ANTHOCYANIN-CONTAINING PLANT EXTRACTS AS AN ALTERNATIVE DYE FOR MICROSCOPIC EXAMINATION OF SOIL-TRANSMITTED HELMINTHS
Background: Eosin is commonly used for microscopic examination of Soil-Transmitted Helminth (STH) infections, but natural anthocyanin-based pigments remain underutilized. Purpose: This study evaluates the potential of anthocyanins extracted from red beans (Phaseolus vulgaris), hibiscus flowers (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis), and amaranth leaves (Amaranthus tricolor) as eosin alternatives for staining STH eggs in stool smears. Method: Extracts were obtained using 96% ethanol for 24, 48, and 72 hours, with nine replications. Stool preparations were stained with these extracts and compared to eosin, assessing color intensity, contrast, and egg layer clarity. Result: Red bean extracts scored 2.1, 2.7, and 2.8 at 24, 48, and 72 hours, with the latter two showing no significant difference from eosin. Hibiscus flower extracts scored 1.6, 2.2, and 2.8, with the 72 hours extract comparable to eosin. Amaranth leaf extracts scored 1.4, 1.7, and 1.9, all significantly different from eosin. Conclusion: Red bean extracts (48 and 72 hours) and hibiscus flower extract (72 hours) provided staining comparable to eosin, with red bean extract being the most promising alternative. These findings suggest that anthocyanin-based stains can serve as viable substitutes for eosin in diagnosing helminthiasis via stool smear microscopy.
Introduction
Clinical laboratories in the modern world of health significantly contribute to diagnosing and managing diseases, especially because of their role in measuring biomarkers and identifying species of microorganisms in specimens or body tissues. This role covers a wide range of disciplines, including clinical chemistry, hematology, clinical microbiology, clinical immunology, and molecular diagnostics, supported by a combination of advanced technology, skilled professionals, and effective management.
In the scope of clinical microbiology, microscopic examination serves as a gold standard for diagnosing diseases caused by parasites, especially helminths, protozoa, and arthropods, with the most representative specimens being blood and feces (Rifai et al., 2022(Rifai, 2022)). This microscopic examination is usually performed on a slide stained with certain dyes to detect microorganisms such as helminth eggs. Typical dyes like iodine, safranin, trypan blue, and eosin Y are used to identify infections caused bySoil-Transmitted Helminths(STH). When compared to the culture approach, the microscopic method is considered more time-effective (Amoah et al., 2017(Amoah et al., 2017)).
Synthetic dyes’ disadvantages include high cost, limited availability, inability to produce independently, potential for irritation, and the need for potentially dangerous solvents. Therefore, reliance on them should be avoided. In addition, synthetic dyes are reported to be toxic to helminth embryos, therefore they can be detrimental if the examination requires observation of live microorganisms (Amoah et al., 2017(Amoah et al., 2017)) for this reason, alternative materials that are safe and can address the aforementioned problems are needed. Anthocyanin is a well-known natural dye that can be found around us. This pigment is a compound from the flavonoid group, which gives plants a red, blue, or purple color, and has an antioxidant effect (Khoo et al., 2017(Khoo et al., 2017)).
Anthocyanins can be found in red beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) (Li et al., 2021(Li et al., 2021); Liu et al., 2023(Liu et al., 2023); Meenu et al., 2023(Meenu et al., 2023)), hibiscus (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis) (Kalpana et al., 2021(Kalpana et al., 2021); Pieracci et al., 2021(Pieracci et al., 2021)), and amaranth (Amaranthus tricolor) (Sarker et al., 2022(Sarker et al., 2022); Sarker and Oba, 2020(Sarker & Oba, 2020)).
Plants have been extensively studied as sources of bioactive substances such as anthocyanins, however less is known about their potential as alternative substances for laboratory diagnoses, particularly in staining parasitological smears. This research aims at exploring the feasibility of using anthocyanins extracted from plants such as red beans, hibiscus flowers, and amaranth leaves as substitutes for eosin in staining parasitological smears to identify STH eggs.
Material and Method
Preparation of anthocyanin-containing plant extract
The natural plants used were obtained from different locations: red beans and amaranth were purchased from a traditional market, while hibiscus flowers were picked from a nearby garden. The selection of materials was based on their physical state, which included being undamaged, free of decay, and free of discoloration to minimize the possibility of natural substances being lost or destroyed. All of these materials were then washed to remove dirt and unnecessary materials.The extraction procedure used the maceration method based on Sugiharto et al. (2020)(Sugiharto et al., 2020)with slight modifications. One hundred grams of each ingredient were soaked in 100 mL of 96% ethanol in three erlenmeyer flasks, sealed with aluminum foil, and stored away from direct sunlight. Maceration of each ingredient was conducted for 24, 48, and 72 hours. There were 9 replications for each ingredient and each maceration time. Filtration was performed using Whatman filter paper after each maceration time for each ingredient.
Qualitative tests on anthocyanins were carried out by administering 2M NaOH drop by drop into a test tube. The red color changed to blue-green and disappeared slowly, proving the presence of anthocyanins (Anggriani et al., 2017(Anggriani et al., 2017))
Stool samples
The feces used in this research were obtained from the Laboratory of Parasitology, Pontianak Ministry of Health Polytechnic, and have been confirmed to contain STH eggs. Prior to use, feces were stored at 4 °C, not exposed to direct sunlight, and not used for other examinations.
Staining of stool smears using anthocyanin-containing plant extracts
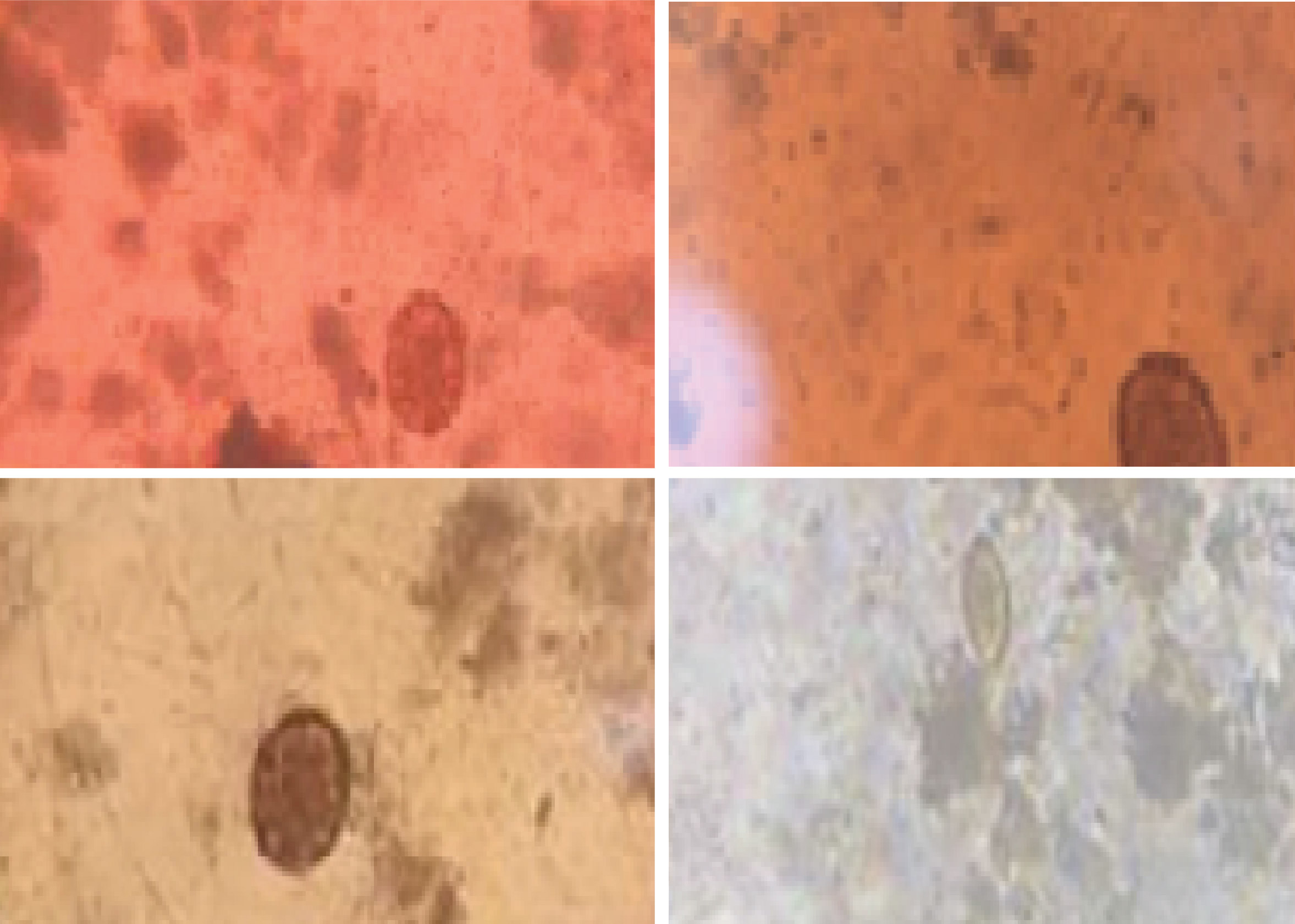
A stool sample was collected using the tip of the stick to prepare a direct smear. The stool sample was flattened to form a circle with a diameter of 1 - 2 cm, followed by the application of 1 - 2 drops of natural extract onto the smear. The smear was then covered with a cover glass and examined under the light microscope at magnifications of 100 and 400 times. The scoring method for staining quality was based on (Oktari and Mutamir, 2017(Oktari & Mutamir, 2017)) and is shown in Table 1Table 1.
Table 1.Scoring of staining quality
Examination of the quality of staining
The quality of anthocyanin staining from three extracts was evaluated using microscopy examination of STH-positive stool samples. The examinations included assessing distinctness and contrast, the effective absorbance of staining by helminth eggs, and the discernibility of the parts of the egg, all of which were scored based on visual perception, to minimize bias in scoring, visual observations were conducted by a single person.
Statistical analysis
The size of the replication unit is determined based on the number of treatment groups (24, 48, and 72 hours) of each natural plant
Alappat, B., Alappat, J., 2020. Anthocyanin Pigments: Beyond Aesthetics. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) Vol. 25(23), Pp. 5500.
Amer, S.A., Al-Khalaifah, H.S., Gouda, A., Osman, A., Goda, N.I.A., Mohammed, H.A., Darwish, M.I.M., Hassan, A.M., Mohamed, S.K.A., 2022. Potential Effects of Anthocyanin-Rich Roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) Extract on the Growth, Intestinal Histomorphology, Blood Biochemical Parameters, and The Immune Status of Broiler Chickens. Antioxidants Vol. 11(3), Pp. 544.
Amoah, I.D., Singh, G., Stenström, T.A., Reddy, P., 2017. Detection and Quantification of Soil-Transmitted Helminths in Environmental Samples: A Review of Current State-of-The-Art and Future Perspectives. Acta Tropica Vol. 169, Pp. 187-201.
Anggriani, R., Ain, N., Adnan, S., 2017. Identification of Phytochemical and Characterization of Anthocyanin Green Coconut Fiber (Cocos nucifera L var varidis). Jurnal Teknologi Pertanian Vol. 18(3), Pp. 163-172.
Aquino-Bolaños, E., GarcaDaz, Y., ChavezServia, J., CarrilloRodrguez, J., VeraGuzman, A., HerediaGarcia, E., 2016. Anthocyanins, Polyphenols, Flavonoids and Antioxidant Activity in Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) Landraces. Emirates Journal of Food and Agriculture Vol. 28(8), Pp. 581-588.
Backes, E., Leichtweis, M.G., Pereira, C., Carocho, M., Barreira, J.C.M., Kamal Genena, A., José Baraldi, I., Filomena Barreiro, M., Barros, L., C.F.R. Ferreira, I., 2020. Ficus carica L. and Prunus spinosa L. Extracts as New Anthocyanin-based Food Colorants: A Thorough Study in Confectionery Products. Food Chemistry Vol. 333, Pp. 127457.
Gecchele, E., Negri, S., Cauzzi, A., Cuccurullo, A., Commisso, M., Patrucco, A., Anceschi, A., Zaffani, G., Avesani, L., 2021. Optimization of A Sustainable Protocol for The Extraction of Anthocyanins as Textile Dyes from Plant Material. Molecules Vol. 26(22), Pp. 6775.
Hossain, M.K., Dayem, A., Han, J., Yin, Y., Kim, K., Kumar Saha, S., Yang, G.-M., Choi, H.Y., Cho, S.-G., 2016. Molecular Mechanisms of The Anti-Obesity and Anti-Diabetic Properties of Flavonoids. International Journal of Molecular Sciences Vol. 17(4), Pp. 569.
Kalpana, V.N.S., Mary, J., Saraswathy, M., Soumya, N., Mondal, S., 2021. Hibiscus rosa sinensis L. Anthocyanins Prevent Lipid Peroxidation and Improve Antioxidant Status in The Liver of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Bioactive Compounds in Health and Disease Vol. 4(10), Pp. 240-255.
Khoo, H.E., Azlan, A., Tang, S.T., Lim, S.M., 2017. Anthocyanidins and Anthocyanins: Colored Pigments as Food, Pharmaceutical Ingredients, and The Potential Health Benefits. Food and Nutrition Research Vol. 61(1), Pp. 1361779.
Li, L., Luo, C., Zheng, X., 2021. Purification of Anthocyanins Derived from Black Kidney Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) by A Simulated Moving Bed. Journal of Chemistry, Pp. e5580756.
Liu, C., Yang, X., He, Y., Chen, Q., Huang, Y., Yan, Z., Liu, D., Feng, G., 2023. Fine Mapping and Characterisation of a PV-PUR Mediating Anthocyanin Synthesis in Snap Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Molecular Breeding Vol. 43(3), Pp. 15.
Lozada-Ramírez, J.D., Ortega-Regules, A.E., Hernández, L.R., Anaya de Parrodi, C., 2021. Spectroscopic andSpectrometric Applications for the Identificationof Bioactive Compounds from Vegetal Extracts.Applied Sciences Vol. 11(7), Pp. 3039.
Lu, W., Shi, Y., Wang, R., Su, D., Tang, M., Liu, Y., Li, Z., 2021. Antioxidant Activity and Healthy Benefits of Natural Pigments in Fruits: A Review. Int J Mol Sci Vol. 22(9), Pp. 4945.
Madushan, R., Vidanarachchi, J.K., Prasanna, P.H.P., Werellagama, S., Priyashantha, H., 2021. Use of Natural Plant Extracts as A Novel Microbiological Quality Indicator in Raw Milk: An Alternative for Resazurin Dye Reduction Method. LWT Vol. 144, Pp. 111221.
Meenu, M., Chen, P., Mradula, M., Chang, S.K.C., Xu, B., 2023. New Insights into Chemical Compositions and Health-Promoting Effects of Black Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Food Frontiers Vol. 4(3), Pp. 1019-1038.
Oktari, A., Mutamir, A., 2017. Optimasi Air Perasan Buah Merah (Pandanus sp.) pada Pemeriksaan Telur Cacing. Jurnal Teknologi Laboratorium Vol. 6(1), Pp. 8-17.
Oliveira Filho, J.G. de, Braga, A.R.C., Oliveira, B.R. de, Gomes, F.P., Moreira, V.L., Pereira, V.A.C., Egea, M.B., 2021. The Potential of Anthocyanins in Smart, Active, and Bioactive Eco-Friendly Polymer-Based Films: A Review. Food Research International Vol. 142, Pp. 110202.
Pieracci, Y., Pistelli, Luisa, Lari, M., Iannone, M., Marianelli, A., Ascrizzi, R., Pistelli, Laura, Flamini, G., 2021. Hibiscus Rosa-Sinensis as Flavoring Agent for Alcoholic Beverages. Applied Sciences Vol.11(21), Pp. 9864.
Rifai, N., 2022. Tietz Textbook of Laboratory Medicine, 7 tb. ed. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Rodríguez Madrera, R., Campa Negrillo, A., Suárez Valles, B., Ferreira Fernández, J.J., 2021. Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity in Seeds of Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Foods Vol. 10(4), Pp. 864.
Sachdev, S.S., Chettiankandy, T.J., Sonawane, S.G., Sardar, M.A., Kende, P.P., Pakhmode, V., 2021. Toward Developing Natural Histologic Stains using Anthocyanins: A Novel Approach. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology: JOMFP Vol. 25(1), Pp. 199.
Sarker, U., Oba, S., 2020. Leaf Pigmentation, Its Profiles and Radical Scavenging Activity in Selected Amaranthus Tricolor Leafy Vegetables. Scientific Reports Vol. 10(1), Pp. 18617.
Sarker, U., Oba, S., Ercisli, S., Assouguem, A., Alotaibi, A., Ullah, R., 2022. Bioactive Phytochemicals and Quenching Activity of Radicals in Selected Drought-Resistant Amaranthus tricolor Vegetable Amaranth. Antioxidants (Basel) Vol. 11, Pp. 578.
Sugiharto, K., Rahman, A.N.F., Zainal, 2020. The Effect of Solvent Type and Extraction Duration on Purple Corn Anthocyanin Compounds (Zea Mays L). IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. Vol. 486(1), Pp. 012055.
Wallace, T.C., Giusti, M.M., 2019. Anthocyanins-Nature’s Bold, Beautiful, and Health-Promoting Colors. Foods Vol. 8(11), Pp. 550.
Wittayathanarattana, T., Wanichananan, P., Supaibulwatana, K., Goto, E., 2022. A Short-Term Cooling of Root-Zone Temperature Increases Bioactive Compounds in Baby Leaf Amaranthus tricolor L. Front. Plant Sci. Vol. 13.
Yang, Y.-C., Mong, M.-C., Wu, W.-T., Wang, Z.-H., Yin, M.-C., 2020. Phytochemical Profiles and Anti-Diabetic Benefits of Two Edible Amaranthus Species. CyTA -Journal of Food Vol. 18(1), Pp. 94-101.
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Vocational Health Studies

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The authors agree to transfer the transfer copyright of the article to the Journal of Vocational Health Studies (JVHS) effective if and when the paper is accepted for publication.
- Legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA), implies that publication can be used for non-commercial purposes in its original form.
- Every publications (printed/electronic) are open access for educational purposes, research, and library. Other that the aims mentioned above, editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation.
Journal of Vocational Health Studies is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License