A CASE REPORT: RISK OF ELECTRIC INJURY ON DELAYED INITIAL TREATMENT
Downloads
Highlights:
- Electric injuries are aggressive burns that can lead to severe tissue necrosis, rhabdomyolysis, and a range of complications, including acute kidney injury (AKI).
- A multidisciplinary approach and early identification of potential complications in electric injury cases are crucial for reducing the risk of Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) and improving patient outcomes.
Abstract:
Introduction: Electric Injury is a very aggressive burn injury with severe functional and aesthetic consequences caused by progressive and prolonged tissue necrosis. Necrosis that attacks the skeletal muscle can lead to rhabdomyolysis which results in complications if not treated properly.
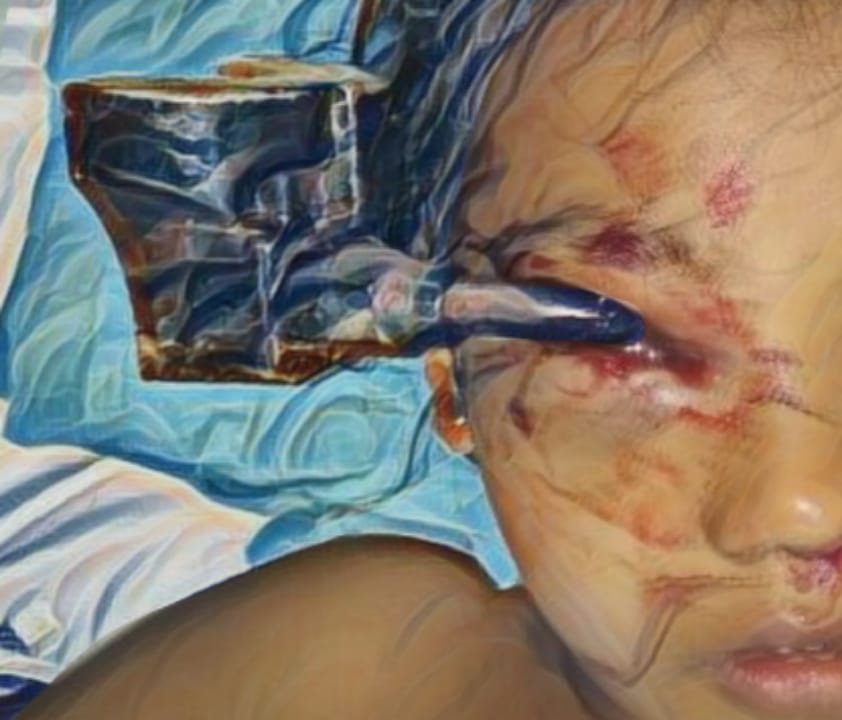
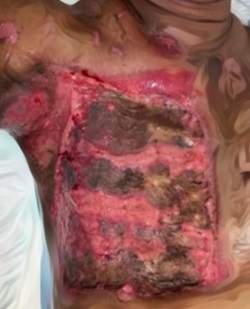
Case Illustration: A complicated case of electric injury in Dr. Soebandi Jember General Hospital, a 26 years old man came to the emergency room with complaints of severe shortness of breath and urinary disorders. The patient had a history of having an electric shock in his right hand when turning on the fan a week prior of admission. The examination showed that the patient had bilateral pulmonary effusion, generalized edema and acute tubular necrosis (ATN) which was characterized by oliguria and even anuria accompanied by hematuria. Other symptoms experienced by patients are anterior uveitis, subconjunctival hemorrhage, and hematemesis.
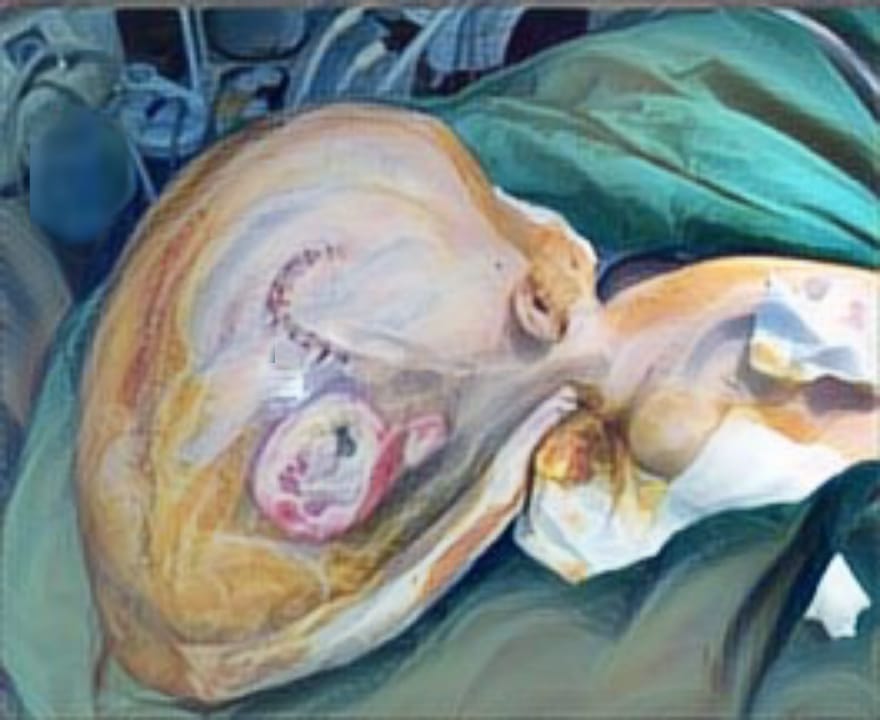
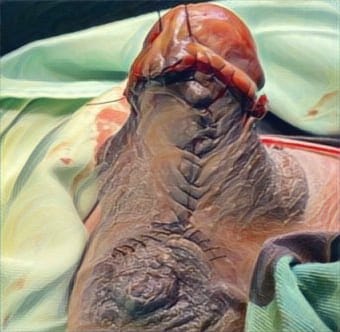
Discussion: Electric injuries can have a wide range of effects on the body, and their management requires a multidisciplinary approach to address the various complications that may arise. Treatment of electric injuries often involves various surgical procedures, including skin grafts, flaps, or amputation, depending on the severity of the injury.
