THE EFFECT OF REPETITIVE METAL CASTING ON THE TENSILE STRENGTH OF DENTURES

Downloads
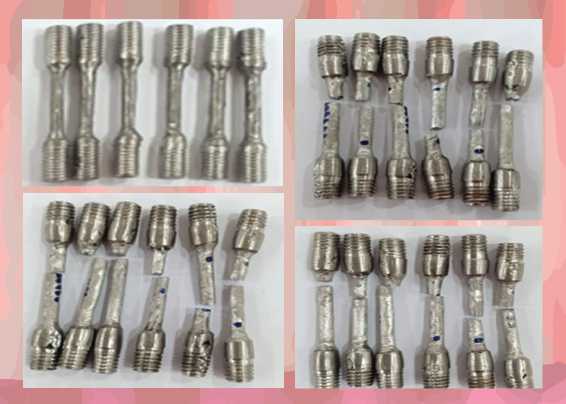
Background: Dentures or prostheses function to replace chewing and dental arch structures. Denture plates used in dentistry are made with acrylic resin, metal, or a combination of acrylic and metal. Metals are shiny, opaque chemical substances and good conductors of heat and can be polished. Recycling or reusing used metal is an option in making prostheses because the price of new metal is increasing, and metal recycling is quite effective. Purpose: To determine the effect of repeated metal casting on the strength of the metal frame denture base. Method: The current research is a laboratory study with a tensile test in the form of dumbbells with iso 22674 with a length of 15 ± 1 mm and a diameter of 3 ± 1 mm. This research used 18 CoCr metal samples divided into three groups, namely 100% new metal group (control), 50% new + 50% repeated composition group, and 100% repeated group. Result: The mean strain of the new 100% CoCr metals group was 0.133%, strain mean of the new 50% CoCr + 50% repeated metals group was 0.1%, and the strain of the 100% repeated CoCr metals group was 0.066%. The average modulus of elasticity (MPa) for the new 100% CoCr metals group is 7866, or 711 MPa, the new 50% CoCr + 50% repeat metals group is 7538, or 833 MPa, the 100% CoCr metals group is 6659, or 336 MPa. Conclusion: The new 100% CoCr metal group has a higher average tensile strength value than the 50% new CoCr metal + 50% repeated group, and the lowest is the 100% repeated CoCr metal group.
Agrawal, A., Hashmi, S.W., Rao, Y., Garg, A., 2015. Evaluation of Surface Roughness and Tensile Strength of Base Metal Alloys Used for Crown and Bridge on Recasting (Recycling). J. Clin. Diagn. Res. JCDR Vol. 9(7), Pp. ZC01-04.
Anusavice, K.J., 2003. Phillips’ Science of Dental Materials -eBook: Phillips’ Science of Dental Materials -eBook, 11 th. ed. Elsevier Health Sciences, USA.
Ariyani, A., Tiffany, T., 2016. Pengaruh Penambahan Serat Kaca terhadap Kekasaran Permukaan dan Penyerapan Air Bahan Basis Gigi Tiruan Nilon Termoplastik. Dentika Dent. J. Vol. 19(1), Pp. 71-77.
Ayad, M.F., Ayad, G.M., 2010. Corrosion Behavior of As-Received and Previously Cast Type III Gold Alloy. J. Prosthodont. Vol. 19(3), Pp. 194-199.
Bandela, V., Kanaparthi, S., 2021. Effect of Recasting on the Quality of Dental Alloys: A Review. Int. Med. J. 1994 Vol. 28(1), Pp. 115-117.
Bauer, J.R. de O., Loguercio, A.D., Reis, A., Rodrigues Filho, L.E., 2006. Microhardness of Ni-Cr alloys under Different Casting Conditions. Braz. Oral Res. Vol. 20(1), Pp. 40-46.
Budi, G.S., 2011. Pengujian Kuat Tarik dan Modulus Elastisitas Tulangan Baja (Kajian terhadap Tulangan Baja dengan Sudut Bengkok ). J. Tek. Sipil Vol. 11(1), Pp. 71-77.
Callister, W.D., 2007. Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction. Wiley, University of Minnesota.
