WOUND HEALING EFFICACY OF MOIST EXPOSED BURN OINTMENT (MEBO) AND SILVER SULFADIAZINE IN PARTIAL-THICKNESS BURNS: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW

Downloads
Highlights:
- Superior efficacy between MEBO and SSD in burn patients.
- Improved Clinical Outcomes of wound healing in burn patients.
- Natural, Plant-Based Alternative for burn patients.
Abstract:
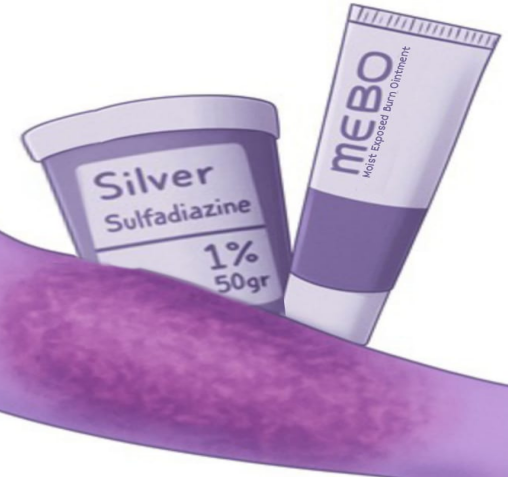
Introduction: Burn injuries are a common global health issue that often require prolonged wound care and can lead to complications such as infections, delayed healing, and surgical interventions. Silver sulfadiazine (SSD) has long been the standard topical treatment for partial-thickness burns, but concerns remain regarding delayed healing and potential side effects. Moist Exposed Burn Ointment (MEBO), a Chinese herbal-based topical agent containing sesame oil, beta-sitosterol, and berberine, has emerged as a potential alternative due to its anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and moisture-retaining properties.
Method: This systematic review aimed to evaluate the efficacy of MEBO compared to SSD in partial-thickness burn wound healing. A comprehensive search of PubMed, Cochrane, and Science Direct using the terms “MEBO,” “SSD,” “Burns,” and “Wound healing” identified five trials conducted between 2000 and 2008.
Result: The results consistently demonstrated that MEBO provided comparable or superior outcomes to SSD, including shorter wound healing time, reduced pain, absence of infection in wound swabs, minimal slough and crust formation, lower complication rates, and reduced need for surgical intervention.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that MEBO is an effective and potentially preferable alternative to SSD for managing partial-thickness burn wounds.
Hirsch T, Ashkar W, Schumacher O, Steinstraesser L, Ingianni G & Cedidi CC. Moist Exposed Burn Ointment (MEBO) in partial-thickness burns: a randomized, comparative open mono-center study on the efficacy of Dermaheal (MEBO) ointment on thermal second-degree burns compared to conventional therapy. Eur J Med Res. 2008;13 (11): 505–510. PMID: 19073386.
Ang ES, Lee ST, Gan CS, See P, Chan YH, Ng LH, et al. The role of alternative therapy in the management of partial-thickness burns of the face: experience with the use of moist exposed burn ointment (MEBO) compared with silver sulphadiazine. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2000; 29(1): 7–10. DOI: 10.47102/ annals-acadmedsg. V29N1p7. PMID: 10748957.
Allam AM, Mostafa W, Zayed E & El-Gamaly J. Management of the acute partial-thickness burned hand: moist exposed burn ointment or silver sulphadiazine cream both combined with a polyethylene bag. Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2007; 20(3): 144–148. PMID: 21991086; PMCID: PMC3188072.
Ang E, Lee ST, Gan CS, Chan YH, Cheung YB & Machin D. Pain control in a randomized, controlled clinical trial comparing moist exposed burn ointment and conventional methods in patients with partial-thickness burns. J Burn Care Rehabil. 2003;24(5):289–296. DOI: 10.1097/01.BCR.0000085846.875 85.B7. PMID: 14501397.
Atiyeh BS, Dham R, Kadry M, Abdallah AF, Al-Oteify M, Fathi O, et al. Benefit–cost analysis of moist exposed burn ointment. Burns. 2002; 28(7): 659–663. DOI: 10.1016/S0305-4179(02)00075-X. PMID: 12417161.
Oaks RJ, Cindass R. Silver Sulfadiazine. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 [cited 2025 Apr 21]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556054/
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J & Altman DG; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. 2009;339:b2535.
Review Manager (RevMan) [Computer program]. Version 9.3.0. The Cochrane Collaboration; 2025 [cited 2025 Jun 2]. Available from: https://revman.cochrane.org
Sterne JA, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2019;366:l4898. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.l4898. PMID:314625 31.
Copyright (c) 2025 Aditya Wardhana, Nadya Farhana

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
JURNAL REKONSTRUKSI DAN ESTETIK by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold copyright of the article without restriction
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessbility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA)