PULSE OXIMETER USAGE IN PATIENT COVID-19 TREATMENT : AT A GLANCE
Downloads
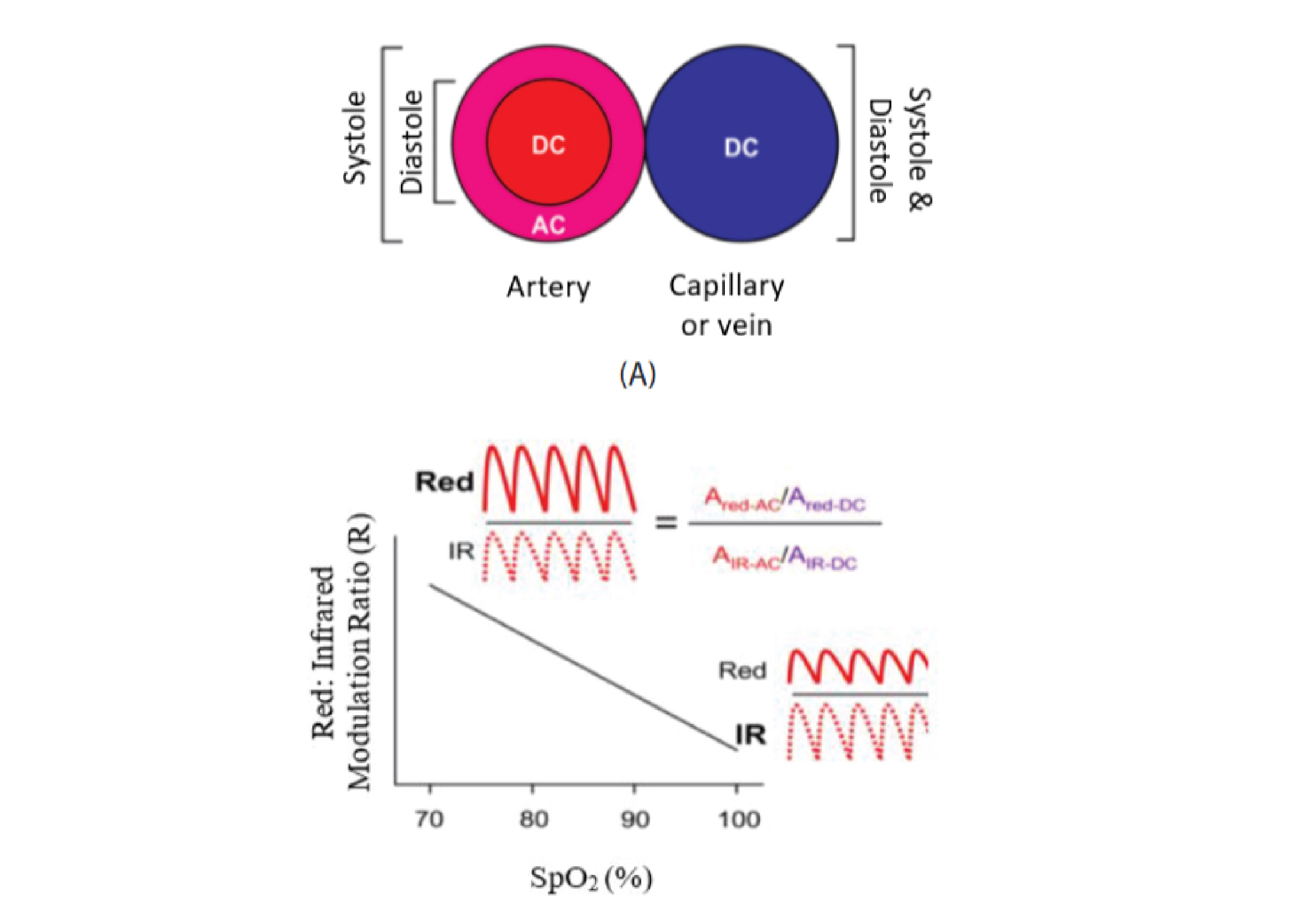
Background: The end of 2019, Wuhan experienced an insurgence of coronavirus within two months of this prolong pandemic. Patients with Covid-19 have chance in suffering a serious damage of respiratory system, which then lead to hypoxemia. The harmful of silent hypoxemia is that either the patients are remain untreated or they will not seek any treatment at all, though their blood oxygen levels (SpO2 levels) slowly decrease. Especially those who isolated at home. Pulse oximeter is a mini device that evaluate the level of arterial blood saturation. Purpose: This article gives a short review about the principle, application, advantage, and disadvantage of pulse oximetry in maintaining the Covid-19 patients with hypoxemia. Review: Two basic principles of pulse oximetry that are important: (a) to differentiate the oxyhemoglobin (HbO2 ) and deoxyhemoglobin (HHb), (b) to get the value of SpO2 from arterial compartment blood. How pulse oximeter detects SpO2 is based on the amount of red and IR light absorbed. Pulse oximeter can detect an abnormality of respiratory system in Covid-19 patients that may cannot be detected earlier. Pulse oximeter also helps diagnosing some severe pneumonia cases. It also can be realiable to diagnose an ARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndroms) if the devices are found limited (WHO, 2020). Beside the advantages of pulse oximeter, there are some erroneous of readings. Conclusion: Pulse oximeter is a mini device which offers many advantages over its limitations. Limitation of pulse oximeter can be early detected and overcame with an introduction evaluation of clinical conditions of each patients.
Chan, E.D., Chan, Michael M., Chan, Mallory M., 2013. Pulse Oximetry: Understanding Its Basic Principles Facilitates Appreciation of Its Limitations. Respir. Med. J. 107, 789–799.
Chatterjee, N.A., Jensen, P.N., Harris, A.W., Nguyen, D.D., Huang, H.D., Cheng, R.K., Savla, J.J., Larsen, T.R., Gomez, J.M.D., Du-Fay-de-Lavallaz, J.M., Lemaitre, R.N., McKnight, B., Gharib, S.A., Sotoodehnia,N., 2021. Admission Respiratory Status PredictMortality in Covid 19. Influ. Respir. Viruses 1–4.
FDA, 2021. Pulse Oximeter Accuracy and Limitation [WWW Document]. FDA Saf. Commun. URL https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safety-communications/pulse-oximeter-accuracy-and-limitations-fda-safety-communication
Guo, Y.-R., Cao, Q.-D., Hong, Z.-S., Tan, Y.-Y., Chen, S.-D., Jin, H.-J., Tan, K.-S., Wang, D.-Y., Yan, Y., 2020. The Origin, Transmission and Clinical Therapies on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak – An Update on The Status. Mil. Med. Res. 7, 1–10.
Joshi, L.R., 2020. Principles, Utility and Limitations of Pulse Oximetry in Managements Covid 19 Patients. J.Lumbini Med. Coll. 8.
Mannheimer, P.D., 2007. The Light-Tissue Interaction of Pulse Oximetry. Anesth. Analg. Journal. 105, 10–17.
Nickson, C., Iwashyna, J., Young, P., 2021. Silent Hypoxemia and COVID-19 intubation [WWW Document]. Life Fastlane. URL https://litfl.com/silent-hypoxaemia-and-covid-19-intubation/
Nitzan, M., Romem, A., Koppel, R., 2014. Pulse Oximetry : Fundamentals and Technology Update. J. Med. Device. 7, 231–239.
Ouassou, H., Kharchoufa, L., Bouhrim, M., Daoudi, N.E., Imtara, H., Bencheikh, N., ELbouzidi, A., 2020. The Pathogenesis of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Evaluation and Prevention. J. Immunol. Res. 1–7.
Perkins, G.D., McAuley, D.F., Giles, S., Routledge, H., Gao, F., 2003. Do Changes in Pulse Oximeter Oxygen Saturation Predict Equivalent Changes in Arterial Oxygen Saturation. Crit. Care 7, 67–71.
Pretto, J.J., Roebuck, T., Beckert, L., Hamilton, G., 2014. Clinical Use of Pulseoximetry : Official guidelines from the Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand. Asian Pacific Soc. Respirol. 19, 38–46.
Sinex, J.E., 1999. Pulse Oximetry : Principles, Uses and Limitations. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 17, 59–66.
WHO, 2011. Pulse Oximetry Training Manual.
WHO, 2020. COVID-19 Clinical management: Living Guidance. In: Organization, W.H. (Ed.), COVID-19 Clinical Management: Living Guidance.
Xie, J., Covassin, N., Fan, Z., Singh, P., Gao, W., Li, G., Kara, T., Somers, V.K., 2020. Association Between Hypoxemia and Mortality in Patients with COVID-19. Natl. Libr. Med. 95, 1138–1147
Copyright (c) 2021 Journal of Vocational Health Studies

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The authors agree to transfer the transfer copyright of the article to the Journal of Vocational Health Studies (JVHS) effective if and when the paper is accepted for publication.
- Legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA), implies that publication can be used for non-commercial purposes in its original form.
- Every publications (printed/electronic) are open access for educational purposes, research, and library. Other that the aims mentioned above, editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation.
Journal of Vocational Health Studies is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License