EFFICACY OF AMNIOTIC MEMBRANE MESENCHYMAL STEM CELL THERAPY FOR BURN WOUNDS: META-ANALYSIS STUDY
Downloads
Highlights:
- The healing potential of stem cell therapy for burn wounds, primarily attributed to angiogenesis and anti-inflammatory effects.
- AM-MSC therapy has a beneficial impact on burn wound healing, particularly by promoting angiogenesis and reducing inflammation.
Abstract:
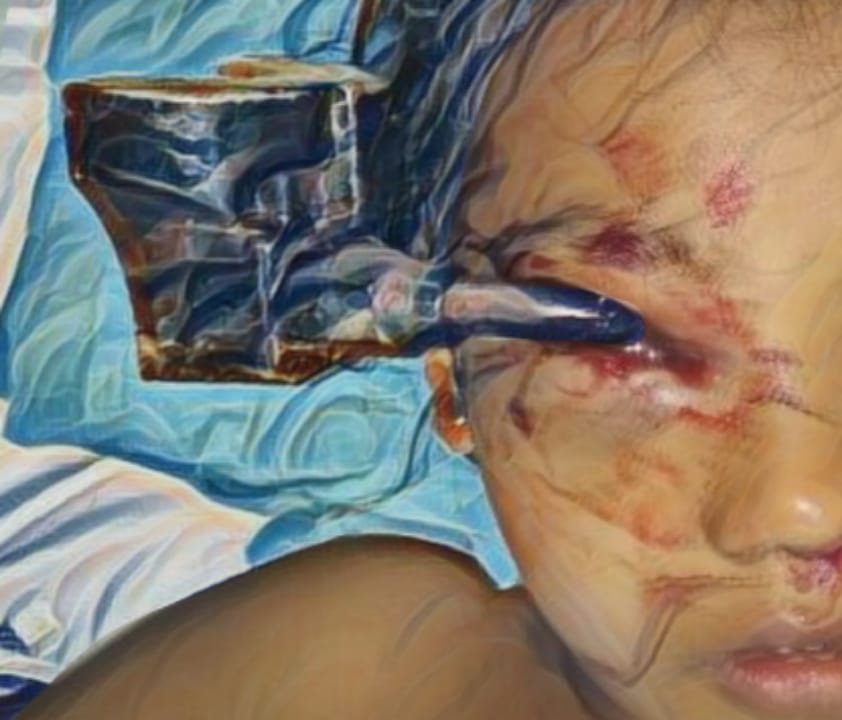
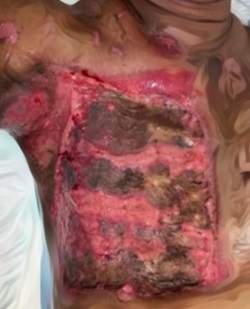
Introduction: Burn injury is a trauma with high morbidity and mortality that requires special management from the start. stem cells have generated great hopes for the treatment of numerous conditions including burns. The Metaanalysis was performed for these preclinical studies to assess the efficacy and possible mechanisms of Amniotic Membrane Mesenchymal Stem Cell (AM- MSC) in treating burn wounds.
Methods: Seven studies identified by searching PubMed, MEDLINE, databases from inception to October 2020. In addition, a manual search of references of studies was performed to obtain potential studies. Stata 16 was used for all data analysis.
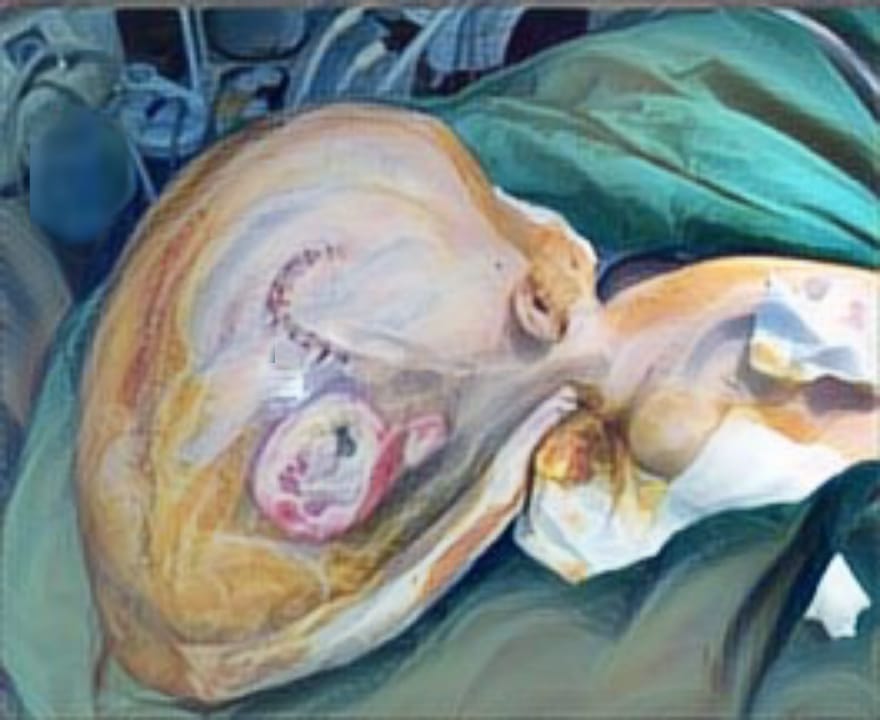
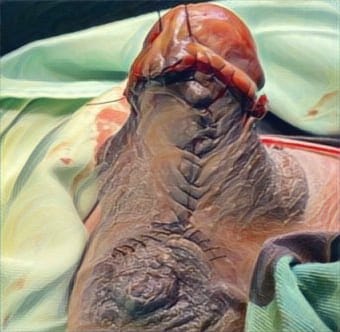
Results: The overall meta-analysis showed that AM-MSC therapy significantly improved burn healing rate (SMD 3.34, 95% CI 1.82 to 4.86), irrespective of transplant type, burn area, and treatment method in the control group.
Conclusions: Meta-analysis showed that AM-MSC therapy exerts appears to exert a positive effect in burn wound healing, mainly through angiogenesis and anti- inflammatory actions. There is, therefore, justification for continued efforts to evaluate variations in future clinical studies using stem cells to treat a burn wound in order to maximize the effectiveness. the use of stem cells as an adjunct to first- line therapies in burns.
Noer mohammad sjaifudin. penangangan luka bakar. 2006;
Li Y, et al. Efficacy of stem cell therapy for burn wounds : a systematic review and meta- analysis of preclinical studies. 2020. 1–12.
Zhang L, et al. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Effectiveness and Safety of Hydrogel Dressings in the Management of Skin Wounds. 2019. 7: 1–16.
Liu L, et al. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Transplantation Promotes Cutaneous Wound Healing of Severe Burned Rats. 2014.9(2).
Caliari-oliveira C, et al. Xenogeneic Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Improve Wound Healing and Modulate the Immune Response in an Extensive Burn Model. 2016. 25(25): 201–15.
Francis E,et al. The effects of stem cells on burn wounds : a review. 2019. 9(1): 1–12.
Hashemi SS, et al. The role of labeled cell therapy with and without scaffold in early excision burn wounds in a rat animal model. 2018.(9).
Guang L, et al. Free Radical Biology and Medicine Differential response of immortalized human amnion mesenchymal and epithelial cells against oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med [Internet] 2019.135:79–86.
Ghieh F,et al. The Use of Stem Cells in Burn Wound Healing : A Review. 2015.
Copyright (c) 2021 Bayu Fasi Bermani, Agus Santoso Budi, Magda Rosalina Hutagalung

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
JURNAL REKONSTRUKSI DAN ESTETIK by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold copyright of the article without restriction
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessbility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA)