CHRONIC WOUNDS : RISK FACTORS AND EVIDENCE-BASED INTERVENTION
Downloads
Highlights:
- Identifies key risk factors for chronic wounds and the underexplored role of genetics and immune dysregulation in healing.
- Explores advanced interventions like smart bandages and bioengineered skin, while addressing accessibility challenges.
- Highlights the potential of personalized medicine and digital health in improving patient-centered wound care.
Abstract:
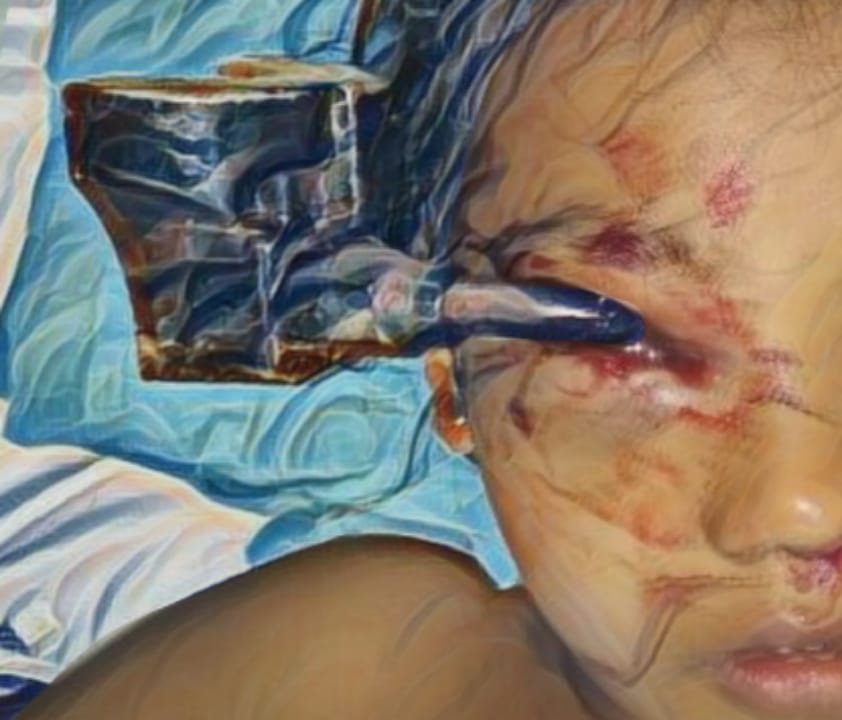
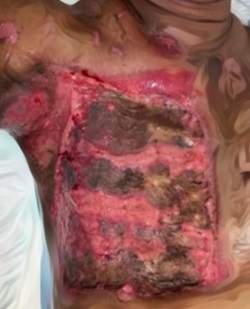
Introduction: Chronic wounds are a pervasive and escalating public health issue, characterized by their inability to progress through the typical phases of healing, resulting in prolonged tissue damage and patient morbidity. Common types include diabetic, pressure, arterial, and venous ulcers. Factors like comorbidities, infection, poor circulation, and inadequate care delay healing. This review aims to explore the risk factors for chronic wounds and evaluate evidence-based interventions to optimize treatment outcomes, thereby improving patient care and reducing healthcare costs.
Methods: A thorough literature review was performed using peer-reviewed journals and reliable medical databases, focusing on articles from the past 10 years for relevance. The search used keywords like "chronic wounds," "risk factors," "management," and "evidence-based interventions," selecting studies that addressed the epidemiology, causes, and treatment of chronic wounds.
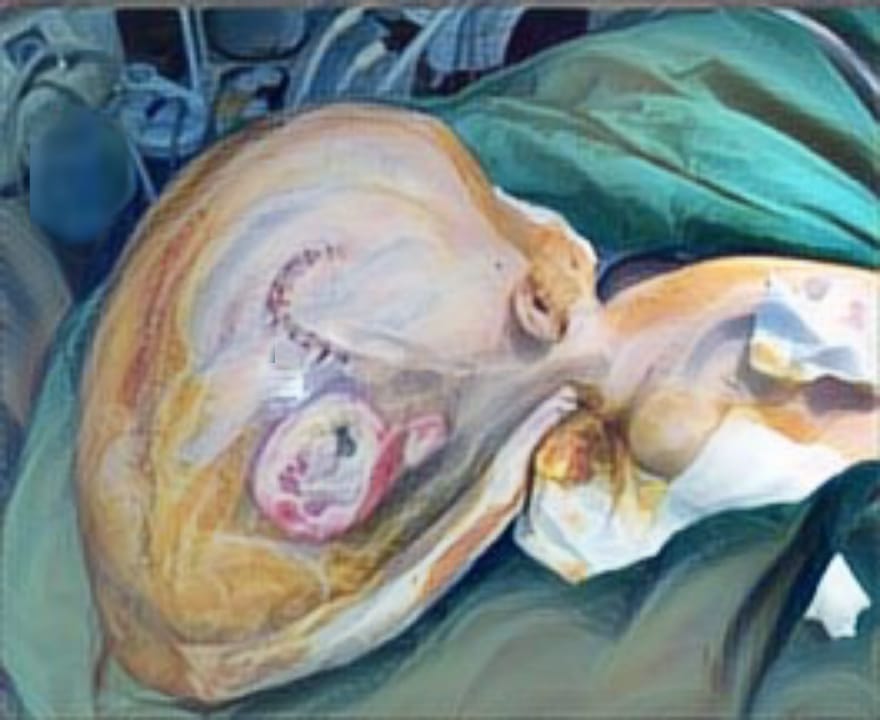
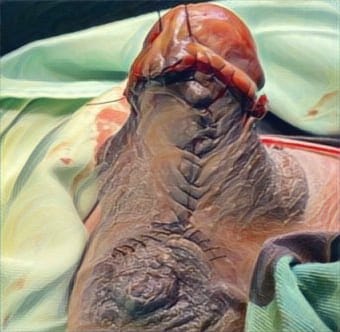
Results: The review identified major risk factors for chronic wounds, such as diabetes, poor circulation, neuropathy, infection, and aging. Effective treatments discussed include advanced dressings, debridement, negative pressure wound therapy, and skin grafts. A multidisciplinary, patient-focused approach was found to improve healing outcomes.