Eka, R.E., Dharmastiti, R., Widjijono, W., 2022. Effect of Co-Cr Alloy Recasting on The Fracture Toughness. Maj. Kedokt. Gigi Indones. Vol. 7(1), Pp. 40-44.
James, J., Julian, J., Rahul, J., Babu Philip, G., Devassy, J.P., Reba, P.B., 2018. Effect of Recasting on Physical Properties of Base Metal Alloys: An In Vitro Study-PMC. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. Vol. 8(5),Pp. 457-462.
Lenggogeny, P., Masulili, S.L.C., 2015. Gigi Tiruan Sebagian Kerangka Logam sebagai Penunjang Kesehatan Jaringan Periodontal. Maj. Kedokt. Gigi Indones. Vol. 1(2), Pp. 123-129.
Manaranche, C., Hornberger, H., 2007. A Proposal for The Classification of Dental Alloys According to Their Resistance to Corrosion. Dent. Mater. Vol. 23(11), Pp. 1428-1437.
Noort, R. van, 2007. Introduction to Dental Materials, 3 RD. ed. Mosby/Elsevier, United Kingdom (UK).
Pimenta, A.R., Diniz, M.G., Paciornik, S., Sampaio, C.A.F., Miranda, M.S. de, Paolucci-Pimenta, J.M., 2012. Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of A Nickel-Chromium Aloy after Casting Process. RSBO Online Vol. 9(1), Pp. 17-24.
Rejeki, P., 2018. Gigi Tiruan Sebagian Kerangka Logam. Universitas Udayana, Program Studi Sarjana Kedokteran Gigi dan Profesi Dokter Gigi,Fakultas Kedokteran.
Shotwell, J., 2008. (PDF) Attachments and Their Use In Removable Partial Denture Fabrication.
Slokar Benić, L., Matković, T., Matković, P., 2004. Microstructure and Hardness of Co-Cr-Ti Alloys for Dental Castings. Metal. -Sisak Then Zagreb. Vol. 43(4), Pp. 273-277.
Souisa, M., 2011. Analisis Modulus Elastisitas dan Angka Poisson Bahan dengan Uji Tarik. BAREKENG J. Ilmu Mat. Dan Terap. Vol. 5(2), Pp. 9-14.
Surdia, T., 1980. Teknik pengecoran logam. P.T. Pradnya Paramita.
Syaja’iy, M.H., 2010. Pengaruh Modulus Elastisitas terhadap Kompatibilitas Dimensional Beton Induk dengan Repair Material Berbahan Tambah Polymer (Skripsi). Universitas Sebelas Maret Surakarta, Jurusan Teknik Sipil Fakultas Teknik.
Thambas A., A.K., Dewi, R.S., 2012. Pengembangan dan Modifikasi Estetik dalam Pembuatan Crown dan Bridge. J. Ilm. Widya Vol. 29(321), Pp. 218683.
Thopegowda, Nandish, Shenoy, K., Shankarnarayana, R., Kukkila, J., Vaddya, S., Ginjupalli, K., 2013. Recycling of Materials used in Dentistry with Reference to its Economical and Environmental Aspects. Int. J. Health Rehabil. Sci. Vol. 2(3), Pp. 140-145.
Wahjuni, S., Mandanie, S.A., 2017. Fabrication of Combined Prosthesis With Castable Extracoronal Attachments (Laboratory Procedure). J. Vocat. Health Stud. Vol. 1(2), Pp. 75-81.
Wise, D.L., 2001. Biomaterials and Bioengineering Handbook. Sens. Rev. Vol. 21(4), Pp. 323-324.
Wylie, C.M., Shelton, R.M., Fleming, G.J.P., Davenport, A.J., 2007. Corrosion of Nickel-based Dental Casting Alloys. Dent. Mater. Vol. 23(6), Pp. 714-723.
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Vocational Health Studies

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The authors agree to transfer the transfer copyright of the article to the Journal of Vocational Health Studies (JVHS) effective if and when the paper is accepted for publication.
- Legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA), implies that publication can be used for non-commercial purposes in its original form.
- Every publications (printed/electronic) are open access for educational purposes, research, and library. Other that the aims mentioned above, editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation.
Journal of Vocational Health Studies is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License