A CASE SERIES : HYMENOPLASTY BASED ON THE TYPE OF THE TEAR OR CLEFT PREOPERATION FINDING FOR GOOD SATISFACTION POSTOPERATIVE RESULT
Downloads
Highlights:
- Surgical hymenoplasty technique based on the type of the tear or cleft finding preoperative for satisfaction postoperative approach yields satisfactory results.
- Surgical hymenoplasty technique, tailored to the specific type of hymenal tear or cleft identified preoperatively.
Abstract:
Introduction: To describe our surgical hymenoplasty technique based on the type of the tear or cleft finding preoperative for satisfaction postoperative.
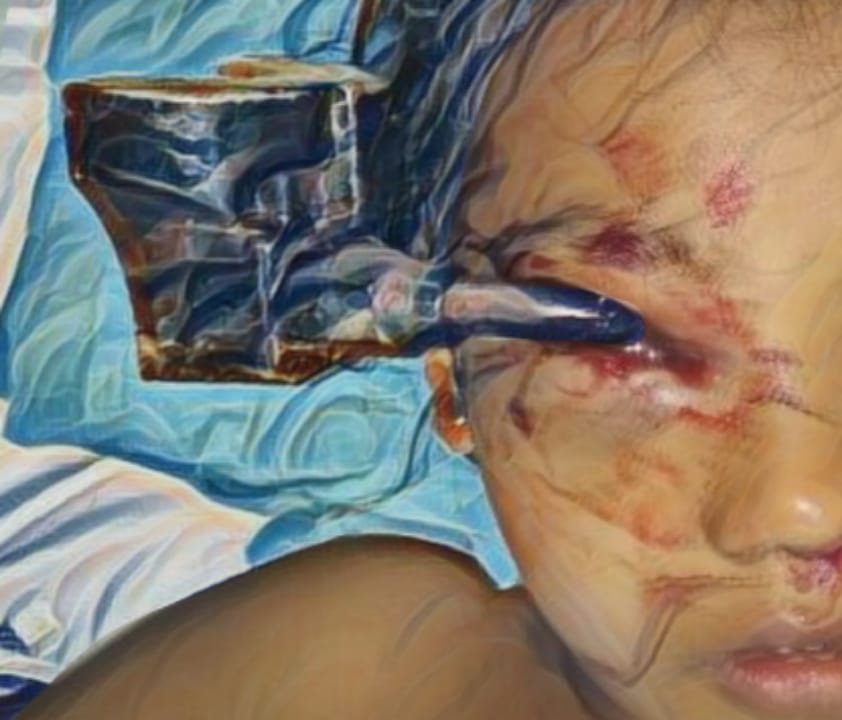
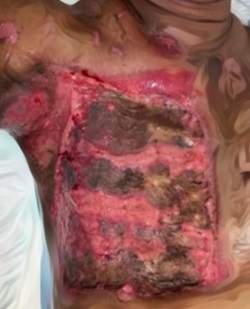
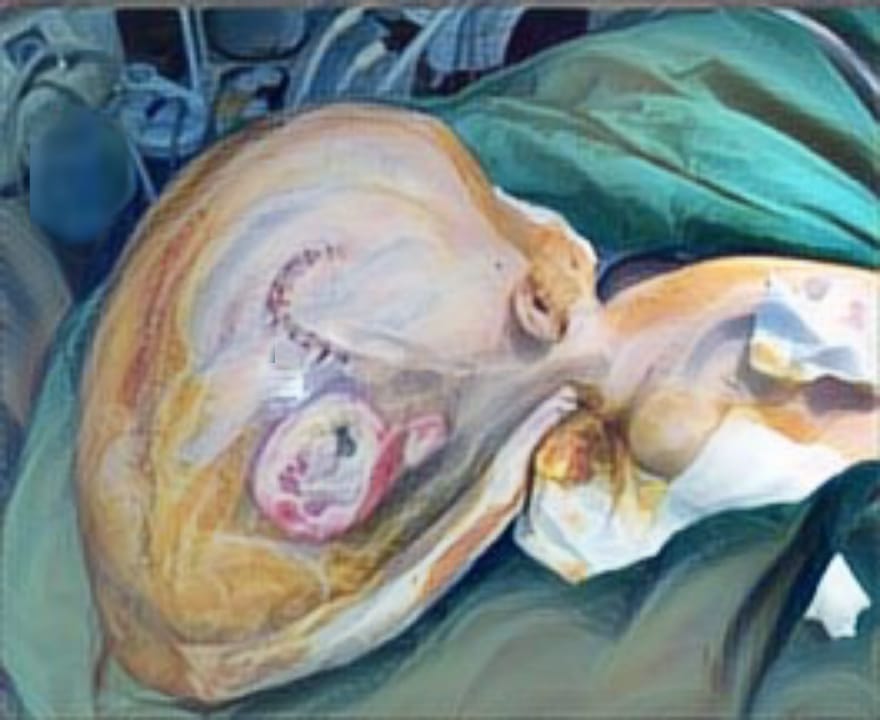
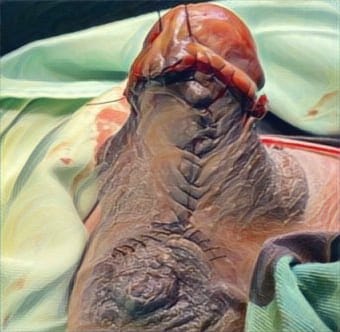
Case Illustration: Hymenoplasty was performed on 4 patient on January 2017 until March 2017, we found three patients with U-type. We performed hymenoplasty which is to create a new surface raw, on the right and left cleft to be stiched, we use a rapid absorbable suture material, with horizontal mattress technique.
Discussion: No complications developed in the patients who had undergone hymenoplasty and all patients stated that the sexual intercourse they experienced was similar to the night of the initial experience.
Conclusion: Our new apporach for hymenoplasty is a technique that has good results, and this is a good approach in doing hymenoplasty. A comprehensive preoperatif consultation is essential to ensure patient and surgeon satisfaction postoperatively. Preoperative evaluation of the hymenal tissue is the basis on which a surgical technique is selected. The surgical technique is determining factor for a succesful hymenorrhaphy.
Hemant A. Saraiya. Surgical revirgination: Four vaginal mucosal flaps for reconstruction of a hymen. Indian J Plast Surg. 2015.48(2):192–195.
Goodyear-Smith FA, Laidlaw TM. Can tampon use cause hymen changes in girls who have not had sexual intercourse? A review of the literature. Forensic Sci Int. 1998. 94(1-2):147-53.
West R, et al. Accidental vulval injuries in childhood. BMJ. 1989;298(6679): 1002-3.
Bond GR, et al. Unintentional perineal injury in prepubescent girls: a multicenter, prospective report of 56 girls. Pediatrics. 1995;95(5):628-31
Dowd MD, et al. The interpretation of urogenital fndings in children with straddle injuries. J Pediatr Surg. 1994;29(1):7-10.
Boos SC. Accidental hymenal injury mimicking sexual trauma. Pediatrics. 1999;103(6 Pt1):1287-90.
Merritt DF. Genital trauma in children and adolescents. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2008.51(2):237-48.
Dağhan Işık, Coşkun Erçel, Rohat Kutlay, Recep Anlatıcı. Re-Virginitation: Hymenoplasty. Turk Plast Surg. 2011. 19 (1).
Wei S-Y, et al. A new surgical technique of hymenoplasty. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2015;130(1):14–8
Hegazy AA, Al-Rukban MO. Hymen: facts and conceptions. theHealth 2012.3(4):13. 109–15.
World Health Organization. Constitution of the World Health Organization. http://www.who.int/governance/eb/who_constituti on_en.pdf.
Copyright (c) 2019 Rianto Noviady Ramli, Agus Santoso Budi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
JURNAL REKONSTRUKSI DAN ESTETIK by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold copyright of the article without restriction
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessbility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA)