THE ZINC STATUS IN CHILDREN WITH ALLERGIES: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS
Downloads
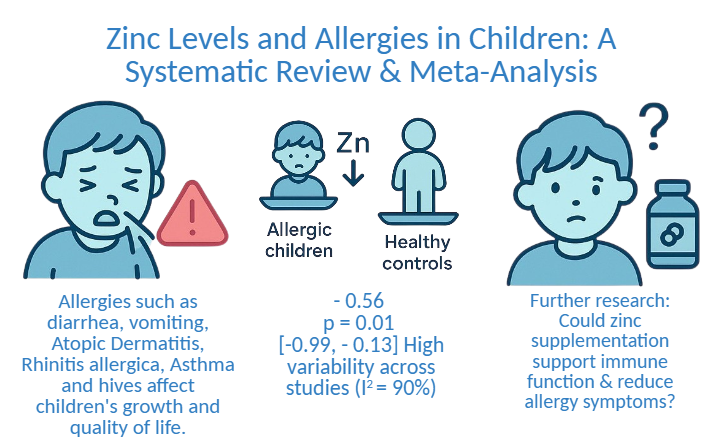
Allergies pose significant health concerns, particularly in children, where they can adversely affect growth and quality of life. Recent studies have suggested that zinc deficiency may play a critical role in the immune dysregulation associated with allergies. The method used in This systematic review followed the PRISMA guidelines and analyzed studies on the relationship between zinc levels and allergies in children, using data from PubMed, Science Direct, EBSCO, and Cochrane Library, and a meta-analysis was conducted to evaluate the effect size and risk of bias assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale to examine the relationship between zinc levels and allergies in children. Our findings indicate that children with allergies may exhibit different zinc levels compared to healthy controls, with a pooled effect size of -0.56 (95% CI: [-0.99, -0.13]). The analysis revealed significant heterogeneity (Tau² = 0.39; Chi² = 79.41, df = 8, p < 0.00001; I² = 90%), highlighting the variability across studies and the necessity for further research to standardize the methodologies. These results were statistically significant (Z = 2.54, p = 0.01), suggesting a potential association between zinc levels and allergies in children. Further investigations are needed to explore whether zinc supplementation can support immune function and alleviate allergic symptoms.
AbdulWahab, A., Zeidan, A., Avades, T., Chandra, P., & Soliman, A. (2018). Serum Zinc Level in Asthmatic and Non-Asthmatic School Children. Children, 5(3), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/children5030042
Alkholy, U., Mohamed, H., Saleh, O., & Gameil, D. (2024). Evaluation of serum levels of zinc, copper, and magnesium in children with asthma and their correlation with disease severity. Zagazig University Medical Journal, 0(0), 0–0. https://doi.org/10.21608/zumj.2024.282190.3326
Bonaventura, P., Benedetti, G., Albarède, F., Miossec, P. (2015). Zinc and its role in immunity and inflammation. Autoimmunity Reviews, 14(4), 277–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2014.11.008
Carneiro, M. F. H., Rhoden, C. R., Amantéa, S. L., & Barbosa, F. (2011). Low Concentrations of Selenium and Zinc in Nails are Associated with Childhood Asthma. Biological Trace Element Research 144(1–3): 244–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-9080-3
Cigerci Gunaydin, N., Celikkol, A., Nalbantoglu, A. (2023). Assessment of intracellular zinc levels in infants with food protein–induced allergic proctocolitis: Allergologia et Immunopathologia, 51(1), 9–15. https://doi.org/10.15586/aei.v51i1.660
Corbo, M. D., & Lam, J. (2013). Zinc deficiency and its management in the pediatric population: a literature review and proposed etiologic classification. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 69(4), 616-624. e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2013.04.028
Di Toro, R., Galdo Capotorti, G., Gialanella, G., Miraglia del Giudice, M., Moro, R., & Perrone, L. (1987). Zinc and copper status in children with allergies Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 76(4), 612–617. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1651-2227.1987.tb10530.x
Domellöf, M., Hernell, O., Abrams, S. A., Chen, Z., & Lönnerdal, B. (2009). Iron supplementation did not affect copper or zinc absorption in the breastfed infants. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 89(1), 185–190. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2008.26887
Endre, L., Gergely, A., Osváth, P., Szolnoky, M., & Nagy, J. (1989). [Incidence of food allergy and zinc deficiency in children treated for atopic dermatitis]. Orvosi Hetilap, 130(46), 2465–2469.
Kamer, B., Wąsowicz, W., Pyziak, K., Kamer-Bartosińska, A., Gromadzińska, J., & Pasowska, R. (2012). The role of selenium and zinc in the pathogenesis of food allergies in infants and young children. Archives of Medical Science, 6, 1083–1088. https://doi.org/10.5114/aoms.2012.32420
Maywald, M. and Rink, L. (2024). Zinc deficiency and supplementation in allergic diseases. Biomolecules, 14(7), 863. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070863
Mehta, H., Groetch, M., Wang, J. (2013). Growth and nutritional concerns of children with food allergies Current Opinion in Allergy & Clinical Immunology, 13(3), 275–279. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACI.0b013e328360949d
Ozdemir, O. (2014). Zinc and allergy relationships MOJ Immunology, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.15406/moji.2014.01.00005
Podlecka, D., Jerzyńska, J., Sanad, K., Polańska, K., Bobrowska-Korzeniowska, M., Stelmach, I., & Brzozowska, A. (2022). Micronutrients and the risk of allergic diseases in schoolchildren. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19(19): 12187. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912187
Rajkumar, S., Bhat, N. K., Kumar, V., Bolia, R., Verma, P. K., Kumar, M., Chacham, S., Mirza, A. A. (2022). Association between serum zinc levels and symptom control of asthma in children and adolescents: A prospective observational study. European Journal of Pediatrics 182(1): 141–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-022-04656-9
Semba, R. D., Bloem, M. W., Piot, P. (Eds.). (2008). Nutrition and Health in Developing Countries. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-464-3
Seo, H.-M., Kim, Y. H., Lee, J. H., Kim, J. S., Park, Y. M., & Lee, J. Y. (2017). Serum Zinc Status and Its Association with Allergic Sensitization: The Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Scientific Reports 7(1): 12637. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13068-x
Seppo, L., Korpela, R., Lönnerdal, B., Metsäniitty, L., Juntunen-Backman, K., Klemola, T., Paganus, A., & Vanto, T. (2005). A follow-up study of nutrient intake, nutritional status, and growth in infants with cow milk allergy fed either soy formula or extensively hydrolyzed whey formula. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 82(1), 140–145. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn.82.1.140
Srivastava, S., Tiwari, V., Singh, S., Karoli, R., Bhattacharya, P., & Gupta, N. (2023). Low serum levels of zinc, selenium, and vitamin D3 are biomarkers for airway inflammation and poor asthma control. Cureus. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.41082
Suzuki, M., Suzuki, T., Watanabe, M., Hatakeyama, S., Kimura, S., Nakazono, A., Honma, A., Nakamaru, Y., Vreugde, S., & Homma, A. (2021). Role of intracellular zinc in the molecular and cellular functions of allergic inflammatory diseases. Allergology International, 70(2), 190–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alit.2020.09.007
Vuralli, D., Tumer, L., Hasanoglu, A. (2017). Zinc deficiency in the pediatric age group is common, but underevaluated. World Journal of Pediatrics, 13(4), 360–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-017-0007-8
Zakharova, I. N., Berezhnaya, I. V., Simakova, M.A. (2023). Growth retardation in children with allergies: a review. Pediatrics. Consilium Medicum, 1, 34–41. https://doi.org/10.26442/26586630.2023.1.202182

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- MEDIA GIZI INDONESIA Journal is the copyright owner of all materials published on this website.
- The formal legal provisions for access to digital articles of this electronic journal are subject to the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0), which means that MEDIA GIZI INDONESIA Journal and readers reserve the right to save, transmit media / format, manage in database, maintain, and publish articles as long as it continues to include the name of the Author.
- Printed and published print and electronic manuscripts are open access for educational, research and library purposes. In addition to these objectives, the editorial board shall not be liable for violations of copyright law.


2.png)





















