SYSTEMATIC REVIEW: ANAPLASTIC LARGE CELL LYMPHOMA FOLLOWING BREAST IMPLANT SURGERY

Downloads
Highlights:
- BIA-ALCL, a T-cell lymphoma associated with breast implants, is posing a growing medical challenge due to the increasing use of implants for cosmetic and reconstructive purposes
- The majority of BIA-ALCL cases were associated with cosmetic reasons for breast implants, and textured implants were predominantly implicated.
Abstract:
Introduction: BIA-ALCL, a T-cell lymphoma associated with breast implants, poses a growing medical challenge despite its relatively low occurrence, due to the increasing use of implants for cosmetic and reconstructive purposes. Our objective is to review the incidence, characteristics of patients, implant types, management, and outcome of BIA-ALCL.
Methods: Pubmed and Science Direct databases were searched to identify case series and observational research. A systematic review was conducted by looking up the keywords "breast implant” and "anaplastic large cell lymphoma”.
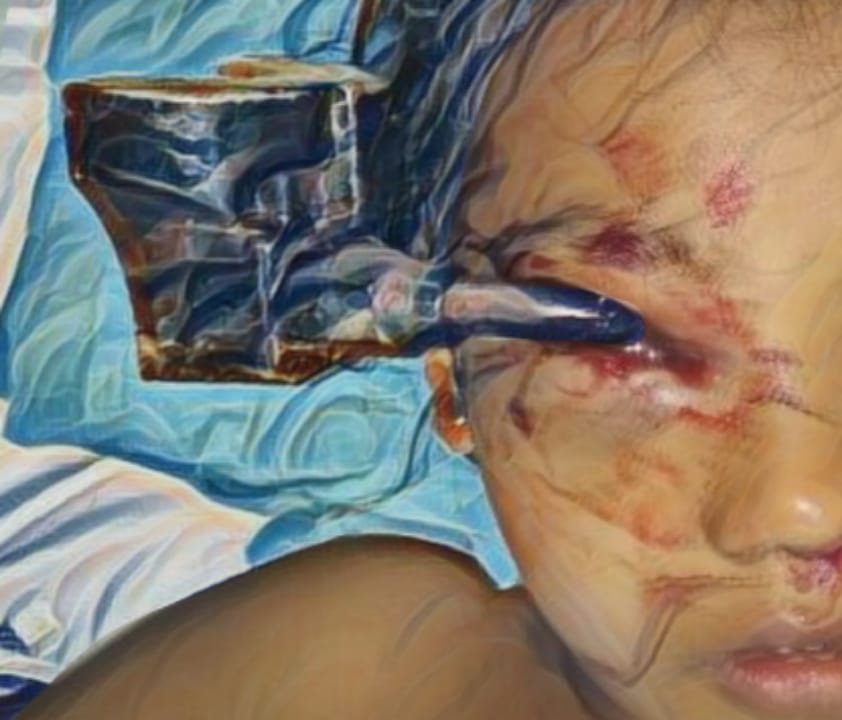
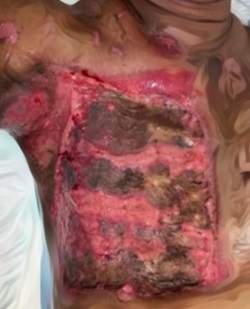
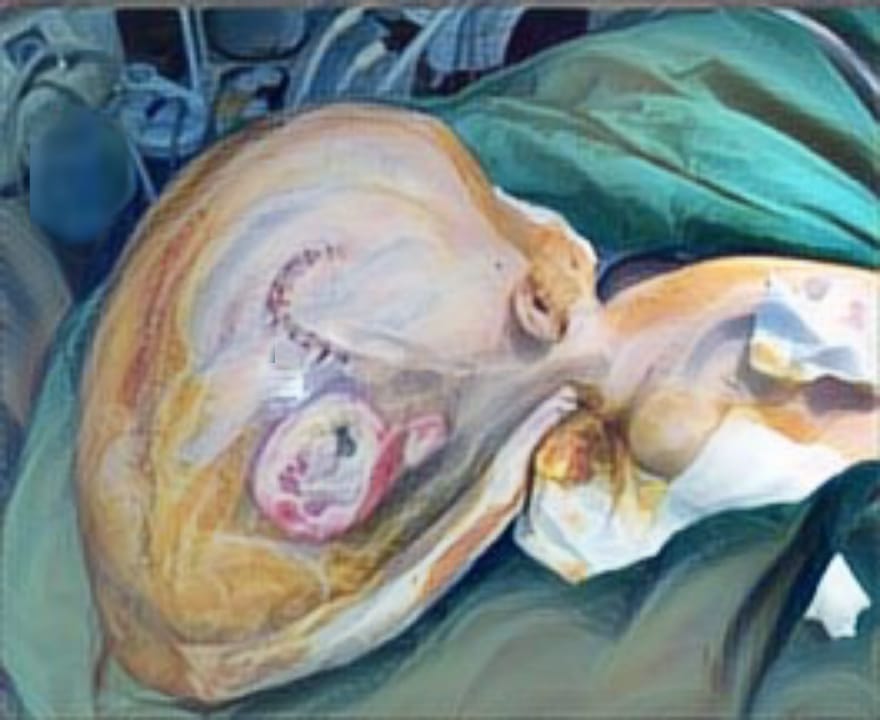
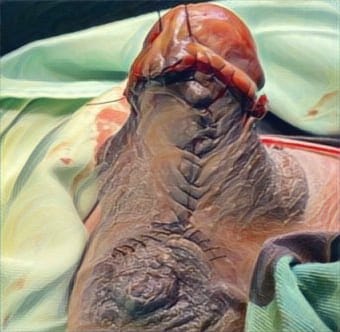
Result: 11 relevant articles were assessed. A total of 353 BIA-ALCL cases have been reported. The mean age at diagnosis was 59.6 years. More than half (53.26%) of the reasons for the breast implants in BIA-ALCL patients were cosmetic. The mean time from breast implant placement to diagnosis was 9.99 years. The majority (71.39%) of documented BIA-ALCL cases have been associated with textured devices. BIA-ALCL patients mainly presented with seroma (54.67%). Outcomes included remission (71%), death because of the disease (4.25%), and recurrence (3.96%) with a mean time of duration of follow-up was 2.53 years.
Conclusion: BIA-ALCL is rare cancer in some patients with breast implants but is increasing in incidence largely due to consistent and long-term follow-up. It is important for physicians involved in the care of patients with breast implants to be aware of BIA-ALCL and do routine breast exams.
Keech, J.A., Jr.; Creech, B.J. Anaplastic T-cell lymphoma in proximity to a saline-filled breast implant. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1997; 100:554–555.
M. Co, T.H. Chan, et al. Breast Implant-associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma - a Systematic Review with Pooled Analysis. Clinical Oncology 32 .2020. 639e646
Brody G, Deapen D, Taylor C, Pinter-Brown L, House-Light- ner SR, Andersen J, et al. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma occurring in women with breast implants: analysis of 173 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg 2015; 135 (3):695e705.
Deva, A.K., Turner, S.D., et al. Etiology of Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL): Current Directions in Research. Cancers. 2020; 12: 3861.
Armitage JO, Weisenburger DD. A new approach to classifying non-Hodgkin's lymphomas: Clinical features of the major histologic subtypes. Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Classification Project. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:2780–2795.
Jeanneret-Sozzi W, Taghian A, Epelbaum R, et al. Primary breast lymphoma: The patient profile, outcome, and prognostic factors. A multicentre Rare Cancer Network study. BMC Cancer .2008;8:86.
Kim, B., Carol Roth, R.N., et al. Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma and Breast Implants: A Systematic Review. American Society of Plastic Surgeons. 2011
Higgins J, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for systematic reviews of in-interventions | Cochrane training. Cochrane Collab 2021 [Online]. Available: 6.2; 2021. https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current.
Liberati A, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ Jul. 2009;339.
Wells G, Shea B, O'Connell D. The Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Ottawa Hosp Research Inst 2013 [Accessed March 18th, 2021]. Available: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_ epidemiology/oxford.asp.
Cordeiro P, Ghione P, Ni A, Hu Q, Ganesan N, Galasso N et al. Risk of breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL) in a cohort of 3546 women prospectively followed long term after sssimplants. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery. 2020;73(5):841-846.
Collins M, Miranda R, Medeiros L, Silva de Meneses M, Iyer S, Butler C, et al. Characteristics and Treatment of Advanced Breast Implant–Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2019;143:41S-50S.
Lamaris G, Butler C, Deva A, Miranda R, Hunt K, Connell T, et al. Breast Reconstruction Following Breast Implant–Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2019;143:51S-58S.
Doren E, Miranda R, Selber J, Garvey P, Liu J, Medeiros L, et al. U.S. Epidemiology of Breast Implant–Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2017;139(5):1042-1050.
Dashevsky B, Gallagher K, Grabenstetter A, Cordeiro P, Dogan A, Morris E, et al. Breast implant"associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma: Clinical and imaging findings at a large US cancer center. The Breast Journal. 2019;25(1):69-74.
Nelson J, Dabic S, Mehrara B, Cordeiro P, Disa J, Pusic A et al. Breast Implant-associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Incidence. Annals of Surgery. 2020;272(3):403-409.
Campanale A, Spagnoli A, Lispi L, Boldrini R, Marletta M. The Crucial Role of Surgical Treatment in BIA-ALCL Prognosis in Early- and Advanced-Stage Patients. Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery. 2020;146(5):530e-538e.
Loch-Wilkinson A, Beath K, Knight R, Wessels W, Magnusson M, Papadopoulos T, et al. Breast Implant–Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma in Australia and New Zealand: high-surface-area textured implants are associated with increased risk. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2017;140(4):645-654.
Johnson L, O'Donoghue J, McLean N, Turton P, Khan A, Turner S, et al. Breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma: The UK experience. Recommendations on its management and implications for informed consent. European Journal of Surgical Oncology (EJSO). 2017;43(8):1393-1401.
Aladily T, Medeiros L, Amin M, Haideri N, Ye D, Azevedo S et al. Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Associated With Breast Implants. American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 2012;36(7):1000-1008.
De Boer M, van Leeuwen F, Hauptmann M, Overbeek L, de Boer J, Hijmering N et al. Breast Implants and the Risk of Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma in the Breast. JAMA Oncology. 2018;4(3):335.
Zarbo RJ, Nakhleh RE: Surgical pathology specimens for gross examination only and exempt from submission: A College of American Pathologists Q-Probes study of current policies in 413 institutions. Arch Pathol Lab Med 123:133-139, 1999
Gurunluoglu R et al. Current trends in breast reconstruction: a survey of American Society of Plastic Surgeons 2010. Ann Plast Surg. 2013;70(1): 103-110.
Leberfinger AN, Behar BJ, Williams NC, Rakszawski KL, Potochny JD, Mackay DR, Ravnic DJ. Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: A Systematic Review. JAMA Surg. 2017 Dec 1;152(12):1161-1168. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.4026. PMID: 29049466.
Hu H, Jacombs A, Vickery K, Merten SL, Pennington DG, Deva AK. Chronic biofilm infection in breast implants is associated with an increased T"cell lymphocytic infiltrate: implications for breast implant"associated lymphoma. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;135(2):319" 329
Hu H, Johani K, Almatroudi A, et al. Bacterial biofilm infection detected in breast implant"associated anaplastic large"cell lymphoma. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;137(6):1659"1669.
Mulligan Ch, Salisbury E, Tschuchnigg M, et al. ALK1- Negative anaplastic large cell lymphoma of the breast from a nonprosthesis. Cyst 2014 PRS Global Open: 1-3
Honghua H, Jacombs A, Vickery K, et al. Chronic biofilm infection in breast implants is associated with an in-creased T-cell lymphocytic infiltrate: implications for breast implant-associated lymphoma. Plastic Reconst Surg 2015;135(2):319–329
Laurent C, Delas A, Gaulard P, et al. Breast implant"associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma: two distinct clinicopathological variants with different outcomes. Ann Oncol. 2016;27(2):306"314.
Clemens MW, Jacobsen ED, Horwitz SM. 2019 NCCN consensus guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL). Aesthet Surg J 2019;39(Supplement_1):S3–S13
Leberfinger AN, Behar BJ, Williams NC, Rakszawski KL, Potochny JD, Mackay DR, Ravnic DJ. Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: A Systematic Review. JAMA Surg. 2017 Dec 1;152(12):1161-1168. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.4026. PMID: 29049466.
Ferreri A, Govi S, Pileri SA, et al. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK-negative. Crit Rev Oncol/Haematol 2013;85:206–2015.
Copyright (c) 2023 Kezia Eveline, Beta Subakti Nata’admadja, Rizqi Shabrina Lestari, Lavonia Berlina Adzalika

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
JURNAL REKONSTRUKSI DAN ESTETIK by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold copyright of the article without restriction
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessbility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA)