The Anthelmintic Potential of Ethyl Acetate Fraction Berenuk (Crescentia cujete L.) Fruit Against Mortality Haemonchus contortus In Vitro
Downloads
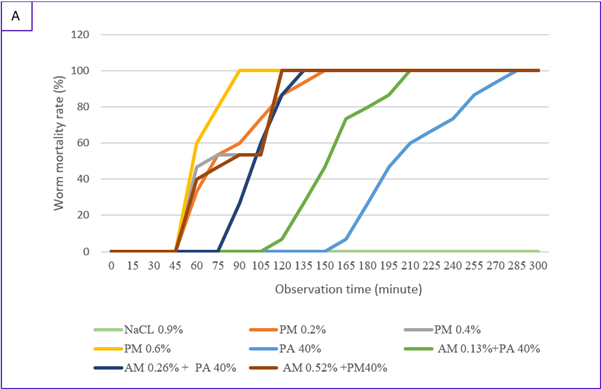
This study aims to determine the anthelmintic potency of the ethyl acetate fraction of berenuk fruit (Crescentia cujete L.) on the mortality of the Haemonchus contortus worms in vitro. The method that was used in the research was a post-test only control group design. There were five treatments and each treatment was carried out in four repetitions. The sample used was twenty H. contortus in each treatment for all replications. Observation and recording of H. contortus mortality was carried out at 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60 minutes, and when all worms in the petri dish died. Data analysis using ANOVA, followed by Duncan's Test and Probit analysis. The results showed that the ethyl acetate fraction of berenuk fruit had anthelmintic activity. The conclusion in this study is that the optimal concentration is found in the 0.5% ethyl acetate fraction concentration, the LC50 at each observation time successively is 1.39%; 0.97%; 0.70%; 0.48%; 0.39%; 0.34%; 0.31%; 0.28%; 0.27%; 0.26%; 0.25%; and 0.24%, while LT50 at a concentration of 0.125%; 0.25%; and 0.5% respectively are 1 hour 17 seconds, 41 minutes 42 seconds, and 20 minutes 58 seconds.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- Every manuscript submitted to must observe the policy and terms set by the Journal of Parasite Science
- Publication rights to manuscript content published by the Journal of Parasite Science is owned by the Journal of Parasite Science with the consent and approval of the author(s) concerned
- Authors and other parties are bound to the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License for the published articles, legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-SA)
- By submitting the manuscript, the author agrees to the requirement that the copyright of the submitted article will be transferred to Journal of Parasite Science as the publisher of the journal. The intended copyright includes the right to publish articles in various forms (including reprints). journal of parasite science retains the publishing rights to published articles.