THE ENHANCEMENT OF GLASS IONOMER CEMENT HARDNESS BY ADDING GOURAMI SCALES POWDER NANOPARTICLES
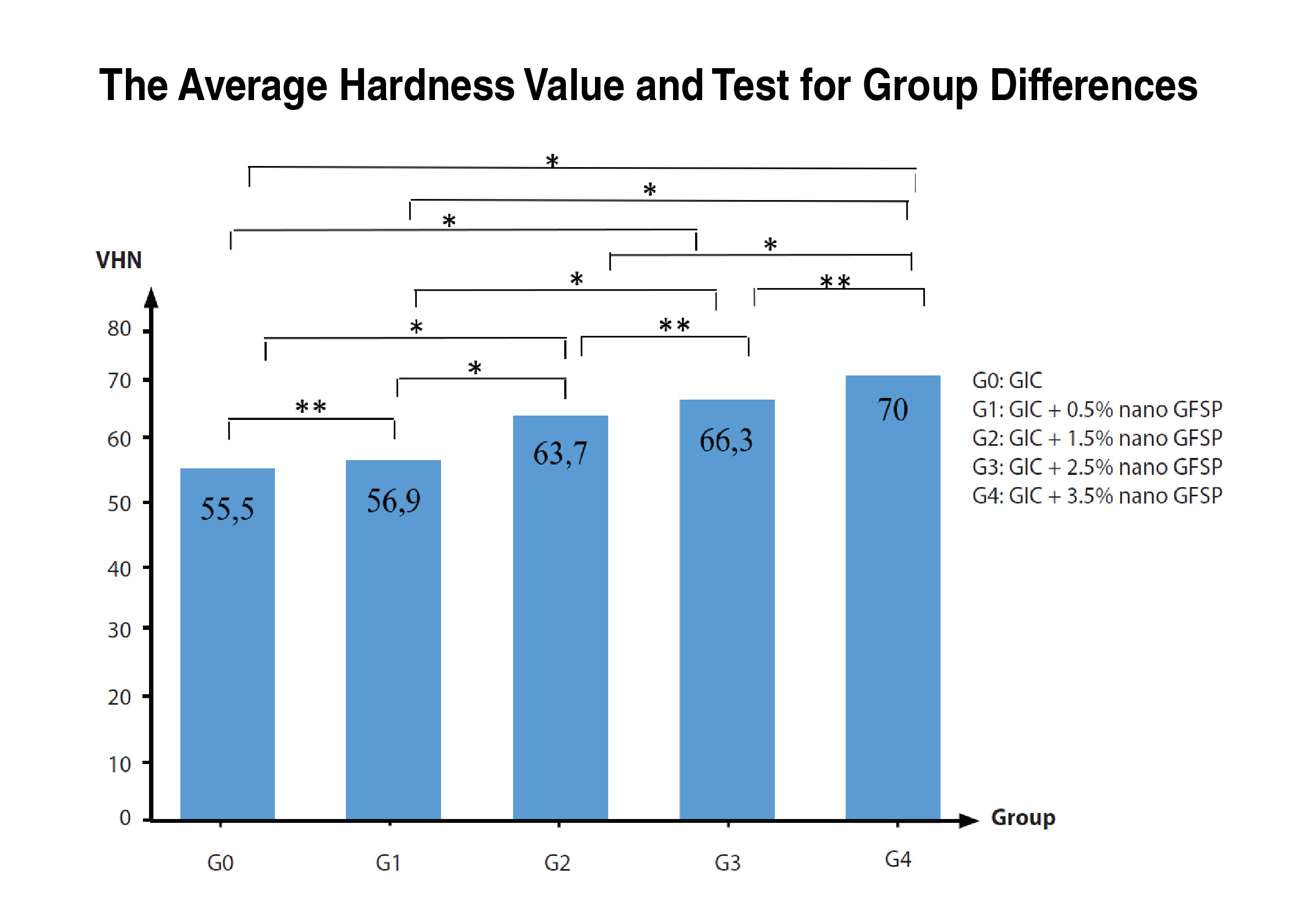
Background: Material hardness in dentistry is used as a measuring tool to determine the ability of a restoration material to withstand the compressive force of masticatory. The hardness of Glass Ionomer Cement (GIC) is a mechanical property related to the abrasion and compressive strength of the GIC. If the material’s hardness is low, it results in low material resistance and causes a fracture. Therefore, it is necessary to add materials that contain hydroxyapatite (HA), which can increase the hardness of GIC, as in gourami fish scales. Purpose: This research aims to determine the influence of adding Gourami Fish Scale Powder (GFSP) nanoparticles to GIC hardness. Method: The twenty five sample is in tablet form and divided into five sample groups, namely G0: GIC without the addition of GFSP, G1: GIC powder + 0.5% GFSP, G2: GIC powder + 1.5% GFSP, G3: GIC powder + 2.5% GFSP, G4: GIC powder + 3.5% GFSP. Hardness test was using Vickers Hardness Tester. Data were analyzed using a One Way ANOVA test. Result: The average values of the hardness results from lowest to highest were the G0 (55.5 ± 2.70 VHN), G1 (56.9 ± 3.36 VHN), G2 (63.7 ± 7.73 VHN), G3 (66.3 ± 1.44 VHN), and G4 (70.1 ± 4.72 VHN), while the One Way ANOVA test results were significant among all groups (p-value < 0.05). Conclusion: The addition of GFSP nanoparticles increased GIC hardness. The highest hardness value was obtained by adding 3.5% GFSP nanoparticles.
Introduction
ConventionalGlass Ionomer Cement(GIC) is often used in dentistry as a restorative material because it has advantages such as being biocompatible with pulp tissue, tooth-colored restorative material, binding well to the tooth structure, and releasing fluoride as an anti-cariogenic (Diansari et al., 2016(V. et al., 2016); Roeroe et al., 2015(Roeroe et al., 2015)). However, it has disadvantages, such as low fracture and wear resistance, so it is not applied for dental restoration with large loads, brittle, sensitivity to moisture, and porosity (Chen et al., 2016(Chen et al., 2016)). The hardness properties of GIC influence that characteristic (Rizzante et al., 2015(Rizzante et al., 2015); Barandehfard et al., 2016(Barandehfard et al., 2016); Rodrigues et al., 2015(Rodrigues et al., 2015); Roeroe et al., 2015(Roeroe et al., 2015); Barandehfard et al., 2016(Barandehfard et al., 2016)).
Hardness is a mechanical property related to restorative materials' abrasion and compressive strength (Khan et al., 2015(Khan et al., 2015)). Material hardness in dentistry is used as a measuring instrument to determine the ability of restorative material to withstand masticatory pressure. The eligible surface hardness of the restorative material affects the restoration's clinical success by increasing its resistance to abrasion and preventing it from deforming under various forces. The restorative material must have high hardness values to preserve the integrity of the restoration against chewing forces in the oral cavity (Karakas et al., 2021(Karakas et al., 2021)). Low hardness leads material to have less resistance, which leads to a fracture (Anusavice et al., 2022(Anusavice et al., 2022)). Therefore, adding hydroxyapatite (HA) to glass ionomer cement aims to improve the mechanical properties (Almuhaiza, 2016(Almuhaiza, 2016)).
Hydroxyapatite can improve the compressive strength, diametrical tensile strength, and flexural strength of GIC (Gjorgievska et al., 2020(Gjorgievska et al., 2020); Kheur et al., 2020(Kheur et al., 2020)). The content of HA (w/w) can be obtained in the scales of gourami fish (Osphronemus gourami) by 16% to 59% (Sockalingam et al., 2015(Sockalingam et al., 2015); Dewanti et al., 2020(Dewanti et al., 2020)). Previous study found that the addition ofGourami Fish Scale Powder(GFSP) to GIC with concentrations of 2.5%, 5%, and 10% influenced the character of GIC. The addition of 2.5% GFSP caused a decrease in the level and diameter of pores, marginal gap, and increased compressive strength. Raising 5% and 10% concentrations increases the level and diameter of pores, marginal gap, and compressive strength (Dewanti et al., 2022(Dewanti et al., 2022); Wulandari et al., 2022(Wulandari et al., 2022)). This result may occur because the GFSP used is not nano-sized.
Nano-size improves the material's mechanical properties (Al-Hamaoy et al., 2018(Al-Hamaoy et al., 2018)). The nanoparticles will be perfectly embedded in the GIC matrix and form good adhesion bonds (Alatawi et al., 2019(R.A.S. et al., 2019); Alobiedy et al., 2019(Alobiedy et al., 2019)). Nano-hydroxyapatite (Nano-HA) was added to conventional GICs and improved mechanical properties such as biaxial flexural strength, compressive strength, and diametral tensile strength compared to the conventional GICs (Amin et al., 2021(F. et al., 2021)). Previous studies showed that adding 0.5%, 1.5%, 2.5%, and 3.5% GFSP nanoparticles increases GIC tensile strength (Cahyanisa et al., 2023(Cahyanissa et al., 2022)) and significantly enhances the antibacterial activity of GIC againstS. aureusandS. mutans(Wulandari et al., 2023(Wulandari et al., 2023)). Thus, this research determines the influence of adding 0.5%, 1.5%. 2.5%, and 3.5% GFSP nanoparticles to the GIC hardness. It is hoped that the addition of GFSP nanoparticles can increase the hardness of GIC.
Material and Method
This research is an experimental laboratory study with a post-test only control group design. The research was conducted in the Bioscience Laboratory Jember Dental and Oral Hospital (RSGM) University of Jember. The number of samples was in a 25 tablets form divided into five groups, each group containing five samples, as described (1) G0/control group: GIC, (2) G1: GIC + 0.5% nano GFSP, (3) G2: GIC + 1.5% nano GFSP, (4) G3: GIC + 2.5% nano GFSP, (5) G4: GIC + 3.5% nano GFSP.
Manufacturing of gourami fish scales powder nanoparticle
The clean gourami scales were dried by freeze drying, mashed with a blender (Cosmos, Jakarta, Indonesia), and sieved using a 200 mesh sieve (ABM Test Sieve Analysis, Jakarta, Indonesia) (Wulandari et al., 2022(Wulandari et al., 2022)).Nano-sized GFSP(nGFSP) was obtained by grounding the powder fish scales using a ball mill (Piraset al., 2019(Piras et al., 2019)). Furthermore, the pH of nGFSP was measured, and particle size was analyzed using a Particle Size Analyzer (Horiba-SZ 100z, California, US) (Cahyanisa et al., 2023(Cahyanissa et al., 2022)).
Sample preparation
Nano-sized GFSP(nGFSP) andGlass Ionomer Cement(GIC) powder (GC Fuji 9 Gold Label High Strength Posterior Extra, Tokyo, Japan) were weighed using analytical scales (Adam typep 254, England, UK) and mixed using avortex(Labinco L46, Breda,Netherland) to be homogeneous (Mawadara et al., 2016(Mawadara et al., 2016)). The ratio and composition of GIC powder and nGFSP can be seen in Table 1Table 1.
Powders in each group were manipulated into GIC liquid in a ratio of 3.4 : 1 over a paper pad using an agate spatel for
Alatawi R.A.S., Elsayed, N.H., Mohamed, W.S., 2019. Influence of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles on the Properties of Glass Ionomer Cement. Journal of Materials Research and Technology Vol. 8(1), Pp. 344-349.
Al-Hamaoy, A.R., Alobiedy, A.N., Alhille, A.H., 2018. Glass Ionomer Cement Mechanical Properties Enhancement Using Hydroxyapatite Micro and Nanoparticle. ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences Vol. 13(6), Pp. 1–6.
Almuhaiza, M., 2016. Glass Ionomer Cement in Restorative Dentistry: A Critical Appraisal. The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice Vol. 17(4), Pp. 331-336.
Amin F., Rahman, S., Khurshid Z., Zafar, M.S., Farshid Sefat, F., Kumar, N., 2021. Effect of Nanostructures on the Properties of Glass Ionomer Dental Restoratives/Cements: A Comprehensive Narrative Review. Materials (Basel) Vol. 14(21), Pp. 6260.
Anusavice, J.K., Shen, C., Rawls, R., 2022. Phillip’s Science of Dental Materials. 13th Edition. United States, Elsevier.
Alobiedy, A.N., Alhelli, A.H.M.A., Al Hamaoy, A.R., 2019. Effect of Adding Micro and Nano-carbon Particles on Conventional Glass Ionomer Cement Mechanical Properties. Ain Shams Engineering Journal Vol 10(4), Pp. 1-5.
Barandehfard, F., Kianpourrad., Hosseinnia, M., 2016. The Addition of Synthesized Hydroxyapatite and Fluorapatite Nanoparticles to A Glass Ionomer Cement for Dental Restoration and Its Effects on Mechanical Properties. Ceramics International Vol. 42(15), Pp. 66–75.
Cahyanissa, K., Wulandari, E., Dewanti, I.D.A.R., 2022. Tensile Strength of Glass Ionomer Cement (GIC) After Addition of Gouramy Fish Scales Powder Nanoparticles. Proceedings Clinical Management in Dentistry “The Application of Advanced Techniques for Dental Practice”, Pp. 136-141.
Chen, S., Cai, Y., Engqvist, H., 2016. Enhanced Bioactivity of Glass Ionomer Cement by Incorporating Calcium Silicates. Biomatter Journal Vol. 6(1), Pp. 1-7.
Dewanti, I.D.A.R., Lestari, P.E., Purwanto, P., Wulandari, E., Yani, R.W.E., Wibisono, S., Burlakovs, J., 2020. Bones, Scales of Upeneus Sulphureus and Osphronemus Gourami Increase Adhesion and Decrease IL-1β Expression on Monocytes Against Streptococcus Mutans. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Health Vol. 23(8), Pp. 1253-1258.
Dewanti, I.D.A.R., Firdausya, D.A., Mantika, S.I., Amalia, A.F., Rifqoh, T., Wulandari, E., 2022. Marginal Gap,Compressive Strength and Bacterial Inhibitionof Gourami Fish (Osphronemus Gourami) ScalesPowder. IOSR Journal of Dental and MedicalSciences (IOSR-JDMS) Vol. 21(1), Pp. 53–59.
Diansari V., Ningsih D.S., Moulinda C., 2016. Evaluasi Kekasaran Permukaan Glass Ionomer Cement (GIC) Konvensional Setelah Perendaman dalam Minuman Berkarbonasi, Cakradonya Dental Journal Vol. 8(2), Pp.111-116.
Gjorgievska, E., John, W.N., Dragana, G., Zeynet, A.G., Ivana, M., Nichola, J.C., 2020. Assessment of The Impact of The Addition of Nanoparticles on The Properties of Glass-Ionomer Cements. Materials (Basel) Vol. 13(2), Pp. 276.
Karakas, S.N., Turgut, H., Kuden, C., 2021. Comparison of Surface Roughness and Microhardness of Reinforced Glass Ionomer Cements and Microhybrid Composite. Journal of Dentistry Indonesia. Vol. 28(3), Pp. 131-138.
Khan, A.A., Siddiqui, A.Z., Mohsin, S.F., Al-Kheraif, A.A., 2015. Influence of Mouth Rinses on the Surface Hardness of Dental Resin Nano-composite. Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 31(6), Pp. 1485– 1489.
Kheur, M., Kanthatia, N., Laka,T., Kheur, S., Husain, N.A., Ozcan, M., 2020. Evaluation of Mechanical and Adhesion Properties of Glass Ionomer Cement Incorporating Nano-Sized Hydroxyapatite Particles. Odontology Vol. 108(1), Pp. 66–73.
Khurshid, Z., Zafar, M., Qasim, S., Shahab, S., Naseem, N., Abureqaiba, A., 2015. Advances in Nanotechnology for Restorative Dentistry. Materials (Basel) Vol. 8(2), Pp. 717–731.
Mawadara, P.A., Mozartha, M., Trisnawaty, K., 2016. Pengaruh Penambahan Hidroksiapatit dari Cangkang Telur Ayam terhadap Kekerasan Permukaan GIC. Jurnal Material Kedokteran Gigi Vol. 2(5), Pp. 8–14.
Moheet, I.A., Luddin, N., Rahman, I.A., Masudi, S.M., Kannan, T.P., Ghani, N.R.N.A., 2020. Evaluation of Fluoride Ion Release and Color Stability of Nano-hydroxyapatite-silica Added Glass Ionomer Cement for Dental Application. Research Report Fluoride Vol. 53(1 Pt 2), Pp. 100-111.
Mozartha, M., 2015. Hidroksiapatit dan Aplikasinya di Bidang Kedokteran Gigi. Cakradonya Dental A Green Technology for the Preparation and Functionalization of Nanocellulose Derivates. Journal of Nanoscale Advances Vol 1, Pp. 937-947.
Piras, C.C., Prieto, S.F., Borggraeve., 2019. Ball Milling: A Green Technology for the Preparation and Functionalization of Nanocellulose Derivates. Journal of Nanoscale Advances Vol 1, Pp. 937-947.
Rahman, I.A., Masudi, S.M., Luddin, N., Shiekh, R.A., 2014. One-pot Synthesis of Hydroxyapatite-Silica Nanopowder Composite for Hardness Enchancement of Glass Ionomer Cement (GIC). Bulletin of Materials Science Vol. 37(2), Pp. 213–219.
Rizzante, F.A.P., Cunali, R.S., Bombonatti, J.F.S., Correr, G.M., Gonzaga, C.C., Furuse, A.Y., 2015. Indications and Restorative Techniques for Glass Ionomer Cement. RSBO Vol.12(1), Pp. 79-87.
Rodrigues, D.S., Buciumeanu, M., Martinelli, A.E., Nascimento, R.M., Henriques, B., Silva F.S., 2015. Mechanical Strength and Wear of Dental Glass-Ionomer and Resin Composites Affected by Porosity and Chemical Composition, Journal of Bio- Tribo-Corrosion Vol. 1(3), Pp. 1–9.
Roeroe, V.M., Wicaksono, D.A., Juliatri., 2015. Gambaran Kekuatan Tekan Bahan Tumpatan Semen Ionomer Kaca yang Direndam dalam Minuman Beralkohol. Jurnal e GiGi Vol. 3(1). Pp. 1-6
Sockalingam, K., Yahya, M.A., Abdullah, H.Z., 2015. Preparations of Hydroxyapatite from Tilapia Scales. Advanced Materials Research Vol. 1087, Pp. 30–34.
Wulandari, E., Wardani, F.R.A., Fatimattuzahro, N., 2022. Addition of Gourami (Osphronemus goramy) Fish Scale Powder on Porosity of Glass Ionomer Cement. Dental Journal Vol. 55(1), Pp. 33–37.
Wulandari, E., Penga, Y.M., Lestari, P.E., Indriana, T., Dewanti, I.D.A.R., 2023. Antibacterial Activity of Nano-Sized Gourami Fish Scales Powder (Osphronemus Gourami) Added to Conventional Glass Ionomer Cement. International Journal of Medical Science and Clinical Research Studies Vol. 3(4), Pp. 679-683.
Yudhit, A., Harahap, K., Nasution, S.C., 2021. Effect of Hydroxyapatite from Nile Tilapia (Oreochromisniloticus) Scale on Surface Hardness of Conventional and Resin Modified Glass Ionomer Cement (In Vitro study). Proceedings of the 1st Aceh International Dental Meeting (AIDEM 2019), Oral Health International Conference on Art, Nature and Material Science Development, Pp. 5-10.
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Vocational Health Studies

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The authors agree to transfer the transfer copyright of the article to the Journal of Vocational Health Studies (JVHS) effective if and when the paper is accepted for publication.
- Legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA), implies that publication can be used for non-commercial purposes in its original form.
- Every publications (printed/electronic) are open access for educational purposes, research, and library. Other that the aims mentioned above, editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation.
Journal of Vocational Health Studies is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License