COMPARATIVE OUTCOMES OF EARLY VERSUS DELAYED WOUND GRAFTING IN BURN PATIENTS: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS
Downloads
Highlights:
- Early wound grafting appears to improve hospital stay duration and functional recovery.
- There is a tendency of higher graft success rates and reduced infection risks compared to delayed grafting in burn patients.
Abstract:
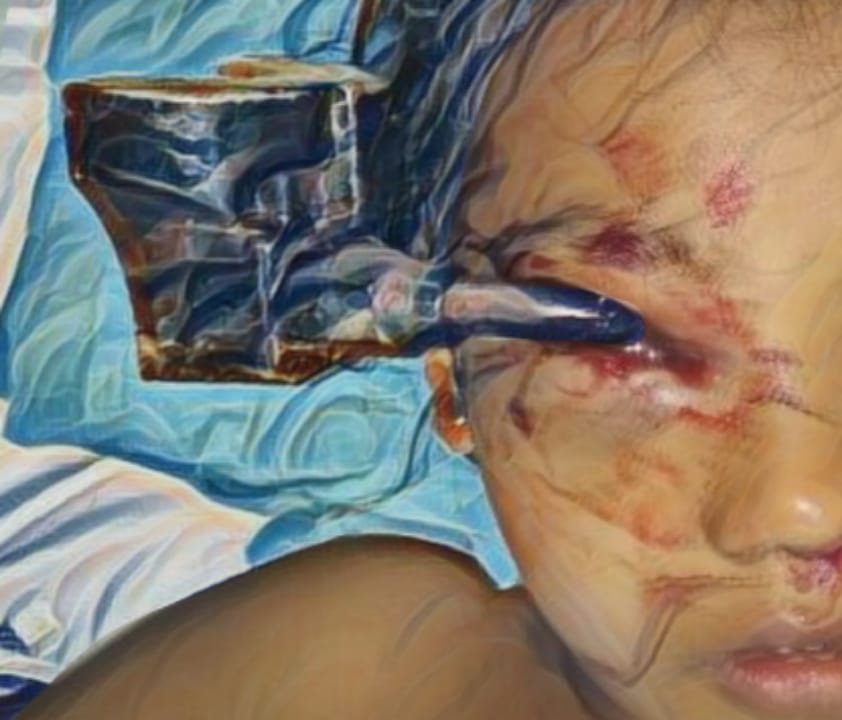
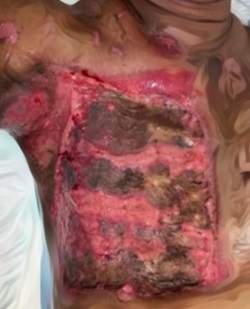
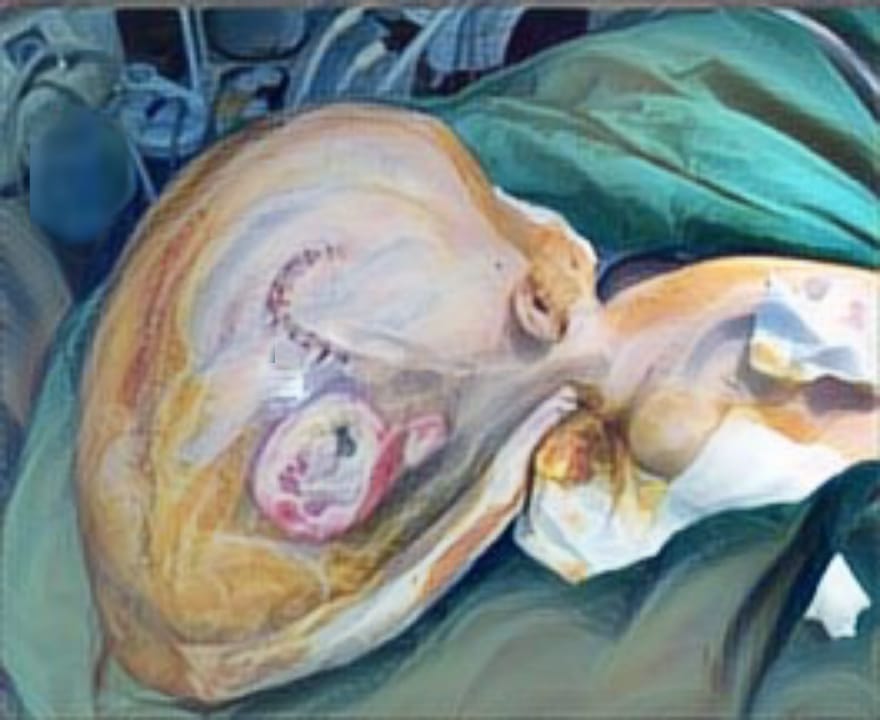
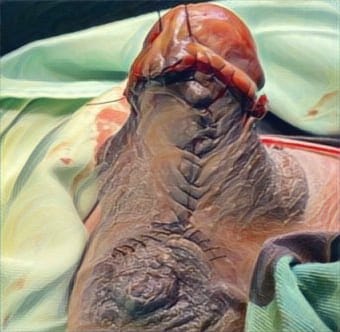
Introductions: Burns are a significant global health issue, with over 265 million cases annually. Effective burn wound treatment is crucial, and the timing of surgical skin grafting plays a key role in recovery. Early excision and grafting, typically within 48 hours, is standard practice as it reduces morbidity, mortality, infection, graft failure, and hospitalization. Delaying grafting increases infection risk, while early intervention has been shown to improve wound healing. However, challenges like poor resuscitation and resource limitations may hinder early grafting, particularly in low-resource settings. This review evaluates the evidence on optimal grafting timing in burn patients.
Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted. A literature search was conducted from July 2024 to January 2025 comparing early (within 3-7 days) versus delayed (after 7 days) grafting. Studies included randomized controlled trials, cohort studies, and observational studies, with outcomes focused on hospitalization duration, infection rates, blood loss, and limb functionality.
Results: Of 250 studies identified, seven met eligibility criteria. Early grafting significantly reduced hospital stay by 8.89 days (95% CI: -12.88 to -4.89) compared to delayed grafting. No significant differences were observed between early and delayed grafting in terms of blood loss, infection rates, or post-operative grip strength. However, early grafting resulted in better post-operative Total Active Movement (TAM) scores (MD: 22.10 [95% CI: 17.95 to 26.24]).
Conclusion: Early grafting improves hospital recovery and functional outcomes. Further research is needed to confirm these findings.
Kuznetsova TA, Andryukov BG, Polovov SF & Gazha AK. Modern aspects of burn injury immunopathogenesis and immuno-biochemical markers of wound healing: a literature review. Klin Lab Diagn. 2022; 67(8): 451–457. DOI:10.51620/0869-2084-2022-67-8-451-457.
Rahman NA, Devina S, Pradana MYB, Ozokolie GE, Daodu LP & Pandey S. Regenerative medicine in burn injury: a bibliometric analysis and literature review. J Rekonstruksi Estetik. 2024; 9(1): 61–77. DOI:10.20473/jre.v9i1.56 491.
Radzikowska-Büchner E, Łopuszyńska I, Flieger W, Tobiasz M, Maciejewski R & Flieger J. An overview of recent developments in the management of burn injuries. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24(22): 16357. DOI:10.3390/ijms242216357.
Hernández DKE, Ursua TPM, Rodriguez HDA, Simonin LJD, Garza LEA, Paniagua EDI, et al. Advanced management of the burn patient. Int J Med Sci Clin Res Stud. 2023;3(10):2277–2280. DOI:10.47191/ ijmscrs/v3-i10-31.
Ruiz Velasco-Cisneros RA, Bracamontes-Gutierrez JC, Acosta-Sandoval MA, Leiva-Rodríguez LE, Siordia-Cruz NS, Guerrero-Andrade A, et al. Comprehensive care for burn patients. Int J Med Sci Clin Res Stud. 2024; 4(8): 1461–1463. DOI:10.47191/ ijmscrs/v4-i08-07.
Ramsey WA, O'Neil CF Jr, Corona AM, Cohen BL, Lyons NB, Meece MS, et al. Burn excision within 48 hours portends better outcomes than standard management: a nationwide analysis. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2023; 95(1): 111–115. DOI:10.1097/TA.000000000 0003951.
Huff ML & Blome-Eberwein S. Providencia rettgeri infection compromising post-burn recovery: a lesson in the importance of follow-up care. Cureus. 2022; 14(5): e25039. DOI:110.7759/cureus.25450
Badr MLA, Keshk TF, Alkhateeb YM & El Refaai AME. Early excision and grafting versus delayed grafting in deep burns of the hand. Int Surg J. 2019; 6(10): 3530–5. DOI:10.18203/2349-2902.isj 20194404.
Griffin B, Bairagi A, Jones L, Dettrick Z, Holbert M & Kimble R. Early non-excisional debridement of paediatric burns under general anaesthesia reduces time to re-epithelialisation and risk of skin graft. Sci Rep. 2021; 11(1): 23753. DOI:10.1038/s41598-021-031 41-x.
Abdelrahman I, Steinvall I, Sjöberg F, Ellabban MA, Zdolsek J & Elmasry M. Pros and cons of early and late skin grafting in children with burns—evaluation of common concepts. Eur Burn J. 2022; 3(1): 180–7. DOI:10.33 90/ebj3010015.
Goswami P, Sahu S, Singodia P, Kumar M, Tudu T, Kumar A, et al. Early excision and grafting in burns: an experience in a tertiary care industrial hospital of Eastern India. Indian J Plast Surg. 2019; 52(3): 337–342. DOI:10.10 55/s-0039-3402707.
Ayaz M, Karami MY, Deilami I & Moradzadeh Z. Effects of early versus delayed excision and grafting on restoring the functionality of deep burn-injured hands: a double-blind, randomized parallel clinical trial. J Burn Care Res. 2019; 40(4): 451–456. DOI:10.1093/jbcr/irz033.
Puri V, Khare NA, Chandramouli M, Shende N & Bharadwaj S. Comparative analysis of early excision and grafting vs delayed grafting in burn patients in a developing country. J Burn Care Res. 2016; 37(5): 278–282. DOI:10.1097/ BCR.0b013e31827e4ed6.
Salehi SH, Fatemi MJ, Sedghi M & Niazi M. Effects of early versus delayed excision and grafting on the return of the burned hand function. J Res Med Sci. 2016; 21(1): 109. DOI:10.4103/1735-1995.193501.
Keshavarzi A, Ayaz M & Dehghankhalili M. Ultra-early versus early excision and grafting for thermal burns up to 60% total body surface area: a historical cohort study. Bull Emerg Trauma. 2016;4(4):197–201. PMID:27853694.
Ayaz M, Bahadoran H, Arasteh P & Keshavarzi A. Less than 15% of total body surface area: a non-randomized clinical trial. Bull Emerg Trauma. 2014; 2(3): 122–127. Available from: https://pesquisa.bvsalud.org/portal/resource/pt/emr-174720
Omar MTA & Hassan AA. Evaluation of hand function after early excision and skin grafting of burns versus delayed skin grafting: a randomized clinical trial. Burns. 2011; 37(4): 707–13. DOI:10.1016/j.burns.2010.12.012.
Luze H, Nischwitz SP, Smolle C, Zrim R & Kamolz LP. The use of acellular fish skin grafts in burn wound management—a systematic review. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022; 58(7): 912. DOI:10.3390/ medicina58070912.
Ambrosio L. The role of biomaterials in burn treatment. Burns Trauma. 2014; 2:150–2. DOI:10.4103/2321-3868.143 608.
Mroueh V, Reiche E, Keller PR, Mroueh J, Marano AA, Suresh V, et al. 97. Androgen Therapy Alters Scar Formation in Gender-Affirming Mastectomy. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery–Global Open, 2023; 11(5S):60-61.DOI:10.1097/01.GOX.0000937976.94422.7a
Elseth A, Lopez ON. Wound grafts. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 [cited 2024 Dec 8]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564382/
Mobayen M, Tolouei M, Dehnadi MA, Homaie RE, Zare N, Jamshidi R, et al. Early graft in patients with burn wounds: A two-year retrospective study of 582 patients at a referral burn center in northern Iran. J Nur Rep Clin Prac, 2024; 2(4): 211-218. DOI:10.325 98/JNRCP.2312.1009
Mohammadi AA, Bakhshaeekia AR, Marzban S, Abbasi S, Ashraf AR, Mohammadi MK, et al. Early excision and skin grafting versus delayed skin grafting in deep hand burns: a randomized clinical controlled trial. Burns. 2011; 37(1): 36–41. DOI:10.1016/j.burns.2010.02.005.
Markiewicz-Gospodarek A, Kozioł M, Tobiasz M, Baj J, Radzikowska-Büchner E & Przekora A. Burn wound healing: clinical complications, medical care, treatment, and dressing types: the current state of knowledge for clinical practice. Int J Env Res and Pub Health, 2022; 19(3):1338. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph 19031338
Game FL, Apelqvist J, Attinger C, Hartemann A, Hinchliffe RJ, Löndahl M, et al. Effectiveness of interventions to enhance healing of chronic ulcers of the foot in diabetes: a systematic review. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016;32(Suppl 1):154–168. DOI:10.1002/dmrr.2707.
Saporito F, Sandri G, Bonferoni MC, Rossi S, Boselli C, Cornaglia AI, et al. Essential oil-loaded lipid nanoparticles for wound healing. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018; 13: 175–186. DOI:10.2147/IJN.S1 52529.
Sharif A & Borrows R. Delayed graft function after kidney transplantation: the clinical perspective. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;62(1):150–8. DOI:10.1053/j.ajkd. 2012.11.050.
Saleem S, Kant BUR, Zafar A, Ahmed S, Akbar AA & Syeda WB. Impact of early versus delayed excision and grafting on wound healing and treatment in burn injuries: a retrospective study. Indus J Biosci Res. 2024; 2(2): 764–772. DOI:10.70749/ijbr.v2i02.268.
Copyright (c) 2025 Rafeni Bunga, Beta Subakti Nata'admaja

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
JURNAL REKONSTRUKSI DAN ESTETIK by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold copyright of the article without restriction
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessbility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA)