OPTIMIZING MOLECULAR TECHNIQUES FOR ACCURATE EXAMINATION OF LEPTOSPIRA SPECIES: A COMPREHENSIVE PRIMER FOR RESEARCHERS
Downloads
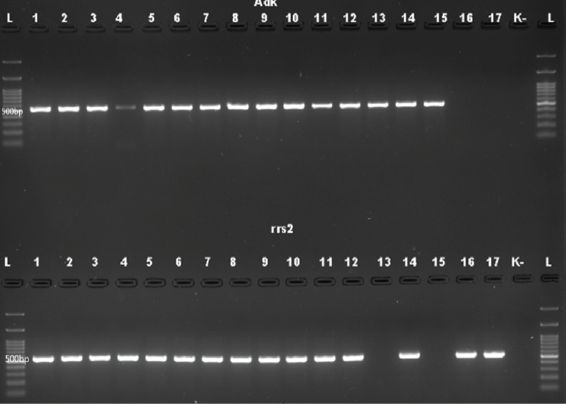
Background: Leptospirosis is a potentially life-threatening disease caused by bacteria of the genus Leptospira. The accurate identification and characterization of Leptospira species are critical for disease surveillance, outbreak investigation, and treatment strategies. Molecular techniques, such as Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequencing, have revolutionized the field of microbiology, providing rapid and accurate identification of Leptospira strains. However, optimizing these molecular techniques for accurate examination of Leptospira species can be challenging due to the genetic diversity and complexity of these bacteria. Purpose: This research aims to identify the most suitable primers for the precise identification of pathogenic Leptospira strains. Method: This research used the PCR method, using LipL32, rrs2, seqY, LipL41, IcdA, and Adk primers. A total of 17 isolates of pathogenic Leptospira bacteria were cultured from Institute of Vector Control and Reservoir Disease (IVRCD) in Salatiga, Indonesia. Result: The results of the research showed that the LipL41 and IcdA primers were found to be effective in distinguishing pathogenic strains, while the seqY, LipL32, Adk, and rrs2 primers required further refinement. The suitable Melting Temperature (TM) or annealing temperature is 58°C with 35 cycles of amplification. DNA concentration and purity had an A260/A280 ratio ranging between 1.8 and 2.8. Conclusion: LipL41 (500 bp) and IcdA (700 bp) are suitable primers for identifying pathogenic Leptospira.
Adler, B., de la Peña Moctezuma, A., 2010. Leptospira and Leptospirosis. Vet Microbiol Vol. 140(3-4), Pp. 287-296.
Ahmed, A.A., Goris, M.G.A., Meijer, M.C., 2020. Development of LipL32 Real-Time PCR Combined with An Internal and Extraction Control for Pathogenic Leptospira Detection. PLoS One Vol. 15(11), Pp. e0241584.
Bharti, A.R., Nally, J.E., Ricaldi, J.N., Matthias, M.A., Diaz, M.M., Lovett, M.A., Levett, P.N., Gilman, R.H., Willig, M.R., Gotuzzo, E., Vinetz, J.M., Peru-United States Leptospirosis Consortium, 2003. Leptospirosis: A Zoonotic Disease of Global Importance. Lancet Infect Dis Vol. 3(12), Pp. 757-771.
Budihal, S.V., Perwez, K., 2014. Leptospirosis Diagnosis: Competancy of Various Laboratory Tests. J Clin Diagn Res Vol. 8(1), Pp. 199-202.
Cheng, X., Hong, X., Khayatnezhad, M., Ullah, F., 2021. Genetic Diiversity and Comparative Study of Genomic DNA Extraction Protocols in Tamarix L. Species. Caryologia Vol. 74(2), Pp. 131-139.
Cosson, J.-F., Picardeau, M., Mielcarek, M., Tatard, C., Chaval, Y., Suputtamongkol, Y., Buchy, P., Jittapalapong, S., Herbreteau, V., Morand, S., 2014. Epidemiology of Leptospira Transmitted by Rodents in Southeast Asia. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases Vol. 8(6), Pp. e2902.
Costa, F., Hagan, J.E., Calcagno, J., Kane, M., Torgerson, P., Martinez-Silveira, M.S., Stein, C., Abela-Ridder, B., Ko, A.I., 2015. Global Morbidity and Mortality of Leptospirosis: A Systematic Review. PLoS Negl Trop Dis Vol. 9(9), Pp. e0003898.
Galloway, R.L., Hoffmaster, A.R., 2015. Optimization of LipL32 PCR Asay for Increased Sensitivity in Diagnosing Leptospirosis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis Vol. 82(3), Pp. 199-200.
Guerra, M.A., 2013. Leptospirosis: Public Health Perspectives. Biologicals Vol. 41(5), Pp. 295-297.
Hartskeerl, R.A., Collares-Pereira, M., Ellis, W.A., 2011. Emergence, Control and Re-emerging Leptospirosis: Dynamics of Infection in The Changing World. Clin Microbiol Infect Vol. 17(4), Pp. 494-501.
Karpagam, K.B., Ganesh, B., 2020. Leptospirosis: A Neglected Tropical Zoonotic Infection of Public Health Importance-an Updated Review. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis Vol. 39(5), Pp. 835-846.
Lau, C., Smythe, L., Weinstein, P., 2010. Leptospirosis: An Emerging Disease in Travellers. Travel Med Infect Dis Vol. 8(1), Pp. 33-39.
Levett, P.N., 2001. Leptospirosis. Clin Microbiol Rev Vol. 14(2), Pp. 296-326.
Levett, P.N., Branch, S.L., Whittington, C.U., Edwards, C.N., Paxton, H., 2001. Two Methods for Rapid Serological Diagnosis of Acute Leptospirosis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol Vol. 8(2), Pp. 349-351.
McBride, Alan JA, Athanazio, Daniel A, Reis, Mitermayer G, Ko, Albert I, 2005. Leptospirosis : Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases. Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases Vol. 18(5), Pp. 376-386.
Moran, M., Guzman, J., Ropars, A.-L., McDonald, A., Jameson, N., Omune, B., Ryan, S., Wu, L., 2009. Neglected Disease Research and Development: How Much Are We Really Spending? PLOS Medicine Vol. 6(2), Pp. e1000030.
Musso, D., La Scola, B., 2013. Laboratory Diagnosis of Leptospirosis: A Challenge. Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection Vol. 46(4), Pp. 245-252.
Nalam, K., Ahmed, A., Devi, S.M., Francalacci, P., Baig, M., Sechi, L.A., Hartskeerl, R.A., Ahmed, N., 2010. Genetic Affinities within a Large Global Collection of Pathogenic Leptospira: Implications for Strain Identification and Molecular Epidemiology. PLOS ONE Vol. 5(8), Pp. e12637.
Picardeau, M., 2013. Diagnosis and Epidemiology of Leptospirosis. Med Mal Infect Vol. 43(1), Pp. 1-9.
Reis, E.A.G., Hagan, J.E., Ribeiro, G.S., Teixeira-Carvalho, A., Martins-Filho, O.A., Montgomery, R.R., Shaw, A.C., Ko, A.I., Reis, M.G., 2013. Cytokine Response Signatures in Disease Progression and Development of Severe Clinical Outcomes for Leptospirosis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis Vol. 7(9), Pp. e2457.
Sakundarno, M., Bertolatti, D., Maycock, B., Spickett, J., Dhaliwal, S., 2014. Risk Factors for Leptospirosis Infection in Humans and Implications for Public Health Intervention in Indonesia and The Asia-Pacific Region. Asia Pac J Public Health Vol. 26(1), Pp. 15-32.
Sethi, S., Sharma, N., Kakkar, N., Taneja, J., Chatterjee, S.S., Banga, S.S., Sharma, M., 2010. Increasing Trends of Leptospirosis in Northern India: A Clinico-Epidemiological Study. PLoS Negl Trop Dis Vol. 4(1), Pp. e579.
Slack, A.T., Symonds, M.L., Dohnt, M.F., Smythe, L.D., 2006. Identification of Pathogenic Leptospira Species by Conventional or Real-Time PCR and Sequencing of The DNA Gyrase Subunit B Encoding Gene. BMC Microbiology Vol. 6(1), Pp. 95.
Torgerson, P.R., Hagan, J.E., Costa, F., Calcagno, J., Kane, M., Martinez-Silveira, M.S., Goris, M.G.A., Stein, C., Ko, A.I., Abela-Ridder, B., 2015. Global Burden of Leptospirosis: Estimated in Terms of Disability Adjusted Life Years. PLoS Negl Trop Dis Vol. 9(10), e0004122.
Vijayachari, P., Ahmed, N., Sugunan, A.P., Ghousunnissa, S., Rao, K.R., Hasnain, S.E., Sehgal, S.C., 2004. Use of Fluorescent Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism for Molecular Epidemiology of Leptospirosis in India. J Clin Microbiol Vol. 42(8), Pp. 3575-3580
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Vocational Health Studies

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The authors agree to transfer the transfer copyright of the article to the Journal of Vocational Health Studies (JVHS) effective if and when the paper is accepted for publication.
- Legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA), implies that publication can be used for non-commercial purposes in its original form.
- Every publications (printed/electronic) are open access for educational purposes, research, and library. Other that the aims mentioned above, editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation.
Journal of Vocational Health Studies is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License