Conclusion: Understanding the risk factors of chronic wounds and applying evidence-based, personalized treatments can significantly improve healing outcomes. Ongoing research and innovation are essential to address gaps in care and enhance patient management.
Sawaya AP, Stone RC, Brooks SR, Pastar I, Jozic I, Hasneen K, et al. Deregulated immune cell recruitment orchestrated by FOXM1 impairs human diabetic wound healing. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):4678. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-18276-0. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32938916.
Vos T, Allen C, Arora M, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Brown A, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016; 388(10053):1545-1602. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6.
Mathews S. Researchers uncover clues to why some wounds don’t heal. NIAMS. 2020. Available from: https://www.niams.nih.gov/newsroom/spotlight-on-research/researchers-uncover-clues-why-some-wounds-dont-heal.
National Institutes of Health. Poor immune response impairs diabetic wound healing. NIH Research Matters. 2020. Available from: https://www.nih.gov/news-events/nih-research-matters/poor-immune-response-impairs-diabetic-wound-healing.
Gupta S, Sagar S, Maheshwari G, Kisaka T & Tripathi S. Chronic wounds: Magnitude, socioeconomic burden, and consequences. Wounds Asia. 2021; 4(1): 8-14.
Gurtner G. To heal a wound. NIH News in Health. 2020. Available from: https://newsinhealth.nih.gov/2023/10/heal-wound.
Jiang Y, Trotsyuk AA, Niu S, Henn D, Chen K, Shih CC, et al. Wireless, closed-loop, smart bandage with integrated sensors and stimulators for advanced wound care and accelerated healing. Nat Biomed Eng. 2020; 4:484-95. DOI: 10.1038/s415 87-022-01528-3.
Porel P, Kaur M, Sharma V & Aran KR. Understanding molecular mechanism of diabetic wound healing: addressing recent advancements in therapeutic managements. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025;24(1):1-15. DOI: 10.1007/s40200-025-01588-7.
Baty M, Chimoriya R, James S, Kritharides L, Behdasht S, Suryawanshi A & Aitken SJ. Diabetes in peripheral artery disease: prevalence, complications, and polypharmacy. J Clin Med. 2025; 14(4): 1383. DOI: 10.3390/jcm14041383.
Orduyan SL, Hakobyan EK & Simonyants LG. Treatment of chronic wounds: Standard approaches and strategies (A literature review). Synthesis. 2024;18:41. DOI: 10.56936/18291775-2024.38-26.
Hierner R, Degreef H, Vranckx JJ, Garmyn M, Massagé P & van Brussel M. Clinics in Dermatology. 2005;23(4):343-352. DOI: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2004.07.028.
Gottrup F. A specialized wound-healing center concept: importance of a multidisciplinary department structure and surgical treatment facilities in the treatment of chronic wounds. Am J Surg. 2004; 187(5Suppl): S38-S43. DOI: 10.10 16/S0002-9610(03)00303-9.
Ho J, Walsh C, Yue D, Dardik A & Cheema U. Current advancements and strategies in tissue engineering for wound healing: a comprehensive review. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2017;6(6):191-209. DOI: 10.1089/wound.2016.0723.
Swezey L. How obesity impacts wound healing. WoundSource. 2015. Available from: https://www.woundsource.com/blog/how-obesity-impacts-wound-healing.
Guo S & DiPietro LA. Factors affecting wound healing. J Dent Res. 2019; 89(3): 219-229. DOI: 10.1177/0022034509359 125.
Diban F, Di Lodovico S, Di Fermo P, D’Ercole S, D’Arcangelo S, Di Giulio M & Cellini L. Biofilms in chronic wound infections: innovative antimicrobial approaches using the in vitro Lubbock chronic wound biofilm model. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1004. DOI: 10.3390/ijms 24021004.
Wu SC, Marston W & Armstrong DG. Wound care: the role of advanced wound healing technologies. J Vasc Surg. 2010; 52 (3Suppl): 59S-66S. DOI: 10.1016/ j.jvs. 2010.06.009.
World Health Organization. Ageing and health. Geneva: WHO; 2021. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health.
Gould L, Abadir P, Brem H, Carter M, Conner-Kerr T, Davidson J, et al. Chronic wound repair and healing in older adults: current status and future research. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015;63(3):427-438. DOI: 10.1111/wrr.12245.
Keenan C, Obaidi N, Neelon J, Yau I, Carlsson AH & Nuutila K. Negative pressure wound therapy: challenges, novel techniques, and future perspectives. Adv Wound Care. 2025;14(1):33-47. DOI: 10.1089/wound. 2023.0157.
Prakashan D, Kaushik A & Gandhi S. Smart sensors and wound dressings: Artificial intelligence-supported chronic skin monitoring–A review. Chem Eng J. 2024; 154371. DOI:10.1016/j.cej.2024. 154371.
Frasier K, Baptiste C, Javaid S, Neman S & Vinagolu-Baur J. Understanding barriers to wound care access and chronic wound management for veterans. Annal Cas Rep Rev. 2024;ACRR-379. DOI: 10.39127/2574-5747/ACRR:1000379.
Mayer DO, Tettelbach WH, Ciprandi G, Downie F, Hampton J, Hodgson H, et al. Best practice for wound debridement. J Wound Care. 2024;33(Sup6b):S1-S32. DOI: 10.12968/jowc.2024.33.Sup6b.S1.
Jain K, Avsar P, Patton D, Moore Z & Murray B. What specific challenges do patients with chronic wounds encounter when attending medical appointments related to wound care? A systematic review. J Tissue Viability. 2025;100865. DOI: 10.1016/j.jtv.2025.100865.
Kumar P, Hasan F, Kumar V, Chawla R & Goyal SK. Diabetic wound healing: Navigating physiology, advancements and research frontiers. J Diabetes Res Rev Rep. 2024; SRC/JDRR-202:181-211. DOI: 10.47363/JDRR/2024(6).
Mishra A, Kushare A, Gupta MN & Ambre P. Advanced dressings for chronic wound management. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024; 7(5): 2660-2676. DOI: 10.1021/acsabm. 4c00138.
Díaz-Herrera MÁ, González-Durán M, Rodríguez-Martínez FJ, Tujillo-Flores G, Tuset-Mateu N, Verdú-Soriano J, et al. The financial burden of chronic wounds in primary care: A real-world data analysis on cost and prevalence. Int J Nurs Stud Adv. 2025;100313. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijnsa.2025.100313.
Basu S, Goswami AG, David LE & Mudge E. Psychological stress on wound healing: a silent player in a complex background. Int J Lower Extrem Wounds. 2024; 23(3): 365-371. DOI: 10.1177/153473462 2107 7571.
Wojda P. Cultural aspects of wound care. Leczenie Ran. 2023;20(1):26-34. DOI: 10.5114/lr.2023.126304.
Natarajan D, Williamson AJ, Stiltz K & Harding K. Advances in wound care and healing technology. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2000; 1(5):269-275. DOI: 10.2165/0012 8071-200001050-00002.
Falanga V, Isseroff RR, Soulika AM, Romanelli M, Margolis D, Kapp S, et al. Chronic wounds. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022;8(1):50. DOI: 10.1038/s41572-02 2-00377-3.
Toppino S, Koffi DY, Kone BV, N’Krumah RT, Coulibaly ID, Tobian F, et al. Community-based wound management in a rural setting of Côte d’Ivoire. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022;16(10):e0010730. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010730.
Barbu VS, Gaboreanu MD, Marinas IC, Paun AM, Ionel IP & Avram S. Implications of biomaterials for chronic wounds. Mini-Rev Med Chem. 2025. DOI: 10.2174/0113895575314580241121080256.
Hossain MI, Zahid MS, Chowdhury MA, Hossain MM, Hossain N, Islam MA & Mobarak MH. Smart bandage: A device for wound monitoring and targeted treatment. Results Chem. 2024;7:101292. DOI: 10.1016/j.rechem.2023.101292.
Derakhshandeh H, Saheb Kashaf S, Aghabaglou F, Ghanavati I & Tamayol A. Smart bandages: The future of wound care. Trends Biotechnol. 2018; 36(12): 1259-1274. DOI: 10.1016/j.tibtech. 2018. 07.007.
Fetterolf DE. Estimating the economic value of emerging technologies in chronic wound therapy. Int Wound J. 2019; 16(6): 1391-1397. DOI: 10.1111/ iwj.13202.
Falcone M, De Angelis B, Pea F, Scalise A, Stefani S, Tasinato R, et al. Challenges in the management of chronic wound infections. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2021; 26: 140-147. DOI: 10.1016/j.jgar. 2021. 05.010.
Copyright (c) 2025 Veronica Abebia Beginanta Pinem, David Sontani Perdanakusuma, Evy Ervianti, Mikiyas Gifawosen Teferi, Harith Ali Al-Taie

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
JURNAL REKONSTRUKSI DAN ESTETIK by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold copyright of the article without restriction
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessbility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA)