RECURRENT TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT ANKYLOSIS CAUSED BY OLD FRACTURE: A CASE REPORT
Downloads
Highlights:
- Adequate physiotherapy is essential to prevent the recurrence of temporomandibular joint ankylosis.
- Surgical treatment alone is insufficient without proper postoperative physiotherapy and patient compliance.
Abstract
Introduction: Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) ankylosis can greatly impact a child's nutrition, mental health, and craniofacial development. Trauma is the main cause. Early and proper treatment is crucial to avoid long-term issues and reoccurrence.
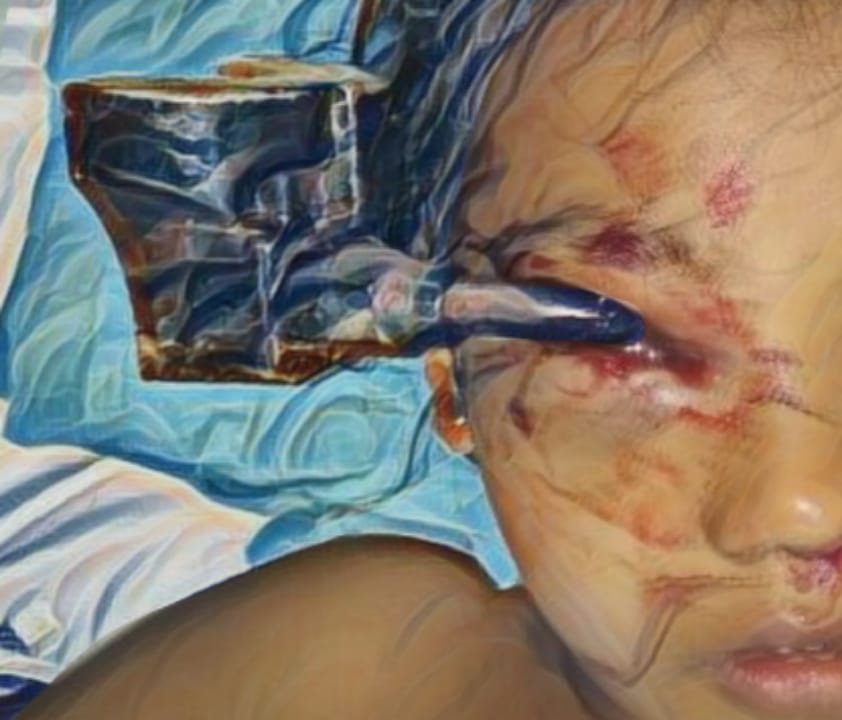
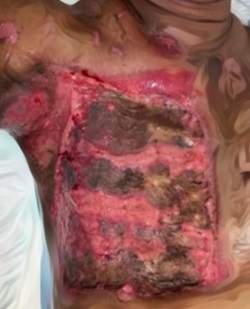
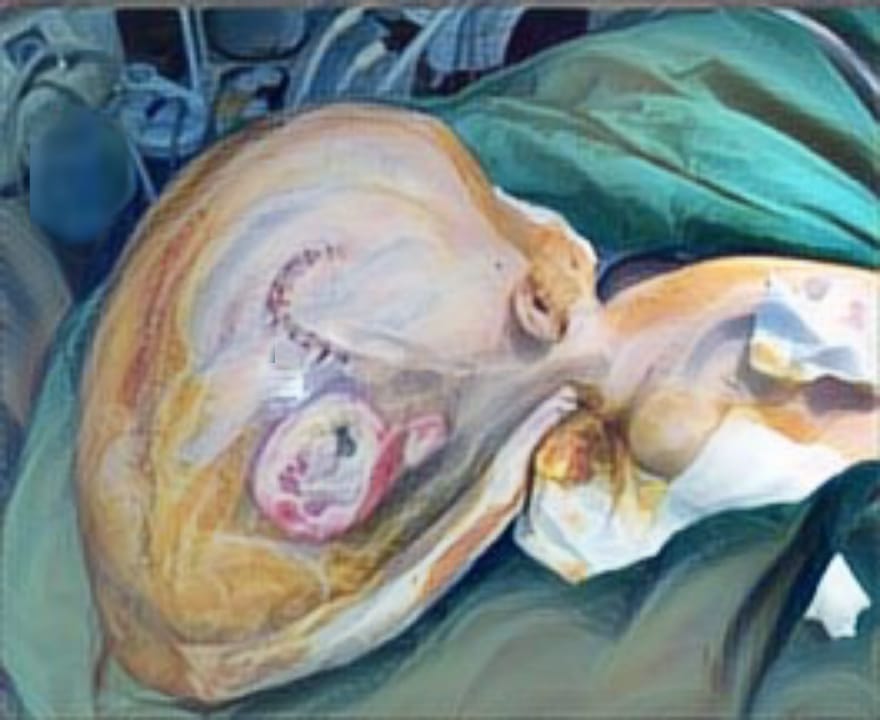
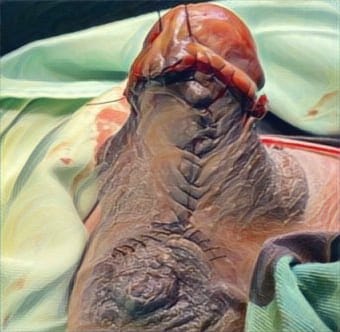
Case Illustration:An 11-year-old girl presented with limited mouth opening and lower jaw pain three years after falling down the stairs. She underwent gradual TMJ distraction using bite blocks under general anesthesia followed by weekly physiotherapy, but her symptoms recurred after four months. A CT scan revealed left TMJ synarthrosis and condylar deformity. With improved adherence to physiotherapy, she achieved significant mouth opening and remained recurrence-free for six months..
Discussion: Gradual distraction with bite blocks, combined with regular physiotherapy, can improve joint mobility and muscle function while lowering the chances of re-ankylosis. This approach offers a less invasive option than surgery, which is especially valuable for children whose growth must be preserved. Closed procedures with structured rehabilitation are preferred because they result in fewer complications and require fewer follow-up appointments.
Conclusion: The effectiveness of a non-invasive approach combining gradual distraction and physiotherapy in managing TMJ ankylosis is presented. The success of this treatment relies heavily on the patient's motivation and commitment. Early conservative treatment could be the main strategy for pediatric cases, potentially delaying or avoiding surgery. Continuous education and monitoring are key to achieving long-term success and preventing relapse.
Mekonnen D, Gizaw A & Kebede B. Temporomandibular joint ankylosis among patients at Saint Paul’s Hospital Millennium Medical College, Ethiopia: a 9-year retrospective study. Int J Dent. 2021;6695664.DOI:10.1155/2021/669566 4
Xu F, Jiang L & Man C. A comparative study of different surgical methods in the treatment of traumatic temporomandibular joint ankylosis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;46(2):198–203.DOI:10.1016/j.ijom. 2016. 08.020
Saini RS, Ibrahim M, Khader MA, Kanji MA, Mosaddad SA & Heboyan A. The role of physiotherapy interventions in the management of temporomandibular joint ankylosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Face Med. 2024;20(1):1–19. DOI: 10.1186/s13005-024-00416
Newman MF, Floodeen E & Gardner Z. Tracheostomy in temporomandibular joint ankylosis – a review of the literature and case report. Adv Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2025;17:100512. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2667147624000347
Rahman SA & Haider IA. Temporomandibular joint ankylosis pattern, causes, and management among pediatric patients attending a tertiary hospital in Bangladesh. J Oral Res Rev. 2021;13(2): 115–20.
Andrade NN, Nerurkar SA, Mathai P & Aggarwal N. Modified cut for gap arthroplasty in temporomandibular joint ankylosis. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2019;9(2): 400–402.
Mishra N, Sharma NK, Dhiman NK, Jaiswara C, Tiwari P & Singh AK. Temporomandibular joint ankylosis: A tertiary center-based epidemiological study. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2021; 12(3):392–396. DOI:10.4103/njms. NJMS _57_20
Anchlia S. Temporomandibular Joint Ankylosis. In: Bonanthaya K, Panneerselvam E, Manuel S, Kumar VV, Rai A, editors. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery for the Clinician. Singapore: Springer;2021:1401–34.DOI:10.1007/978- 981-15-1346-6_65
Wang WH, Xu B, Zhang BJ & Lou HQ. Temporomandibular joint ankylosis contributing to coronoid process hyperplasia. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016; 45(10): 1229–33.DOI: 10.1016/ j.ijom.2016.04.018
d’Apuzzo F, Minervini G, Grassia V, Rotolo RP, Perillo L & Nucci L. Mandibular coronoid process hypertrophy: diagnosis and 20-year follow-up with CBCT, MRI and EMG evaluations. Appl Sci.2021;11(10):4504. DOI:10.3390/app11 10450
Sharma A, Paeng JY, Yamada T & Kwon TG. Simultaneous gap arthroplasty and intraoral distraction and secondary contouring surgery for unilateral temporomandibular joint ankylosis. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016; 38 (1):58. DOI: 10.1186/s40902-016-0058-0
Park MW, Eo MY, Seo BY, Nguyen TTH & Kim SM. Gap arthroplasty with active mouth opening exercises using an interocclusal splint in temporomandibular joint ankylosis patients. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;41(1):29. DOI: 10.1186/s40902-019-0220-z
Alam MK, Rashid ME, Akhter K, Abdelghani A, Babkair HA & Sghaireen MG. Surgical vs. non-surgical management of temporomandibular joint disorders: clinical outcomes. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024;16(Suppl 1):S678–80.
Kalita F & Arunkumar KV. Temporomandibular joint re-ankylosis: a case report and literature review. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2023; 49(4): 218–222. DOI: 10.5125/jkaoms. 2023.49.4. 218
Yadav P, Roychoudhury A & Bhutia O. Strategies to reduce re-ankylosis in temporomandibular joint ankylosis patients. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021; 59(7): 820–825. DOI: 10.1016/j.bjoms. 2021.02.0 07
Malhotra P, Venkatesh R, Shah D, Badi K & Chandalia S. Management of unilateral temporomandibular joint ankylosis by interpositional arthroplasty and bilateral coronoidectomy. J Sci Soc. 2023;50(3): 41 0–413.
Makayasa Putri KK & Nugroho DS. Assessment of maxillofacial trauma in Kanjuruhan General Hospital Malang using Facial Injury Severity Scale (FISS) scoring system. Jurnal Rekonstruksi dan Estetik.2025;10(1):47–55.DOI: 10.20473/ jre.v10i1. 70277.
Morisada MV, Tollefson TT, Said M, Hwang J, Hsieh TY & Funamura JL. Pediatric mandible fractures: mechanism, pattern of injury, fracture characteristics, and management by age. Facial Plast Surg Aesthet Med. 2022;24(5):375–81. DOI: 10.1089/fpsam.2022.0031.
Hofmann E, Koerdt S, Heiland M, Raguse JD & Voss JO. Pediatric maxillofacial trauma: insights into diagnosis and treatment of mandibular fractures in pediatric patients. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2023;16(3):499–509. DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2401.
Pratiwi CA, Amirsyah M & Putra TN. Implementation of an occlusal wafer in severe mandibular fracture cases with post-ORIF malocclusion: a case series. Jurnal Rekonstruksi dan Estetik. 2024; 9(2):91–9. DOI: 10.20473/ jre.v9i2.54889.
Perdanakusuma AR, Primawati A & Budiman. Microautologous fat transplantation (MAFT) sebagai rekonstruksi lanjutan pada kasus deformitas maksilofasial pasca trauma. Jurnal Rekonstruksi dan Estetik. 2021; 6(2): 44–52. DOI: 10.20473/jre.v6i2.31 832.
Buschang PH, Santos-Pinto A & Demirjian A. Incremental growth charts for condylar growth between 6 and 16 years of age. Eur J Orthod. 1999; 21(2): 167–173. DOI: 10.1093/ejo/21.2.167
Gravaldi LP, Bonetti F, Lezzerini S & De Maio F. Effectiveness of physiotherapy in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Healthcare (Basel). 2022; 10(1): 132. DOI: 10.3390/ healthcare10010132
Andrade NN, Kapoor P, Mathai P, Gupta V, Lakshmi VK & Sharma S. Management of paediatric ankylosis. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2023;13(2): 191–201. DOI: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2023.01. 006
Shetty V, Nanda Kishore P, Khanum A, Yadav A & Sailer HF. Retrospective analysis of a TMJ ankylosis protocol with a 9-year follow-up. J
Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2019; 47(12):1903–12. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcms. 2019.11.003
Copyright (c) 2025 Siti Isya Wahdini, Fina Idamatussilmi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
JURNAL REKONSTRUKSI DAN ESTETIK by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold copyright of the article without restriction
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessbility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA)