THE INFLUENCE OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE SEVERITY ON SURGICAL OUTCOMES

Downloads
Highlights:
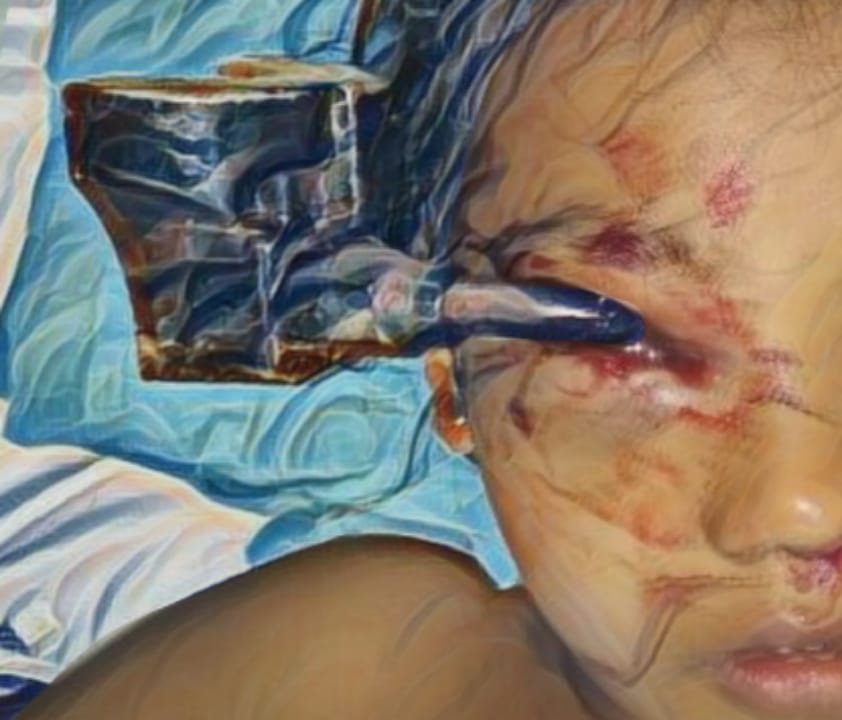
- The severity of unilateral CLP was assessed by categorizing preoperative photo data based on the severity of the cleft, and this severity was then correlated with the surgical outcomes.
- The way wounds heal is influenced by the width of the gap and suture tension, which are crucial factors in determining surgical outcomes.
Abstract:
Introduction: An orofacial cleft is a congenital abnormality in which an abnormal opening or cleft of the lips and/or palate. Data in 2017 showed that the most encountered characters are patients with cleft lip and palate. The distribution of the incidence of cleft lip and palate at Cleft Lip and Palate (CLP) Center Faculty of Medicine University of Muhammadiyah Malang was dominated by the complete unilateral type, which was 45.22%. Generally, the severity of cleft lip and/or palate is influenced by the severity of the preoperative cleft.
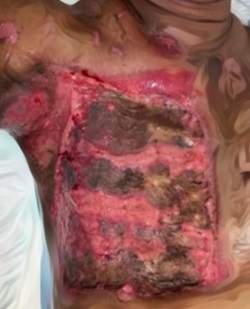
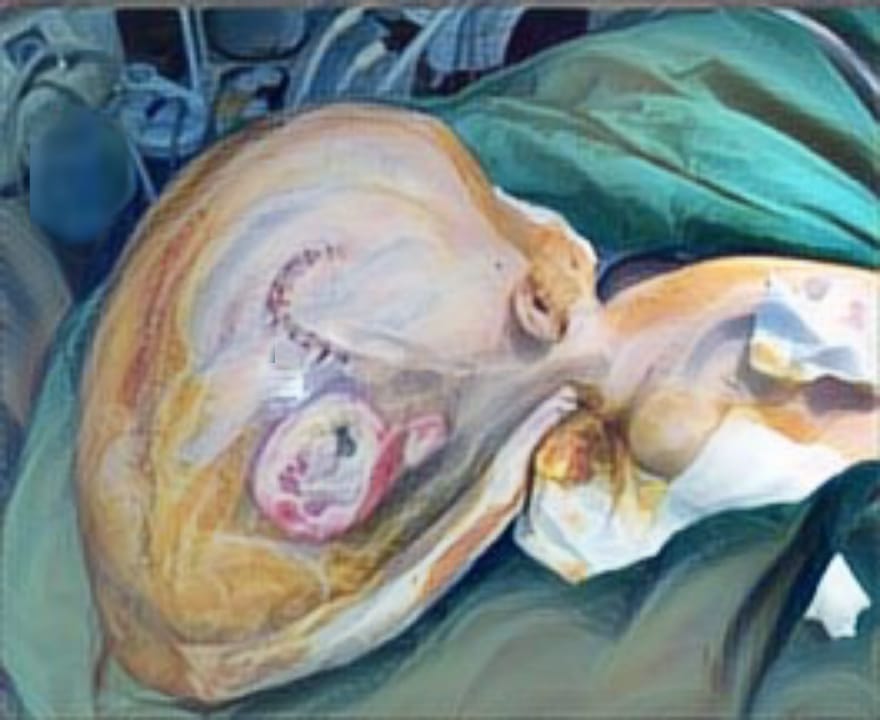
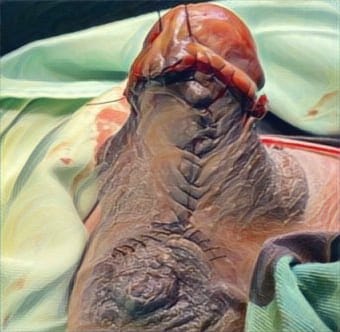
Methods: This study used a retrospective cohort design taken from 40 medical records at Cleft Lip and Palate (CLP) Center Faculty of Medicine University of Muhammadiyah Malang. The preoperative photo data were categorized according to the severity of the cleft, then postoperative photos were assessed according to the Visual Rating Chart (VRC) indicator.
Results: The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) reliability test between evaluators has a strength of > 0.8 on the outcome of lip and nose surgery and also > 0.9 on the outcome of the palate, indicating that there was no perception gap between evaluators. The Mann-Whitney non-parametric test had a significance of p < 0.05, indicating that there was a positive correlation between the severity of unilateral cleft lip and palate and the outcome of surgery.
Conclusion: There is a correlation between the severity of the unilateral cleft lip and palate and the surgical outcome.
Lanteri AC, et al. A Cross-sectional Comparison of Cleft Lip Severity in 3 Regional Populations. Eplasty 2012; 12: e10.
V J. Penanganan Bibir sumbing dan malformasi langit"langit. Intisari Sains Medis 2015; 2: 19–21.
Davita TR, Narmada S SH. Permasalahan orang tua peserta bakti sosial operasi bibir dan langit-langit sumbing di Gunungkidul, DI Yogyakarta. Cermin Dunia Kedokt 2017; 44: 607–9.
AR R. Distribusi Sumbing bibir dan langit-langit di Cleft Lip and Palate Center Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Muhammadiyah Malang Indonesia. Saintika Med 2017; 11: 76–7.
Campbell A, et al. Validation of the unilateral cleft lip severity index for surgeons and laypersons. Plast Reconstr Surg - Glob Open 2017; 5: e1479.
Campbell A, et al. Influence of severity on aesthetic outcomes of unilateral cleft lip repair in 1,823 patients. Plast Reconstr Surg - Glob Open 2019; 7: e2083.
Adeola AO OA. Developing a visual rating chart for the esthetic outcome of unilateral cleft lip and palate repair. Ann Maxillofac Surg 2015; 5: 55–61.
Ittiwut, et al. Epidemiology of cleft lip with or without cleft palate in Thais. Asian Biomed 2017; 10: 335–338.
Yow, M., Jin, A., & Yeo GSH. Epidemiologic trends of infants with orofacial clefts in a multiethnic country: a retrospective population-based study. Sci Reports, 2021; 11: 7556.
Wang M, et al. Prevalence of Orofacial Clefts among Live Births in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Birth Defects Res 2017; 109: 1011–1019.
Sharif F, et al. Incidence and management of cleft lip and palate in Pakistan. J Pak Med Assoc 2019; 69: 632–639.
Nagappan N, John J. Oral hygiene and dental caries status among patients with cleft lip, cleft palate and cleft lip, alveolus and palate in Chennai, India. J Cleft Lip Palate Craniofacial Anomalies 2015; 2: 49.
Khajanchi MU, et al. Unmet Burden of Cleft Lip and Palate in Rural Gujarat, India: A Population-Based Study. World J Surg 2015; 39: 41–46.
Jaisani, Mehul R.; et al. Oro-facial clefts at a tertiary level hospital of eastern Nepal: A retrospective insight. J Cleft Lip Palate Craniofacial Anomalies 2022; 9: 30–35.
Borno HT, et al. Incidence of Cleft Lip and Palate in the Palestinian Territories: A Retrospective Study from the Makassed Hospital Neonatal Unit. Cleft Palate-Craniofacial J 2014; 51: 472–475.
Elfiah, U., et al. ANALISIS KEJADIAN SUMBING BIBIR DAN LANGIT: STUDI DESKRIPTIFBERDASARKAN TINJAUAN GEOGRAFIS. J Rekonstruksi Dan Estet 2021; 6: 34–43.
Carroll K, Mossey PA. Anatomical Variations in Clefts of the Lip with or without Cleft Palate. Plast Surg Int 2012; 2012: 1–6.
Azzaldeen A. Genetic of Non-syndromic Cleft Lip and Palate. Dentistry; 01. Epub ahead of print 2012. DOI: 10.4172/scientificreports.510.
Chairunnisa, R., & Syafrinani HR. Feeding Plate Fabrication for Infants with Cleft Palate Congenital Disorder at Mitra Sejati Hospital Medan and Grandmed Hospital Lubuk Pakam. dentika Dent journal 2022; 25: 15–21.
Vyas T, et al. Cleft of lip and palate : A review. J Fam Med Prim Care 2020; 9: 2621–5.
Zainul Abidin SNN, et al. Evaluation of the post-labioplasty result according to the comprehensive assessment performed by Indonesian Cleft Center team. Padjadjaran J Dent; 27. Epub ahead of print 31 March 2015. DOI: 10.24198/pjd.vol27no1.26688.
Chopan M, et al. Surgical Techniques for Treatment of Unilateral Cleft Lip. In: Designing Strategies for Cleft Lip and Palate Care. InTech. Epub ahead of print 22 March 2017. DOI: 10.5772/67124.
Rajanikanth BR, et al. Assessment of Deformities of the Lip and Nose in Cleft Lip Alveolus and Palate Patients by a Rating Scale. J Maxillofac Oral Surg 2012; 11: 38–46.
Abdurrazaq T, et al. Surgical outcome and complications following cleft lip and palate repair in a teaching hospital in Nigeria. African J Paediatr Surg 2013; 10: 345–57.
Rossell-Perry P, et al. Association Between Palatal Index and Cleft Palate Repair Outcomes in Patients With Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate. JAMA Facial Plast Surg 2014; 16: 206–210.
Copyright (c) 2023 Ruby Riana Asparini, Nur Khalida Zia, Bragastio Sidharta, Jeyasree Sakthivel, Bhuvana Sri Naga

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
JURNAL REKONSTRUKSI DAN ESTETIK by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold copyright of the article without restriction
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessbility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA)