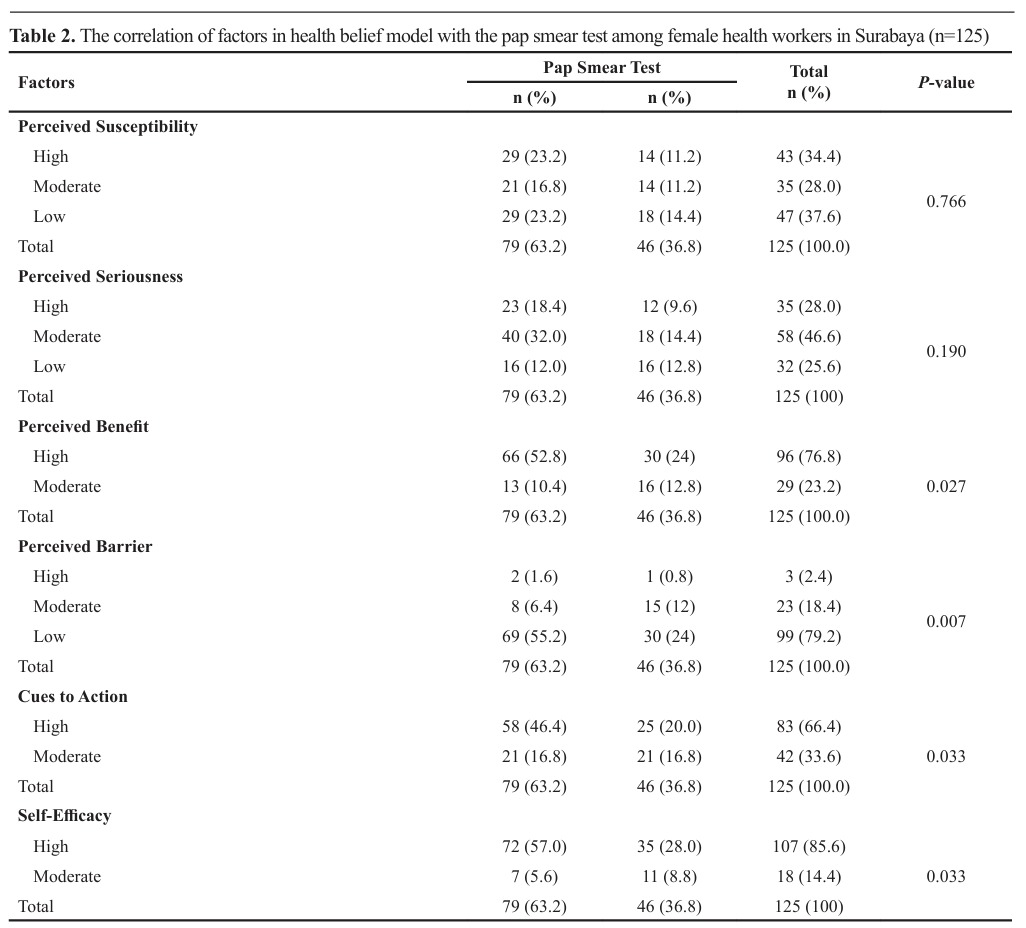
Results: The results showed that the P-value for perceived susceptibility was 0.766, P-value=0.190 for perceived seriousness, P value=0.027 for perceived benefits, P-value=0.007 for perceived barriers, P-value=0.033 for cues to action, and P-value=0.033 for self efficacy.
Conclusion: Perceived susceptibility and perceived seriousness are not associated with Pap smear tests among female health workers in this study, whereas perceived benefit, perceived barrier, cues to action, and self-efficacy are associated with Pap smear tests among female health workers. It is expected to conduct research related to factors that influence perceived susceptibility and perceived seriousness in health workers to a Pap smear test.
Keywords: cervical cancer; female health workers; health belief model; pap smear; women’s health
Copyright (c) 2025 Retnayu Pradanie, Elyta Zuliyanti, Praba Diyan Rachmawati, Mira Triharini, Khatijah Lim Abdullah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions.
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY).