CORRELATION BETWEEN APOPROTEIN B/APOPROTEIN A-I RATIO WITH HOMA IR VALUE (HOMEOSTATIC MODEL ASSESMENT INSULIN RESISTANCE) IN TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
Downloads
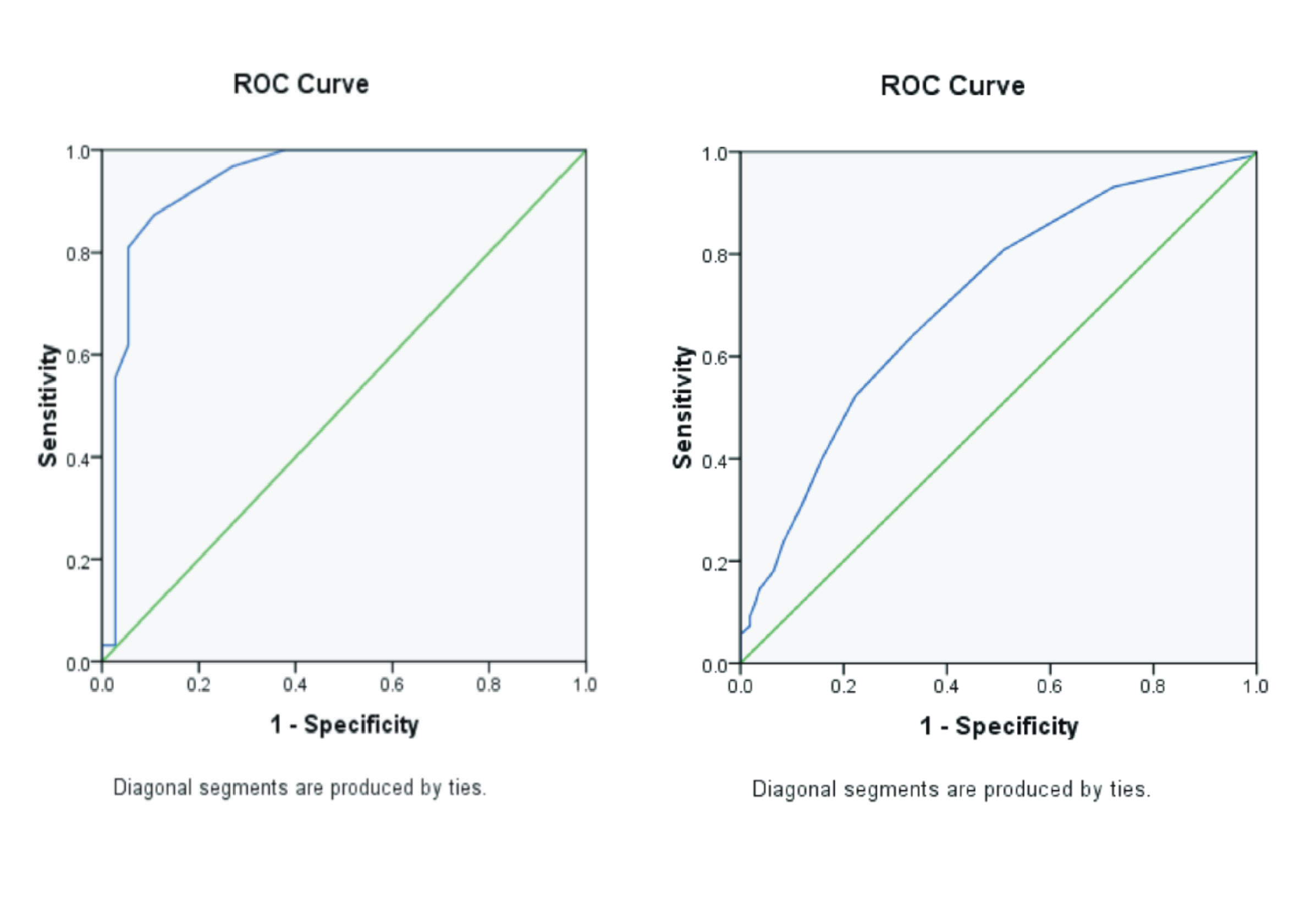
Background: Diabetes mellitus (DM) is the seventh leading cause of death in the world (the occuring rate has reached 400 million people). Type2 DM is caused by the body cells' inability to respond normally to insulin (insulin resistance). Homeostatic Model Assessment-Insuline Resistance (HOMA-IR) is a calculation method which function is to measure the body insulinresistance. Diabetes mellitus can cause lipid metabolism disorders (dyslipidemia) resulting in an increased level of LDL cholesterol and decreased HDL cholesterol. The apoprotein B/apoprotein A-I ratio is the result of comparisons of apoprotein B (LDLprotein constituent) and apoprotein A-I (HDLprotein constituent). The apo B/apo A-I ratio represents a balance between LDL cholesterol (atherogenic) and HDL (anti-atherogenic). It isastrong signifier in predicting heart disease.Purpose: This study aim to determine the correlation between the apoprotein B/apoprotein A-I ratio with HOMA-IRin patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Method:Observasional, consecutive, 100 people with type 2 diabetes mellitus who is examined in apoprotein B, apoprotein A-I test that calculating the ratio in which ratio are calculated, as well as HOMA-IRin Parahita Clinical Laboratory Surabaya. This study uses Pearson correlation test method with SPSS 22.0 for Windows program.Result:The result of Pearson correlation test between apoprotein B/apoprotein A-I ratio with HOMA-IR in 100 samples is a strongand significant correlation value (r=0,610, p<0,05). Conclusion:There is a strong correlation between the apoprotein B/apoprotein A-I ratio with HOMA-IRin patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
ADA (American Diabetic Association). 2018. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2018. Diabetes Care Vol. 41(Suppl.1). Pp. 13-27.
Aryansyah, G. 2016. Hubungan Antara Kadar Apoprotein A terhadap nilai HOMA-IR (Homeostatic Model Assessment-Insulin Resistance) Pada Penderita Diabetes Mellitus Tipe II. Skripsi. Surabaya: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Airlangga.
Belfki, S., Ben Ali, S., Bougatef. 2011. The Apolipoprotein B/Apolipoprotein A1 ratio in relation to metabolic syndrome and its components in a sample of the Tunisian population. Experimental and Molecular Pathology Vol. 91(2). Pp. 622–625.
Elovson, J., Chatterton, J. E., Bell, G. T., Schumaker, V. N., Reuben, M. A., Puppione, D. L., Reeve, J. R. 1988. Plasma very low density lipoproteins contain a single molecule of apolipoprotein B. J Lipid Res Vol. 29. Pp. 1461–73.
Harding, Anne-Helen, Day, N. E., Khaw, Kay-Tee, Bingham, S., Luben, R., Welsh, A., Wareham, N. J. 2004. Dietary Fat adn Risk of Clinic Type Diabetes. American Journal of Epidemiology Vol. 159(1). Pp. 150-9.
Linawaty, S., Suparyatmo, J. B., Tahono. 2013. Angka Banding Apo B/Apo A-I Pada Gejala Koroner Akut. Majalah Patologi Klinik Indonesia dan Laboratorium Medik Vol. 20(1). Pp. 29-33.
Lind, L. 2006. The Apolipoprotein B/AI Ratio and the Metabolic Syndrome Independently Predict Risk for Myocardial Infarction in Middle-Aged Men. dari Departments of Medical Sciences (L.L., J.S.) dan Public Health and Caring Sciences (B.V., J.S.). Sweden: Uppsala University and Astra Zeneca R&D (L.L.), Mo¨lndal.
Purnomo, H. 2009. Pencegahan dan Pengobatan Penyakit yang Paling Mematikan. Yogyakarta: Buana Pustaka.
Sniderman A. D., Furberg, C. D., Keech, A., Roeters, V. L. J. E., Frohlich, J., Walldius, G. 2003. Apolipoproteins versus lipids as indices of coronary risk and as targets for statin treatment. Lancet Vol. 361. Pp. 777–80.
Sniderman, A. D., Scantlebury, T., Cianflone, K. 2001. Hypertriglyceridemic hyperapoB: unappreciated atherogenic dyslipoproteinemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med Vol. 135(6). Pp. 47–459.
Soegondo, S., Sukardji, K. 2008. Hidup Secara Mandiri dengan Diabetes Mellitus Kencing Manis Sakit Gula. Jakarta: FK UI.
Suhartono, T. Dislipidemia pada Diabetes Melitus. Dalam: Darmono, Suhartono, T., Pemayun T. G. D., Padmomartono, F. S. 2007. Diabetes Melitus Ditinjau dari Berbagai Aspek Penyakit Dalam. Semarang: Badan Penerbit Universitas Diponegoro. Pp. 31-34.
Tjokroprawiro, A., Hendromartono, Sutjahjo, A., Pranoto, A., Murtiwi, S., Adi, S., Wibisono, S. Diabetes Mellitus. Dalam : Tjokroprawiro, A., Setiawan, Boedi S., Pranoto, A., Nasronudin, Santoso, D., Soegiarto, G., editor. 2007. Buku Ajar Ilmu Penyakit Dalam. Surabaya: Airlangga University Press.
Walldius, G., Jungner, I. 2004. Apolipoprotein B and apolipoprotein A-I: risk indicators of coronary heart disease and targets for lipidmodifying therapy. J Intern Med Vol. 255(2). Pp. 188–205.
Walldius, G., Jungner, I. 2006. The apoB/apoA-I ratio: a strong, new risk factor for cardiovascular disease and a target for lipid-lowering therapy–a review of the evidence. J Intern Med Vol. 259. Pp. 493–519.
Walldius, G., Jungner, I., Holme, I., Aastveit, A. H., Kolar, W., Steiner, E. 2001. High apolipoprotein B, low apolipoprotein A-I, and improvement in the prediction of fatal myocardial infarction (AMORIS Study): a prospective study. Lancet Vol. 358. Pp. 2026–33.
Copyright (c) 2019 Journal of Vocational Health Studies

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The authors agree to transfer the transfer copyright of the article to the Journal of Vocational Health Studies (JVHS) effective if and when the paper is accepted for publication.
- Legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA), implies that publication can be used for non-commercial purposes in its original form.
- Every publications (printed/electronic) are open access for educational purposes, research, and library. Other that the aims mentioned above, editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation.
Journal of Vocational Health Studies is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License













