Conclusions: Early identification of potential complications in electric injury cases and effective patient follow-up can reduce the risk of Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) occurrence in patients with electric injuries.
Lisa A. Foris; Martin R. Huecker. Electrical Injuries. StatPearls Publishing LLC: Januari 2018. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK4 48087/
Waldmann, et al. Electrical Injury. BMJ 2017;357.
Liu, H., Q. et al. The Clinical and Medicolegal Analysis of Electrical Shocked Rats: Based on the Serological and Histlogical Methods. Biomed Research International. 2016;1-12.
Suzan, R., and D. E. Andayani. Management of Nutrition in Patient with Burns Electricity. JMJ. 2017.5(1):1-13.
Martina, N. R., and A. Wardhana. Mortality Analysis of Adult Burn Patients. Journal of Plastic Reconstruction. 2013;2(2): 96-100.
Djunaedi, Annisa Sarfina, Ulfa Elfiah. Thesis: Analysis of Rat Vessels Based on Distance of Post-Exposure Electrical Injuries. Jember University. 2018.
Karimi, H., M. et al. Long Term Outcome and Follow Up of Electrical Injury. Journal of Acute Disease. 2015.107- 111.
Koumbourlis, Anastassios C. Electrical injuries. Crit Care Med 2002; 30[Suppl.]:S424–S430.
Ungureanu M. Electrocutions– treatment strategy (case presentation). Journal of Medicine and Life. 2014. 7(4):623-626
Buja Z., et al. Electrical Burn Injuries. An Eight-Year Review. Annals of Burns and Fire Disasters. 2010.23(1).
Pudjiastuti, A. Difference in the Frequency of Wistar Rat Heart Muscles Due to Exposure to Electric Current Directly and through Water Media. Not Published. Thesis. Semarang: Faculty of Medicine, Diponegoro University. 2009.
Seng, et al. Management of an Electrocuted Burn Injury in a District Hospital-A Case Report and Literature Review. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 2018, 12(5): PD11-PD12
Guntheti, et al. Pattern of Injuries due to Electric Current. J Indian Acad Forensic. 2012. 34(1)
Cushing, Tracy A, Ronald K Wright. Electrical Injuries in Emergency Medicine.
Yasti, Ahmet Çınar, et al. Guideline and treatment algorithm for burn injuries. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg, 2015, 21(2).
Duman, et al. Unilateral uveitis, cataract and retinal detachment following low-voltage electrical injury. Burns & Trauma. 2015; 3:19
American Optometric Association. Optometric Clinical Practice Guideline Care of The Patient with Anterior Uveitis. AOA: 243 N. Lindbergh Blvd., St. Louis, MO 63141-7881. 2004.
Kumar, Arige Subodh, Gogulapati Venkata Sudhakar. Upper gastrointestinal lesions and bleed in burn injuries: An endoscopic evaluation. Indian Journal of Burns. 2014.22(1).
Moenadjat, Y. Burns: Problems and Management. Fourth edition. Jakarta: Hall of Publishers of the Faculty of Medicine Indonesia University. 2009.
Sato, tetsuo. Differential Diagnosis of Effusion Pleura. 2006. JMAJ 49 (9-10):315-319
Chauhan, D. C, et al. Correlation of renal complications with extent and progression of tissue damage in electrical burns. Indian J Plastic Surg. 2004.37(2).s
Emara S.S., Alzaylai A.A. Renal Failure in Burn Patients: A Review. Annals of Burns and Fire Disasters. 2013.26(1).
Naqvi, Rubina, et al. Acute Kidney Injury with Rhabdomyolysis: 25 Years Experience from a Tertiary Care Center. Journal of nephrology: 2015,5:67-74.
Copyright (c) 2019 Ulfa Elfiah, Dissa Yulianita Suryani

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
JURNAL REKONSTRUKSI DAN ESTETIK by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold copyright of the article without restriction
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessbility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA)